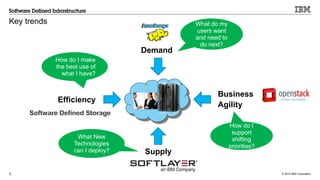
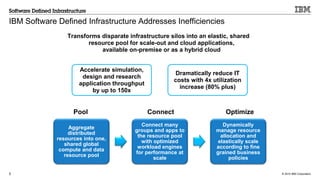
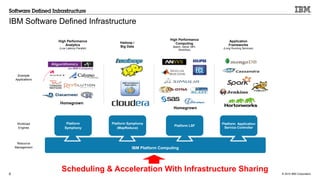
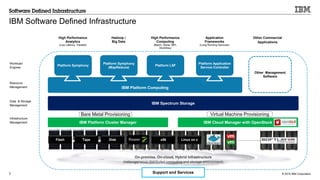
IBM's software-defined infrastructure aims to transform traditional IT inefficiencies by creating an elastic, shared resource pool for scale-out and hybrid cloud applications. It addresses the challenges of increasing project demands, infrastructure requirements, and resource management while enhancing organizational agility and reducing costs. The implementation at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute exemplifies the benefits of utilizing IBM's solutions for optimizing high-performance computing capacity.