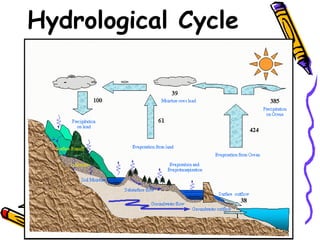
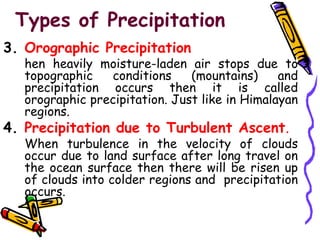
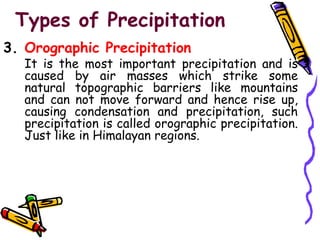
The document discusses the hydrologic cycle and precipitation. It defines the hydrologic cycle as the continuous process by which water evaporates from bodies of water into the atmosphere, condenses into clouds, and falls back to the Earth's surface as precipitation such as rain, snow, sleet or hail. It then describes the different forms and types of precipitation, including liquid precipitation like rain and drizzle, frozen precipitation like sleet and hail, and types like cyclonic, convective, and orographic precipitation. Finally, it discusses characteristics of rainfall such as size, shape, intensity and duration.