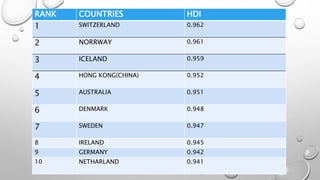
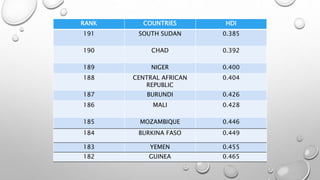
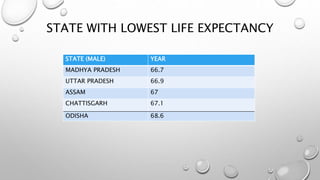
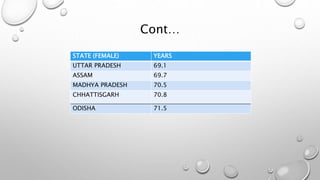
The document discusses the Human Development Index (HDI), which is a metric used to measure development in countries based on life expectancy, education, and income indicators. It provides background on what the HDI measures, how countries are ranked, and examples of countries with high and low HDI scores. Key factors that influence India's HDI ranking, such as public spending, poverty, and environmental issues are also examined.