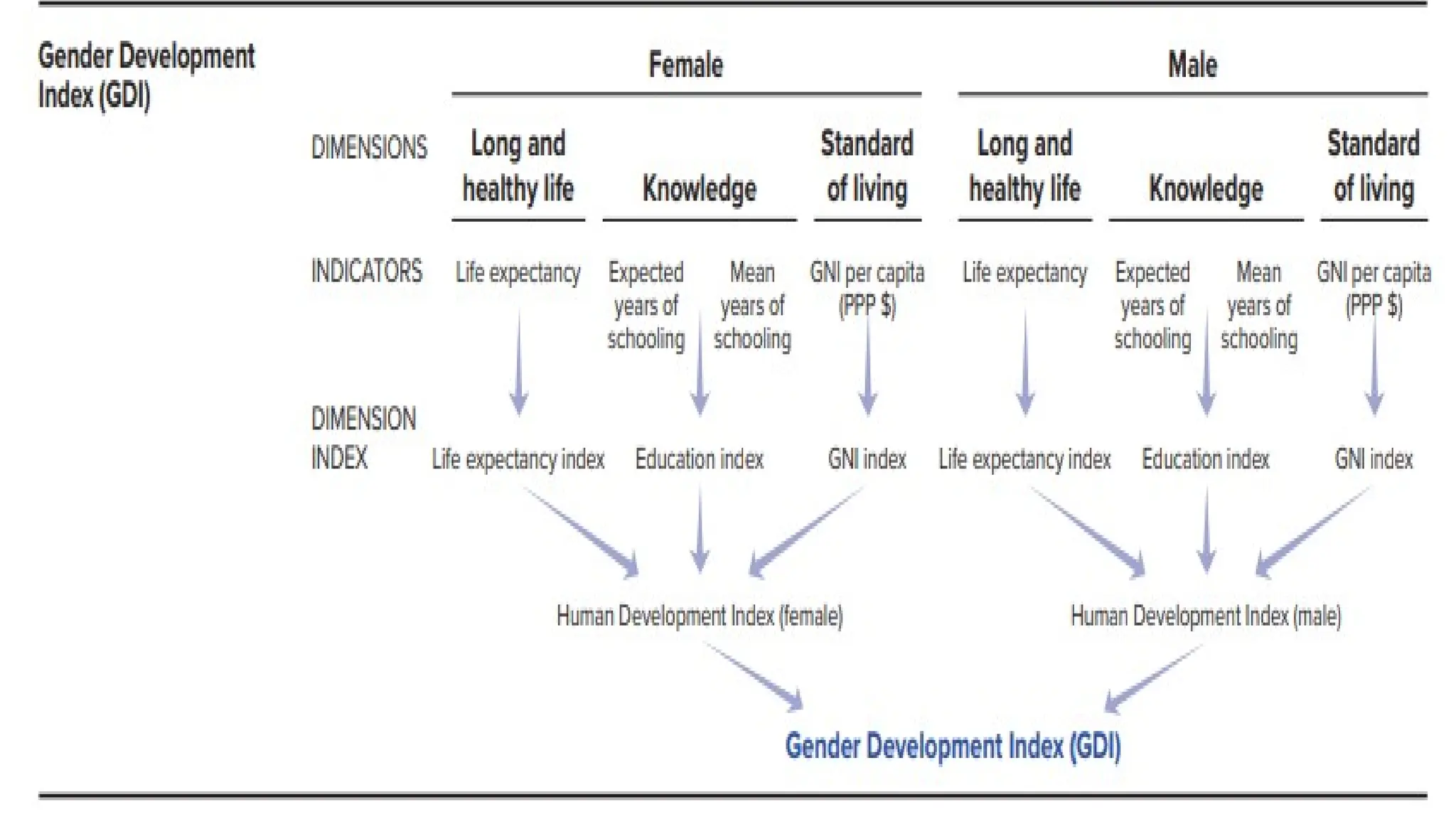
The Gender Development Index (GDI), introduced in the 1995 Human Development Report by the UNDP, measures gender inequalities in health, education, and income to address disparities between men and women. It calculates the GDI as the ratio of female to male Human Development Index (HDI), reflecting the extent of gender parity or disparity in human development outcomes. GDI values range from 1, indicating perfect gender parity, to values less than 1, indicating disparity favoring men, or, rarely, greater than 1, indicating disparity favoring women.