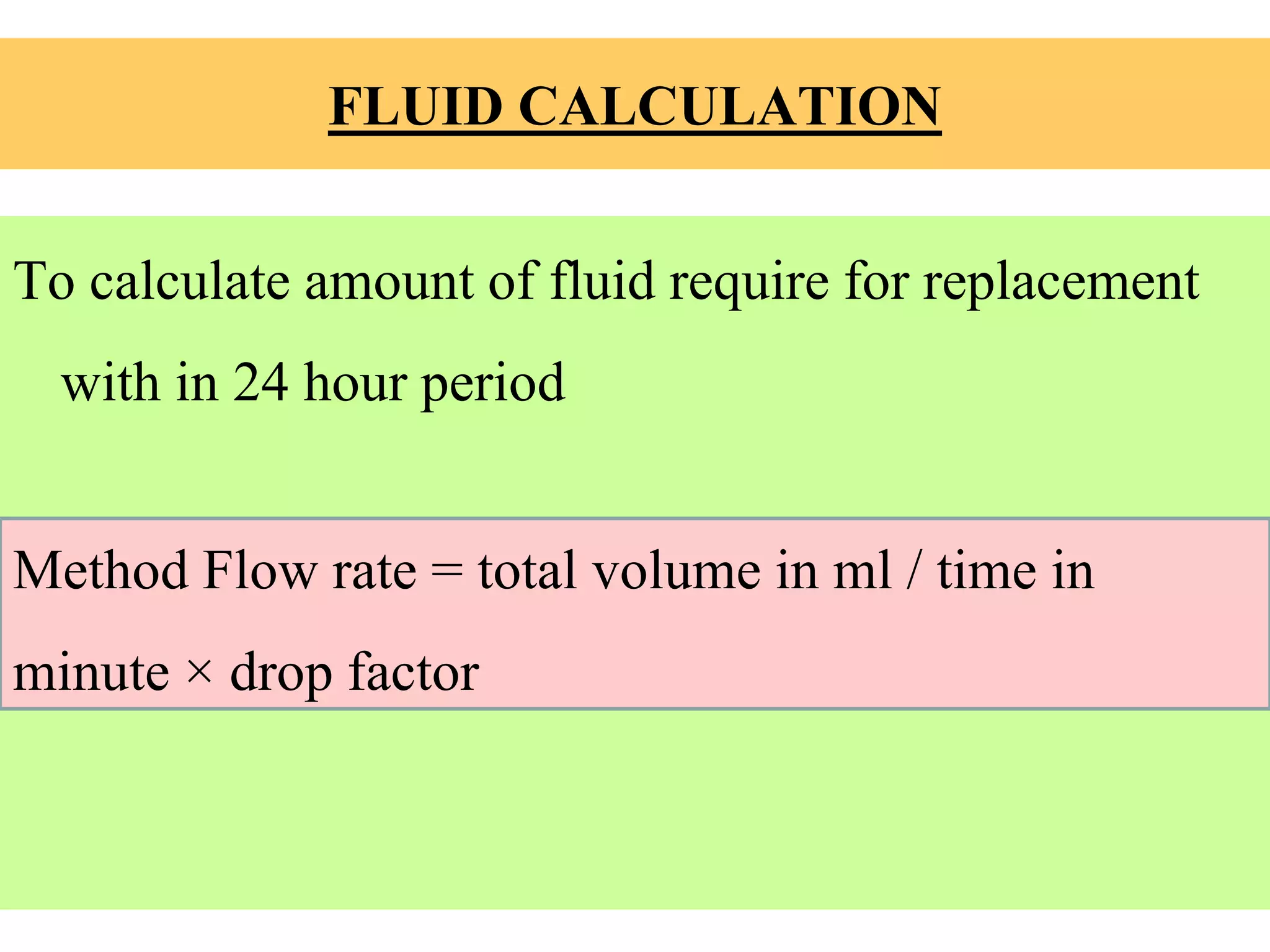
Intravenous fluid is liquid administered directly into a vein. There are two main types of IV fluids - crystalloids and colloids. Crystalloids are water and electrolyte solutions that can be hypotonic, isotonic, or hypertonic depending on solute concentration. Colloids contain larger molecules that do not cross membranes. IV fluids are used to treat dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, blood loss, and other conditions. The amount of IV fluid given over time is calculated using the fluid volume, administration time, and drop factor of the delivery set.