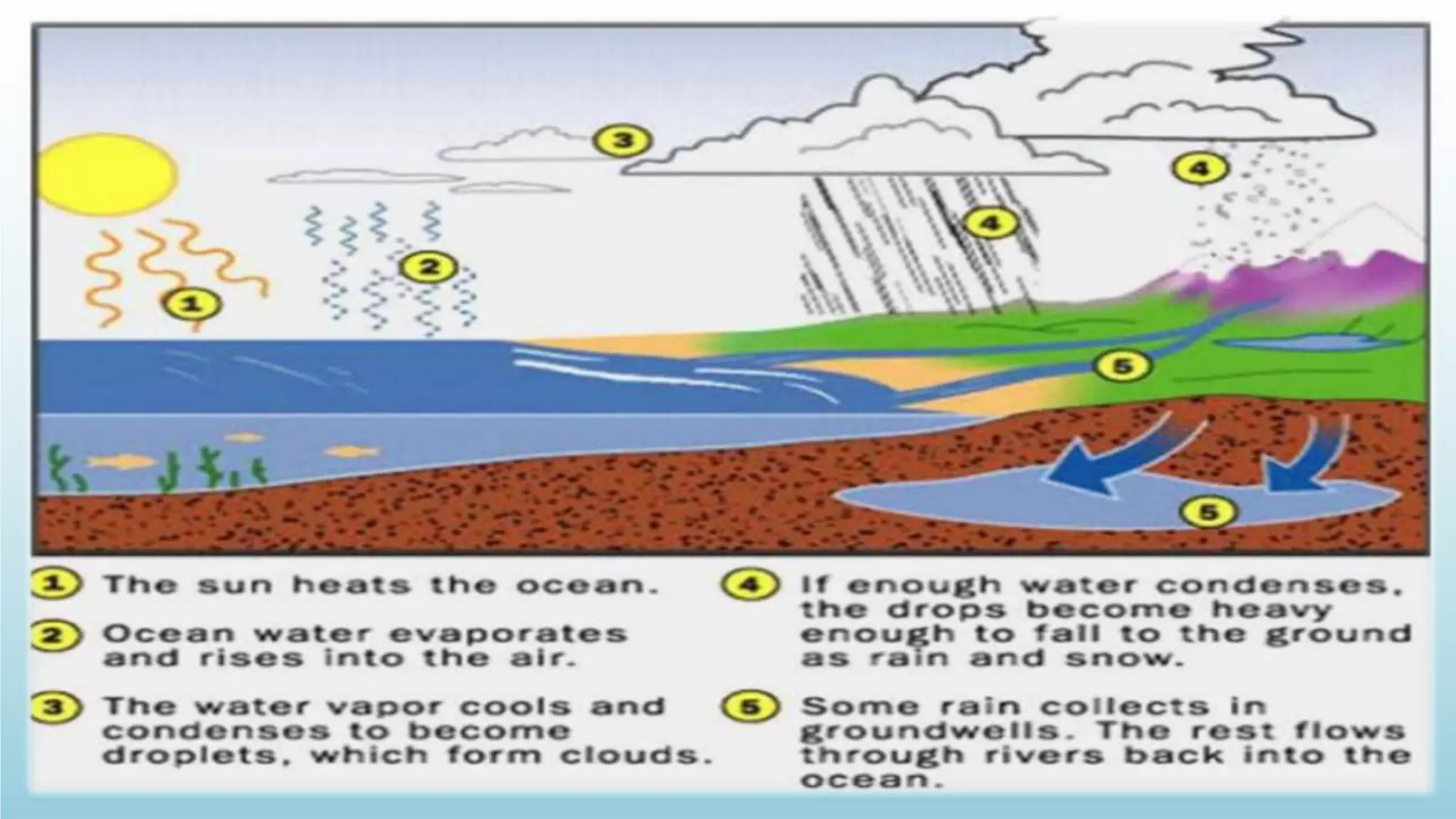
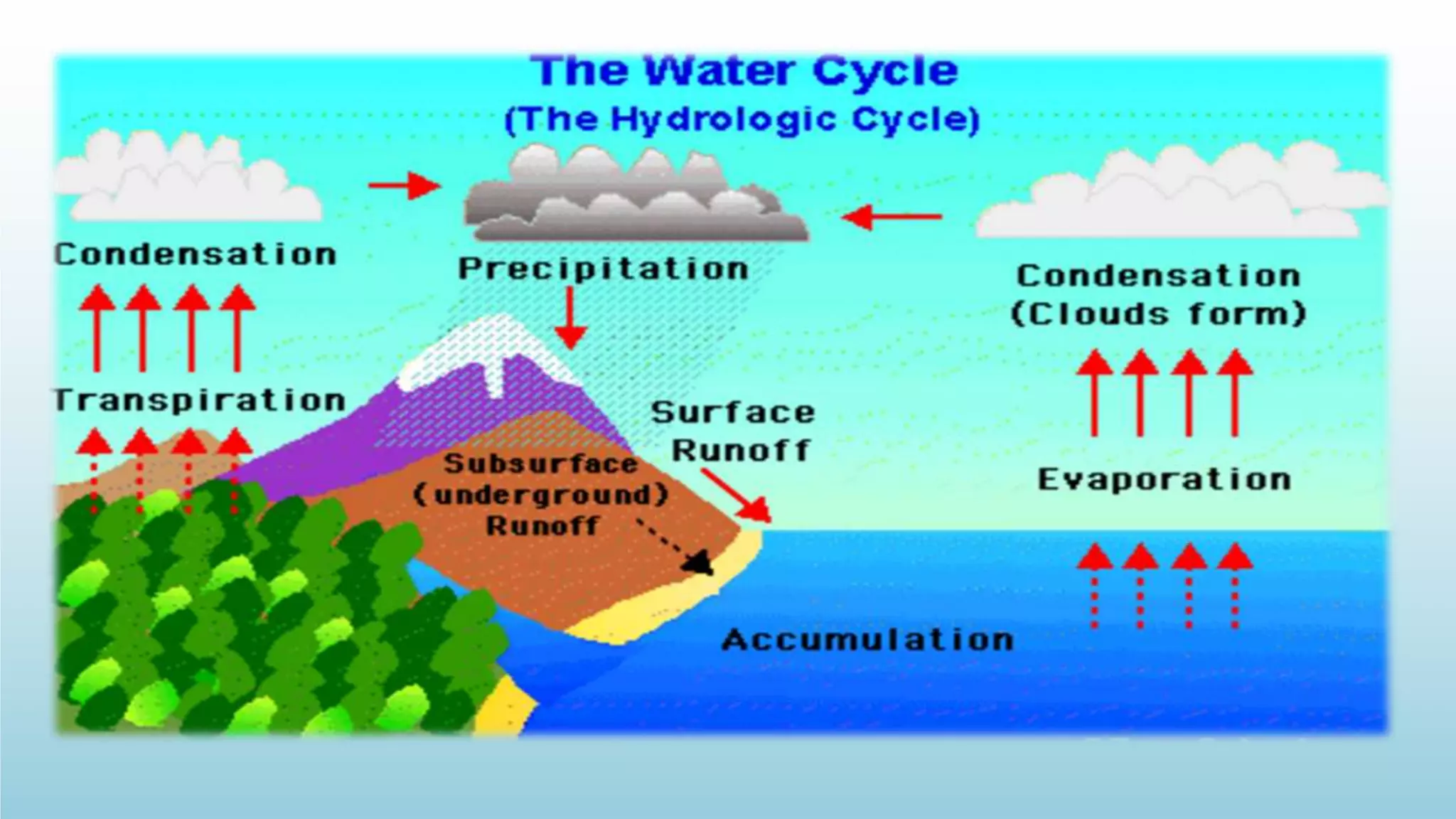
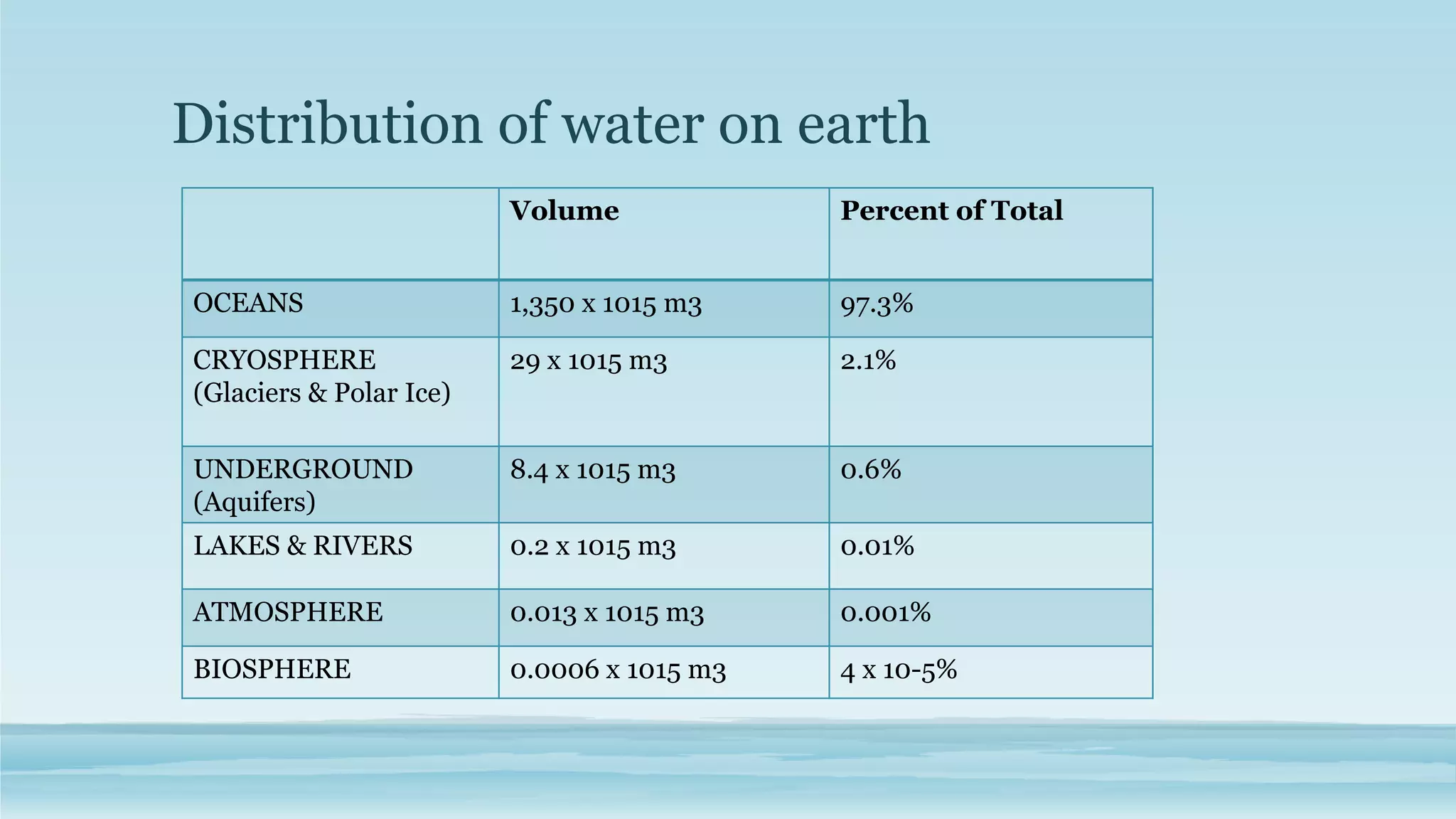
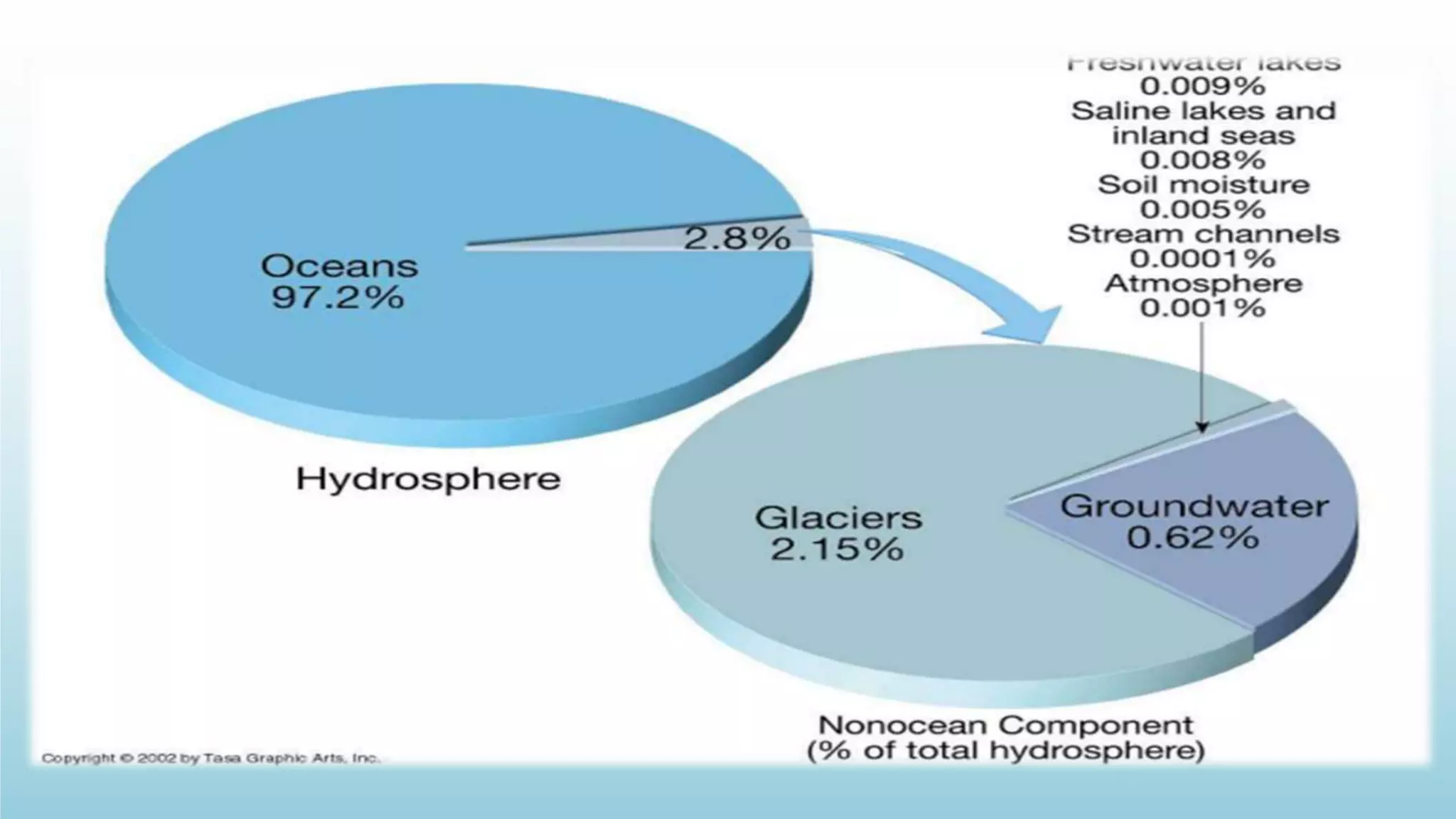
The document discusses the hydrosphere, which refers to all water on Earth's surface and in its atmosphere and interior. It describes theories about how water originated on Earth through impacts from comets and asteroids when the planet first formed. The water cycle is explained as the continuous movement of water between the oceans, atmosphere, and continents through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transportation by rivers. The majority of Earth's water is contained in the oceans, with smaller amounts in glaciers, underground aquifers, lakes, and the atmosphere. The hydrosphere plays a crucial role in sustaining life and regulating Earth's climate.