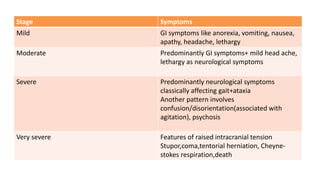
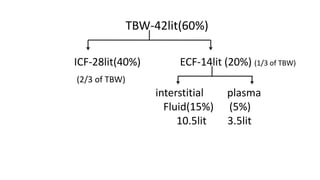
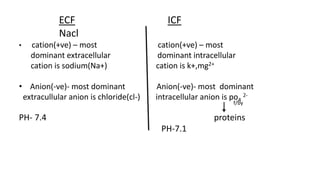
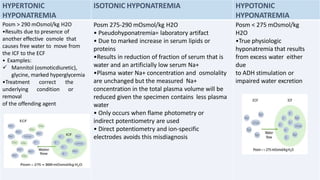
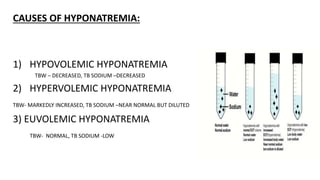
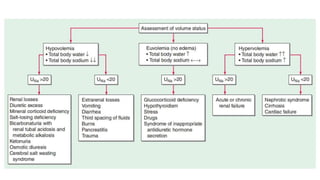
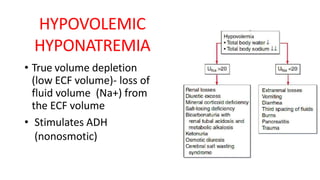
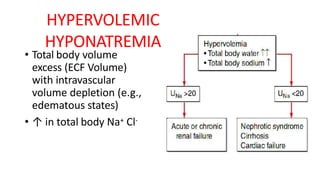
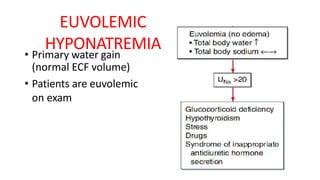
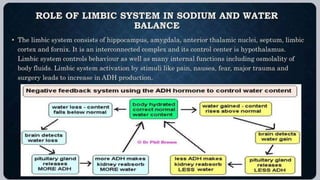
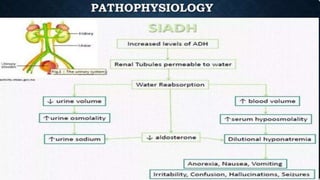
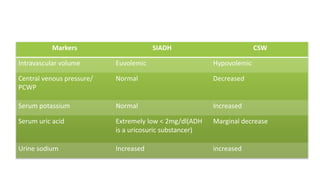
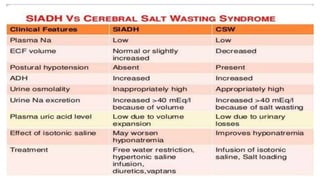
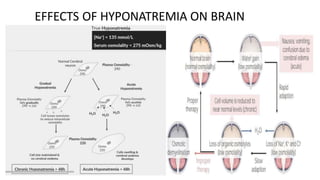
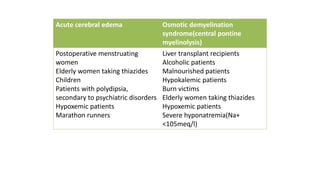
Hyponatremia, defined as a serum sodium level below 135 mEq/L, is the most common electrolyte disorder. It can be caused by excess water intake relative to sodium, and inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion is a common cause. Hyponatremia is categorized as hypervolemic, euvolemic, or hypovolemic based on total body water status. Symptoms range from mild gastrointestinal issues to serious neurological effects like seizures or coma if severe. Diagnosis involves assessing sodium, osmolality, and urine studies. Treatment depends on chronicity and severity, with hypertonic saline used for acute cases and fluid restriction or vasopressin receptor antagon