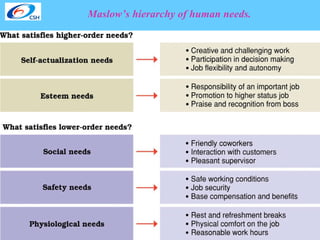
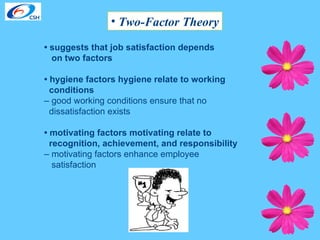
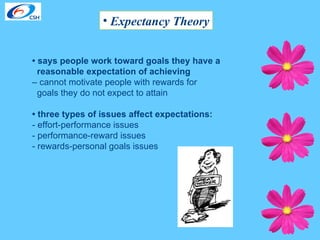
The document discusses various theories of motivation and ways to motivate employees. It covers classical theories focusing on money, behavioral theories that any attention increases productivity, and contemporary theories emphasizing good human relations. Specific theories covered include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, equity theory, and goal setting theory. The document also provides examples of programs companies use to enhance job satisfaction, such as reinforcement, participative management, and modified work schedules. Finally, it lists factors that are great motivators like meaningful work and good relationships, and tips for appreciating employees.