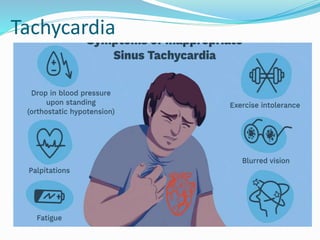
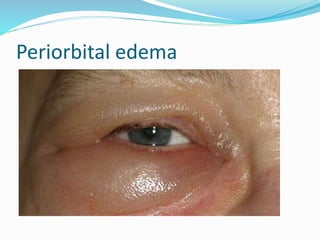
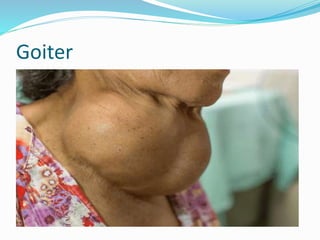
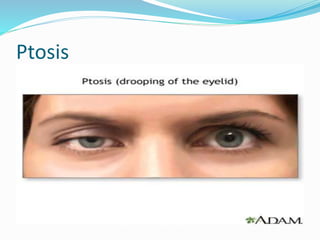
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive and produces too many hormones. Some common causes include Graves' disease, infection, and excessive iodine intake. Symptoms include increased sweating, weight loss, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, and bulging eyes. The condition is diagnosed based on physical exam, hormone levels, and thyroid scans. Treatment options include antithyroid medications, beta blockers, radioactive iodine, or thyroid surgery if other options fail.