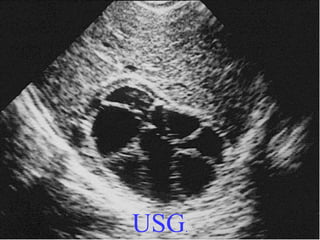
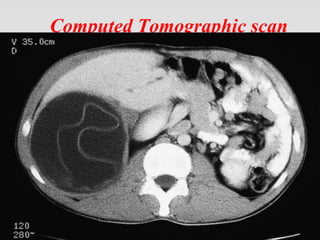
This document provides tips and instructions for using a PowerPoint presentation on Hydatid disease:
1. The PPT can be freely downloaded, edited, and modified. It includes blank slides to engage students by asking questions before providing information.
2. The presentation is to be used for active learning sessions where blank slides are first shown to elicit student responses, followed by the content slides.
3. This format allows for repetition and revision of content through multiple iterations of questioning and answering.