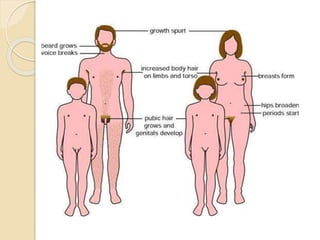
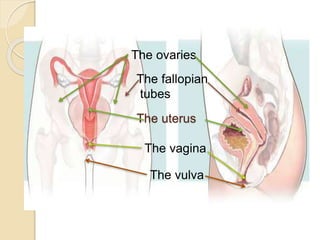
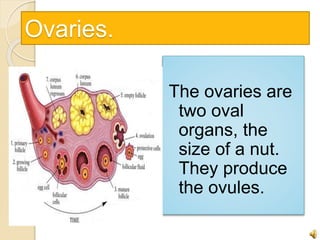
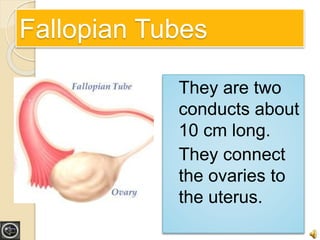
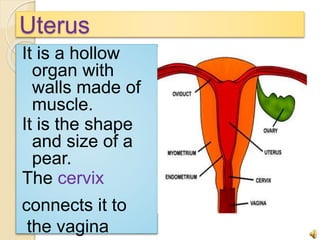
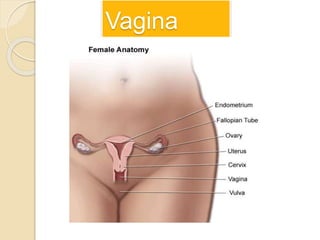
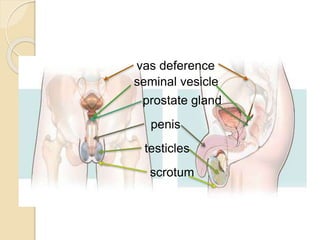
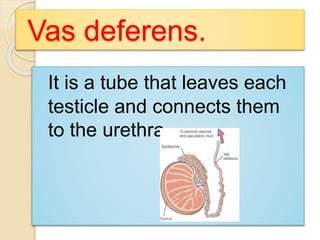
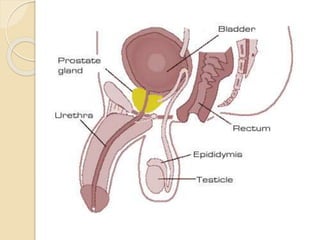
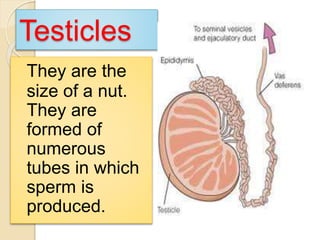
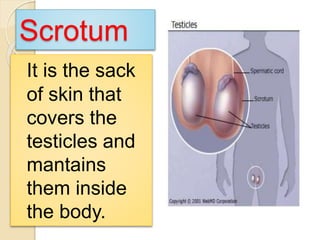
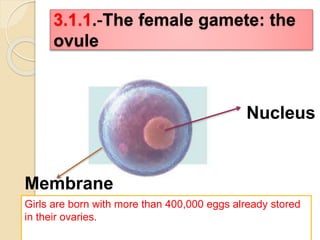
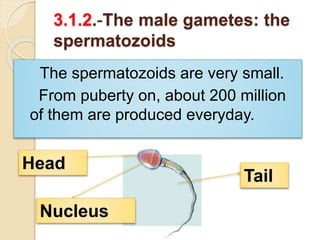
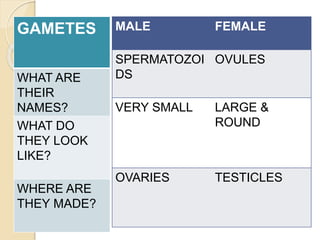
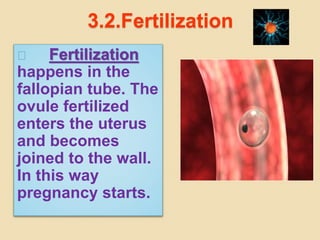
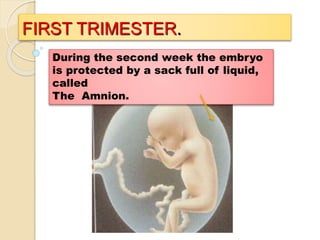
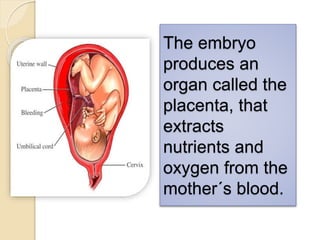
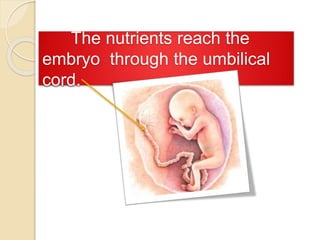
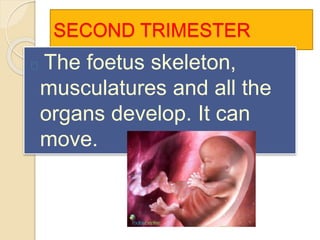
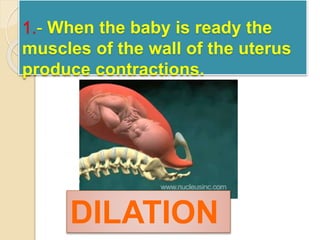
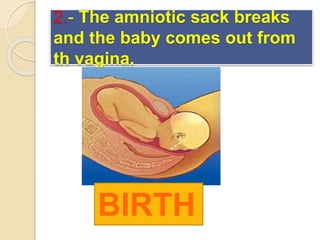
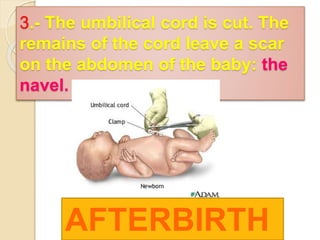
The document provides an overview of human reproduction including sexual characteristics, the reproductive systems of males and females, and the processes of reproduction. It describes puberty and the development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics. It then details the key parts of the male and female reproductive systems such as ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, testes, and penis. The document concludes by explaining the processes of gamete production, fertilization, pregnancy, and childbirth.