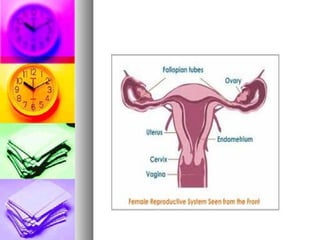
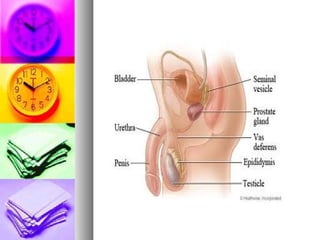
Human reproduction involves the combining of male and female sex cells through sexual reproduction. During puberty, between ages 11-15, individuals develop primary and secondary sex characteristics that allow for reproduction. The female reproductive system includes the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, and vulva. The male reproductive system includes the testicles, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, and prostate. Fertilization occurs when sperm meets an egg in the fallopian tubes. A fertilized egg implants in the uterus and develops over 9 months into a baby, receiving nutrients from the placenta via the umbilical cord. Birth occurs in three stages of dilation, expulsion, and afterbirth