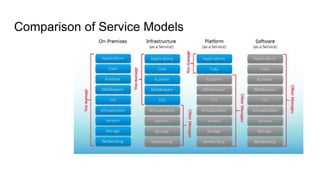
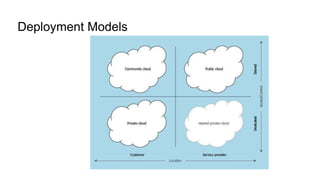
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides essential computing resources such as servers, networking, and storage over the cloud, enabling scalability, reliability, and cost-efficiency for organizations. It allows clients to dynamically manage resources and emphasizes characteristics like availability, performance optimization, and ease of access. Various deployment models, including private, public, and hybrid clouds, cater to different organizational needs and regulatory considerations.