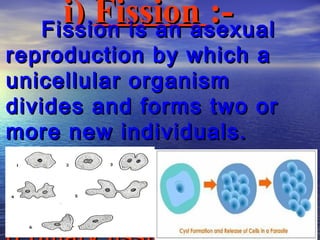
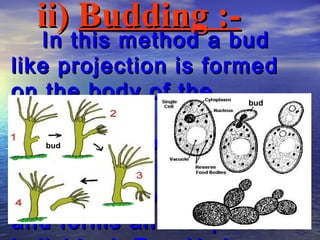
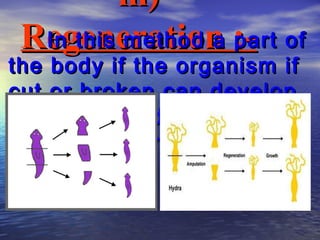
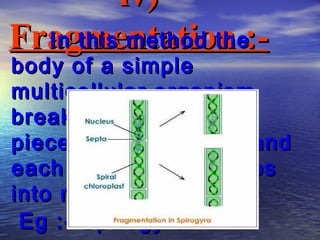
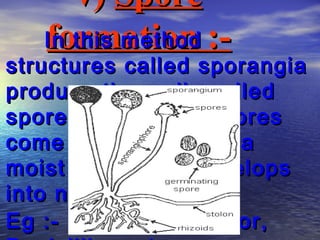
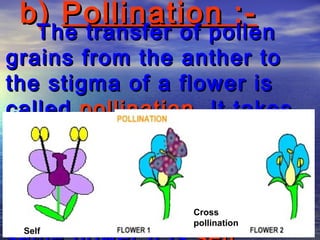
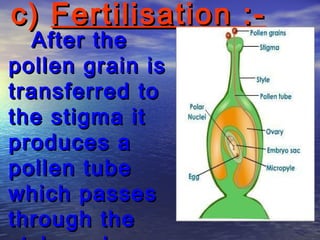
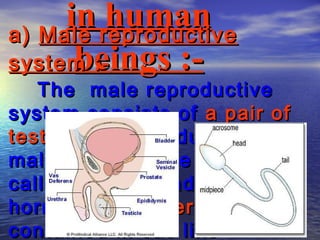
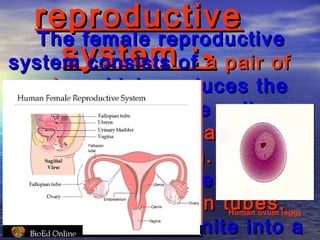
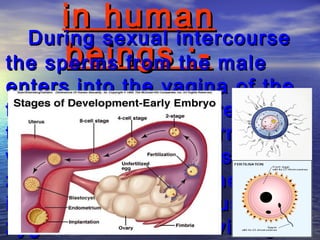
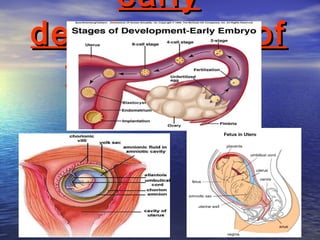
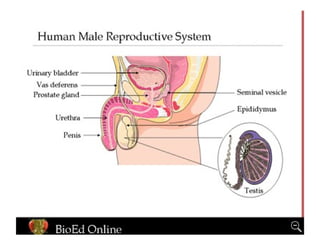
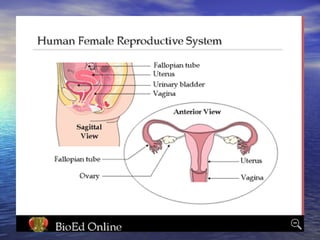
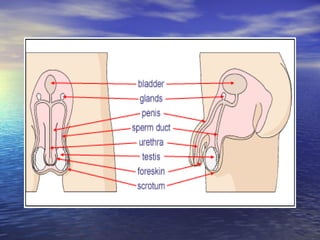
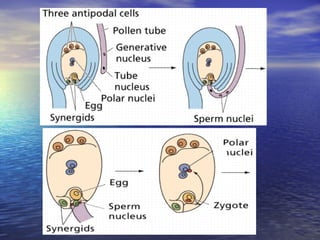
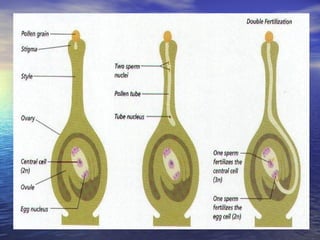
Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals of the same species. There are two main types of reproduction: asexual reproduction, which involves a single parent producing new individuals, and sexual reproduction, which involves genetic contribution from two parents. In humans, the male reproductive system produces sperm and the female reproductive system produces eggs. During sexual intercourse, sperm from the male enters the female's vagina and travels to the egg, where fertilization can occur if a sperm fuses with the egg to form a zygote.