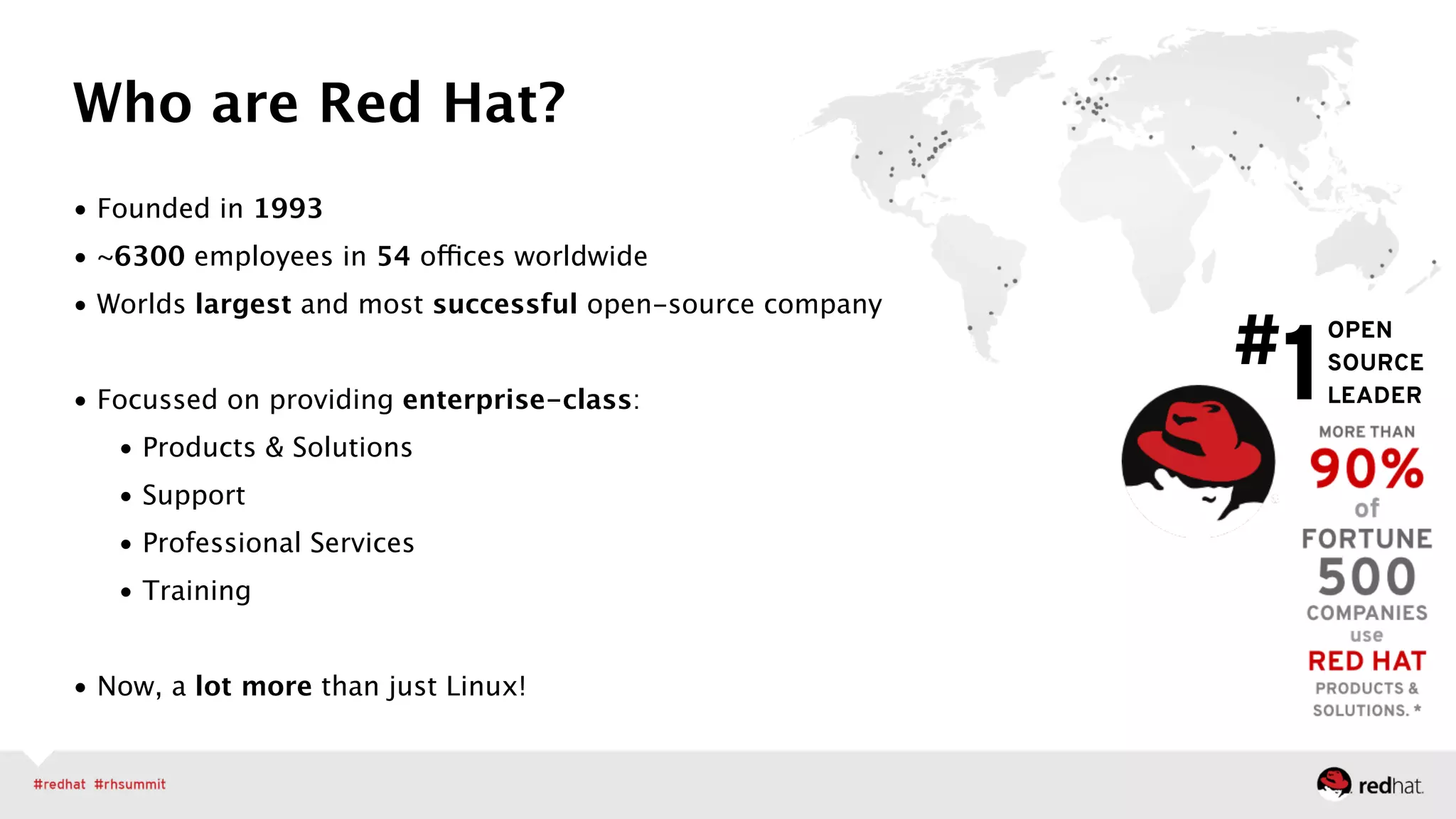
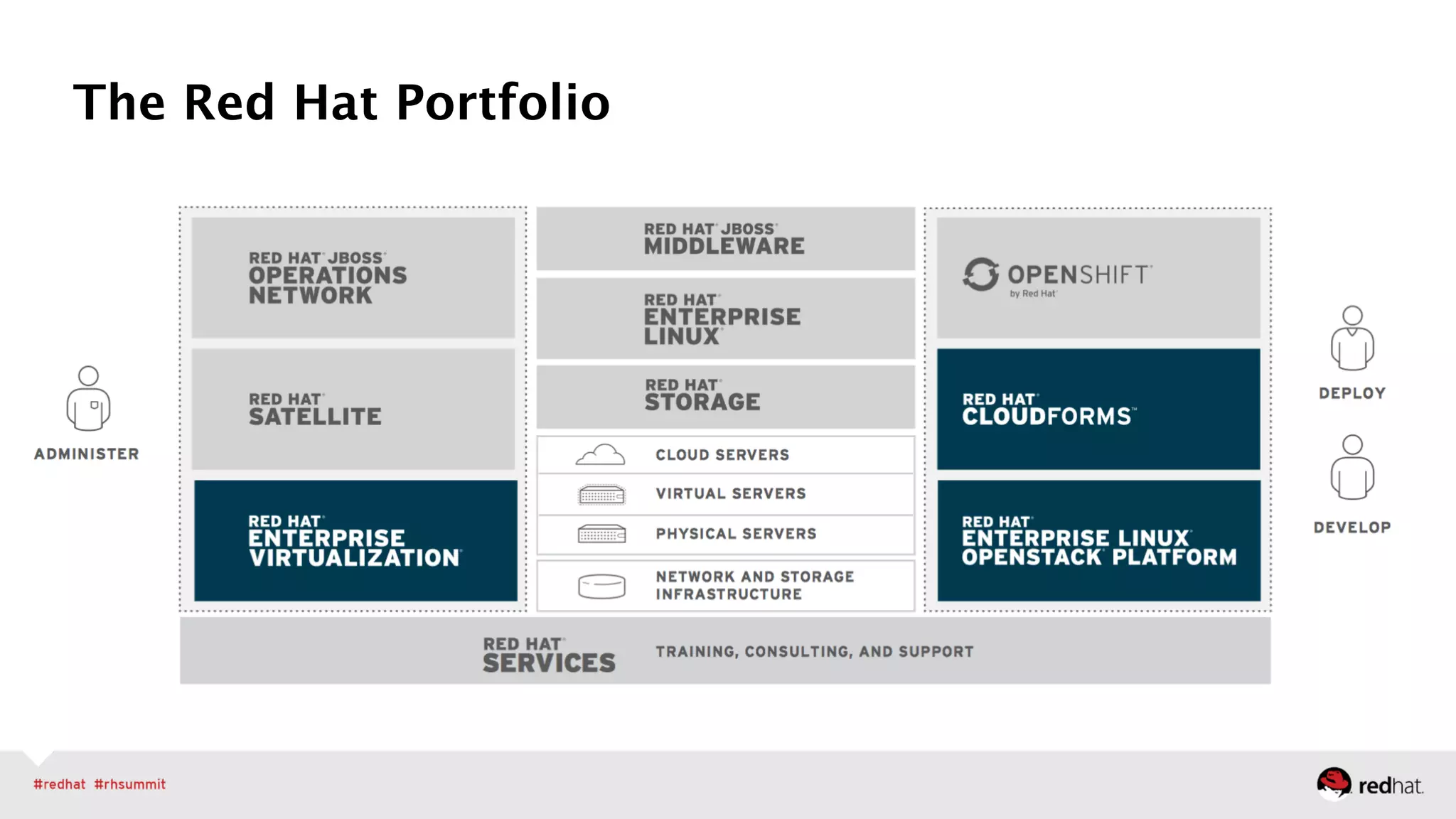
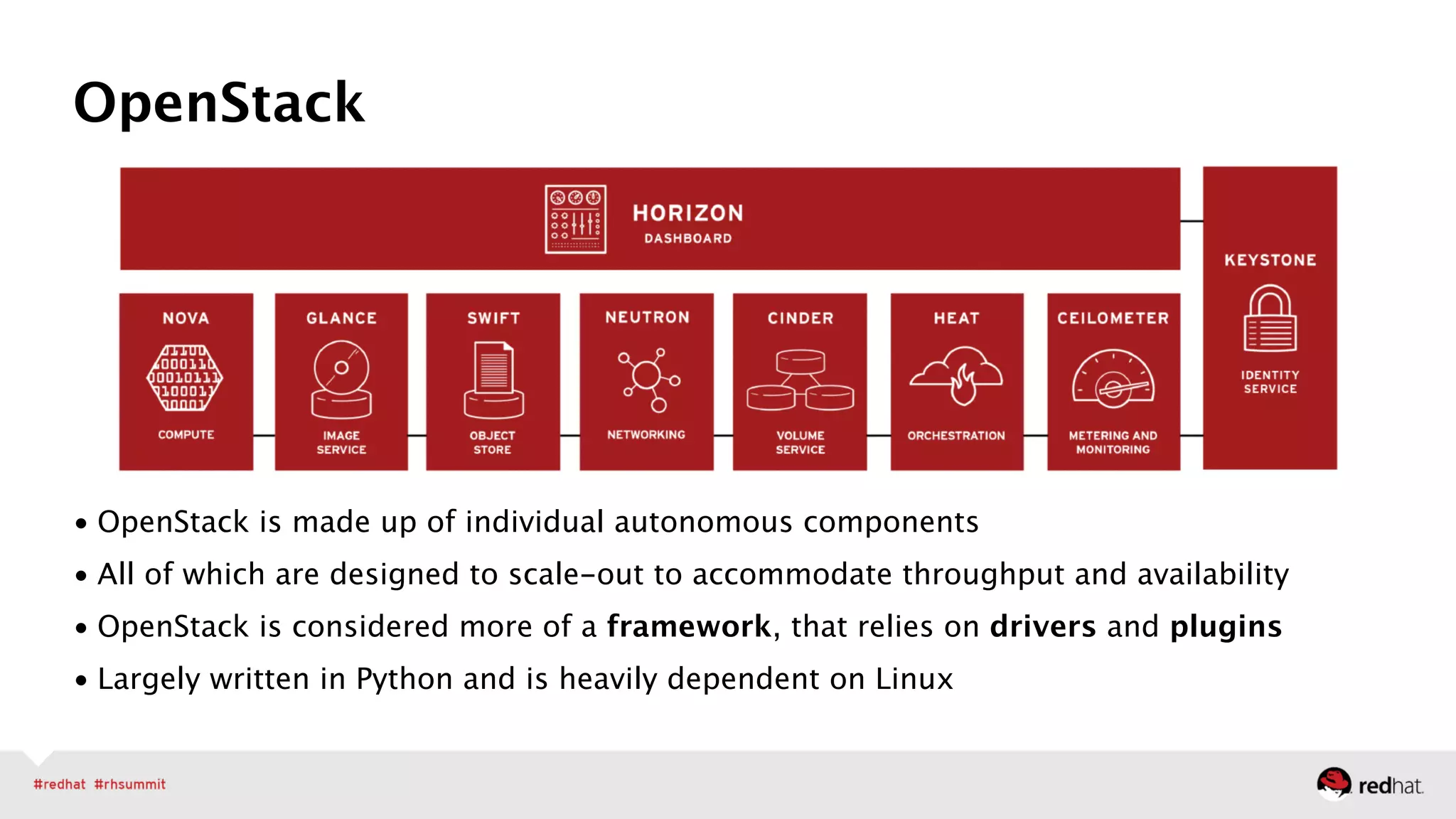
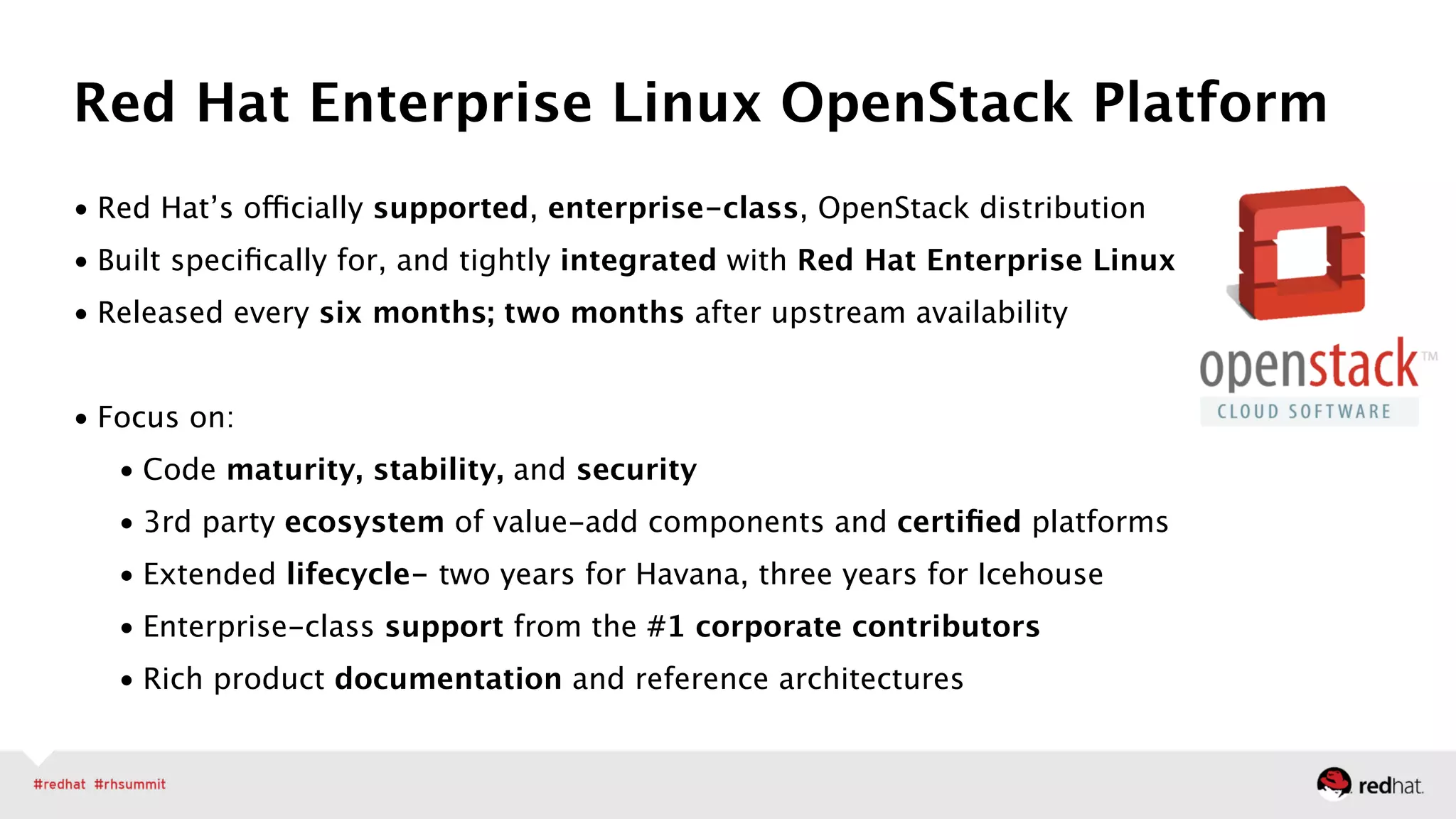
