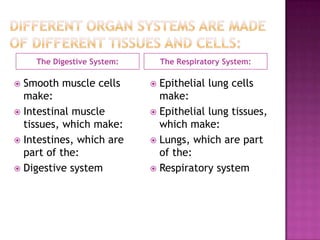
Cells combine to form tissues, tissues combine to form organs, and organs combine to form organ systems which make up an organism. The document then provides examples of how smooth muscle cells and epithelial lung cells form tissues that make up organs in the digestive and respiratory systems respectively. It proceeds to define the main tissue types and organ systems in the human body, describing their main functions. Finally, it explains how feedback loops control bodily functions, with negative feedback maintaining homeostasis and positive feedback driving processes away from their set points.