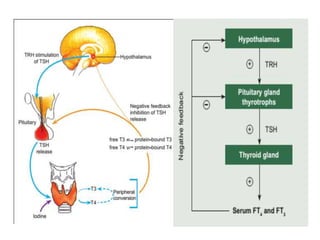
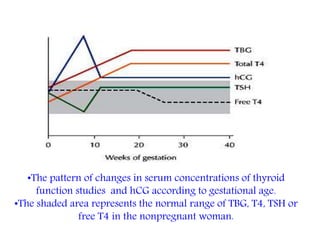
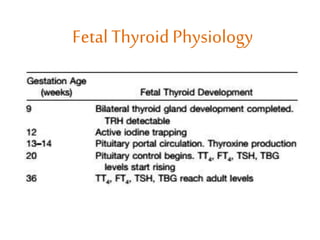
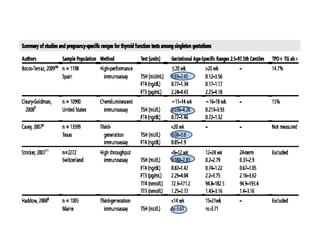
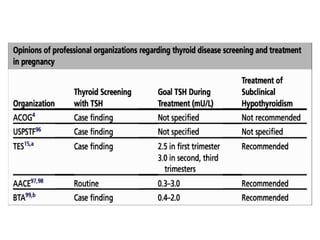
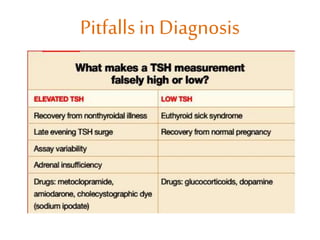
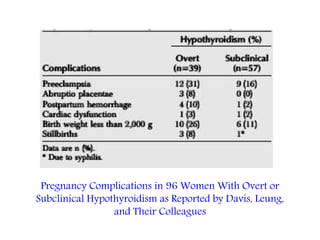
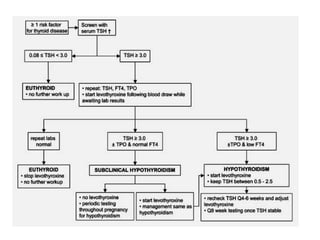
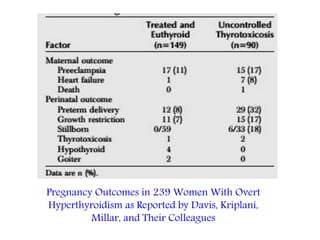
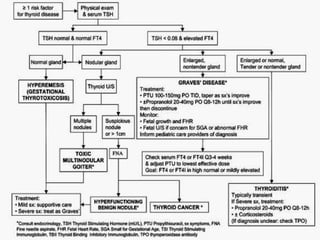
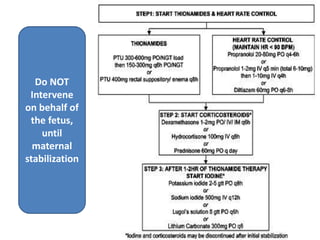
This document discusses thyroid disorders in pregnancy. It notes that thyroid disorders are common in pregnancy, affecting 1-2% of pregnancies with overt disease and 3-5% with subclinical disease. Thyroid screening and treatment in pregnancy can help improve outcomes for both mother and baby, though guidelines vary on who and when to screen. The document reviews thyroid changes in pregnancy, screening recommendations, treatment of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, and complications like postpartum thyroid dysfunction.