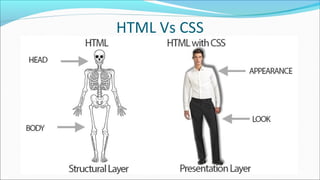
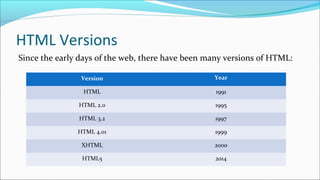
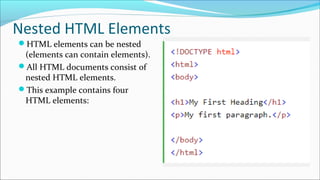
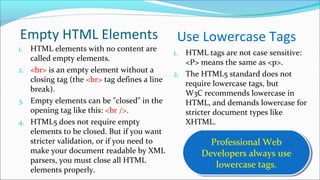
The document provides a comprehensive overview of HTML, describing it as the standard markup language for creating web pages with elements defined by tags that structure the content. It explains the basic structure of an HTML document, including the purpose of various tags and the importance of the <!doctype> declaration. It also emphasizes the significance of using proper syntax, including the use of pairs of start and end tags, and best practices such as employing lowercase tags for consistency.