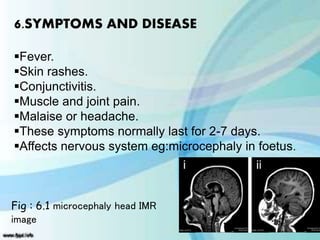
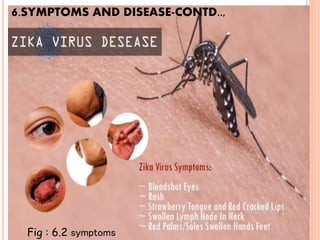
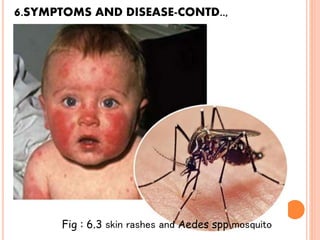
Zika virus was first isolated in 1947 in Uganda and has since spread across the Pacific and Americas. It is transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes and causes fever, rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis. While symptoms are usually mild and short-lived, Zika can also cause microcephaly in fetuses when mothers are infected during pregnancy. The virus is diagnosed through blood and other tests and treated through symptom relief only. Prevention focuses on mosquito bite protection as there is currently no vaccine.

















![9.PREVENTION
The best form of prevention is protection against
mosquito bites.
Repellents should contain DEET (N, N-diethyl-3-
methylbenzamide), IR3535 (3-[N-acetyl-N-butyl]-
aminopropionic acid ethyl ester) or icaridin (1-
piperidinecarboxylic acid, 2-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-
methylpropylester).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanimmunalresponseagainstzika-160310234341/85/Human-immunal-response-against-zika-23-320.jpg)



