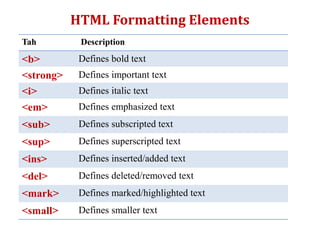
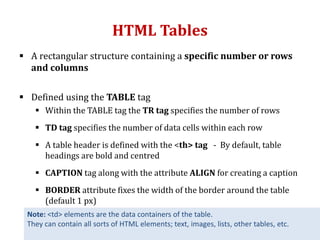
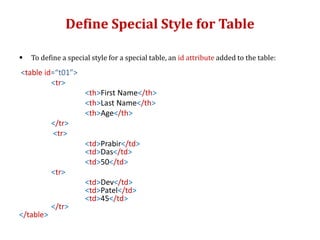
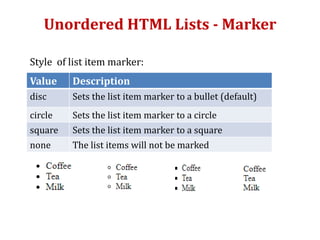
The document provides information on various HTML elements for styling and formatting text, including comments, style attributes, colors, fonts, borders, padding, and margins. It also covers CSS for defining styles through inline, internal, and external stylesheets. Additional topics include HTML tables, lists, links, and images. Key elements covered are tags for headings, paragraphs, bold, italics, superscript, formatting text size and color, and applying styles through CSS selectors like id and class.