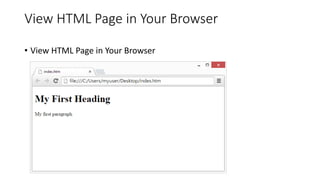
HTML, or Hyper Text Markup Language, is a markup language used to describe web pages through a series of tags. It provides structure to content with elements such as headings, paragraphs, links, and images, each defined by specific tags. HTML documents can be created and edited using simple text editors like Notepad, and understanding attributes within tags is essential for controlling additional aspects of content display.