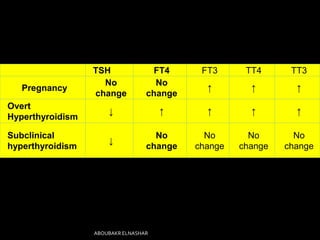
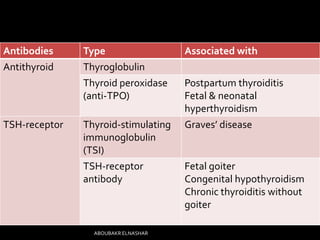
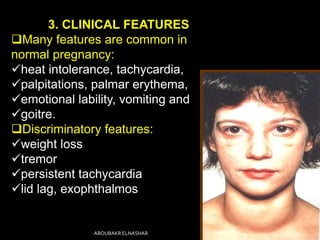
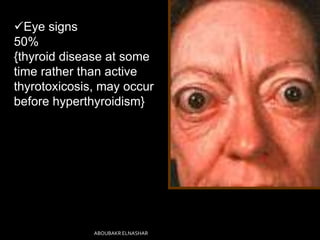
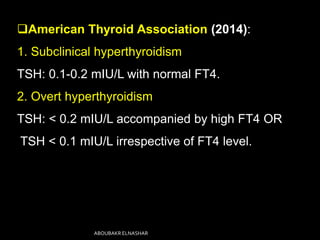
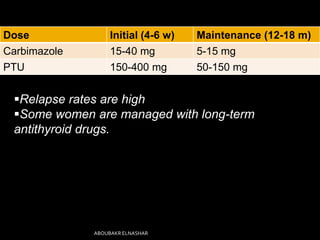
This document discusses hyperthyroidism during pregnancy. It covers the incidence, types, causes, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, effects of pregnancy on thyrotoxicosis and vice versa, and management. The most common cause is Graves' disease. Left untreated, thyrotoxicosis can cause complications for both mother and fetus like miscarriage. Treatment involves antithyroid medications like PTU or carbimazole to maintain euthyroidism while minimizing risk to the fetus. Surgery and radioactive iodine are generally avoided during pregnancy. Careful monitoring is needed to balance control of the mother's condition and fetal well-being.