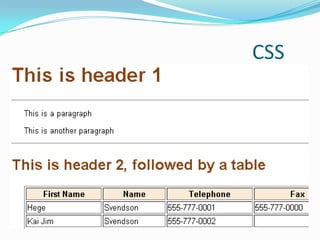
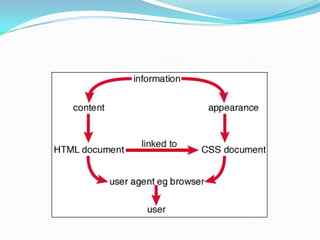
CSS is a style sheet language used to describe the presentation of HTML and XML documents. It can be applied through inline styles, internal style sheets embedded in HTML <style> tags, or external style sheets linked via <link> tags. CSS uses selectors to target elements and properties to style them by setting values like font sizes, colors, spacing and more. This allows separation of document structure/semantics from presentation.






![Selector
Selector
HTML Tags
Class Name
Example
[HTML Tags:Style] H2{ background-color : #191970 }
[HTML Tags:Style] P{ text-indent: 3em }
[Class Name:Style] .note { font-size : small }
[Class Name:Style] .normal{ color : blue }
[Class Name:Style] .special{ color : red }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cascadingstylesheets-111112054510-phpapp02/85/html-9-320.jpg)