Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


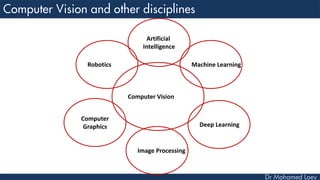
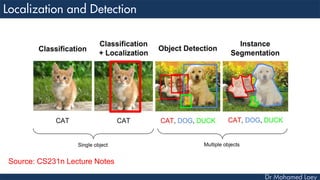




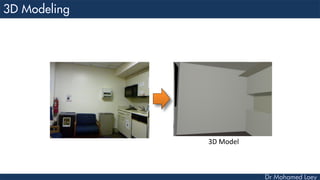


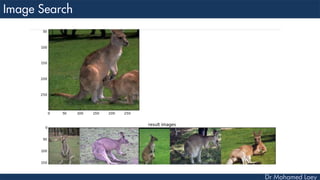

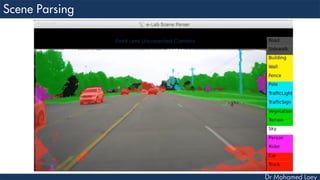







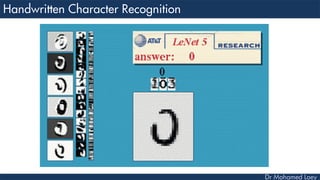

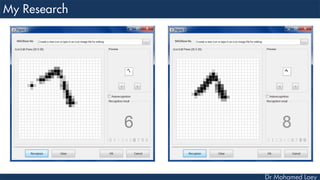
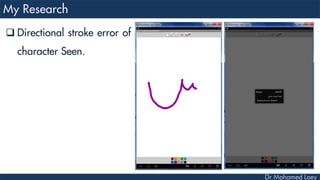



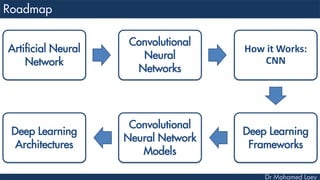





This document discusses how deep learning has helped advance computer vision capabilities. It notes that deep learning can help bridge the gap between pixels and meaning by allowing computers to recognize complex patterns in images. It provides an overview of related fields like image processing, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and computer graphics. It also lists some specific applications of deep learning like object detection, image classification, and generating descriptive text. Students are then assigned a task to research how deep learning has improved one particular topic and submit a two-page summary.
