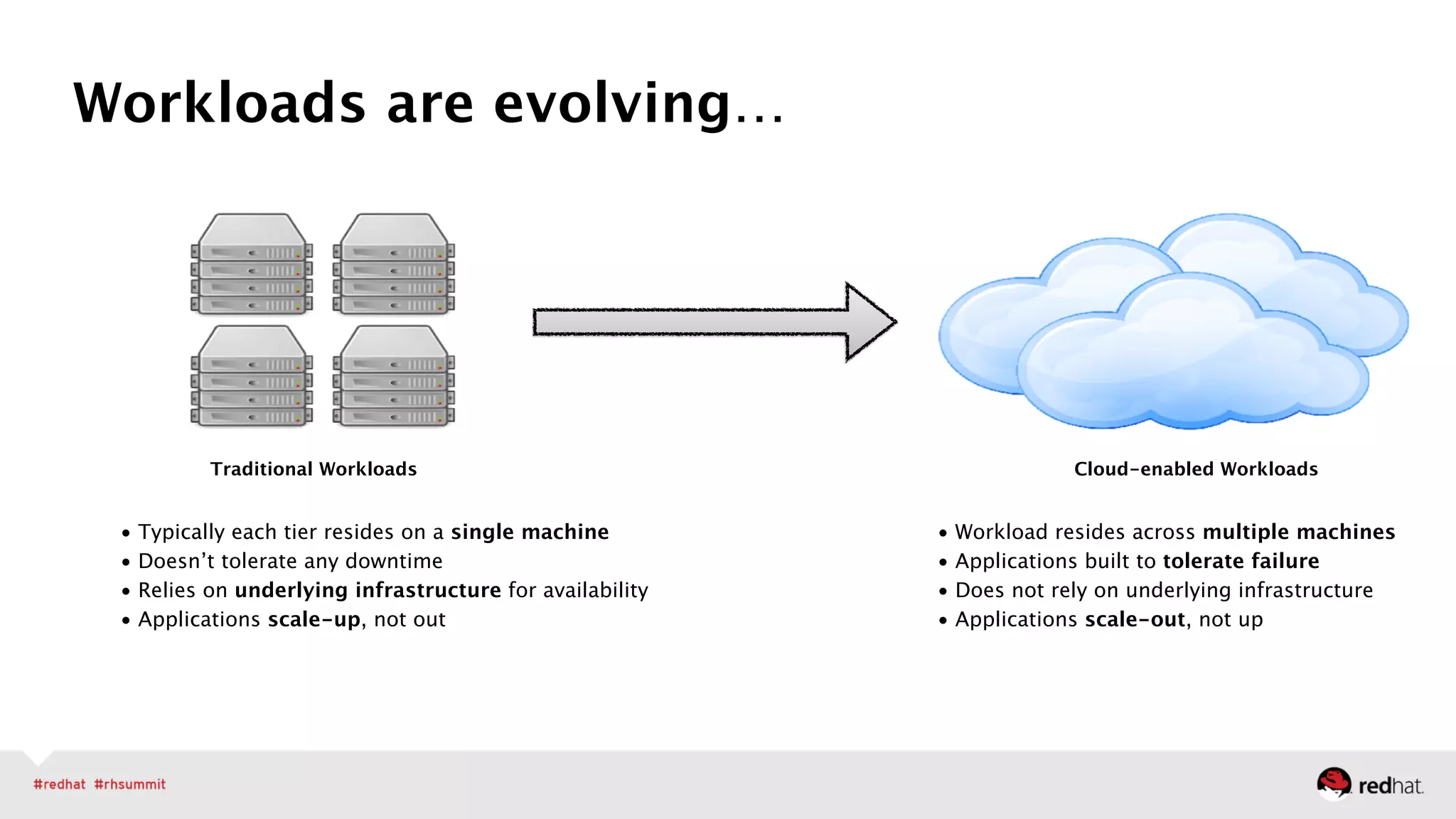
The document outlines Red Hat's leadership in open-source solutions, particularly focusing on OpenStack as a scalable framework for cloud infrastructure. It highlights Red Hat's enterprise-class OpenStack distribution, which is integrated with Red Hat Enterprise Linux and emphasizes the need for cloud solutions due to evolving workloads and unstructured data. Additionally, it presents various customer success stories demonstrating OpenStack's applications in fields like biomedical research and network virtualization.