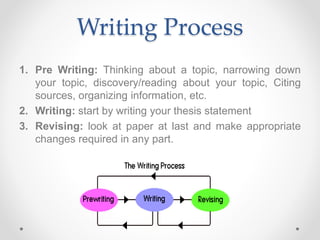
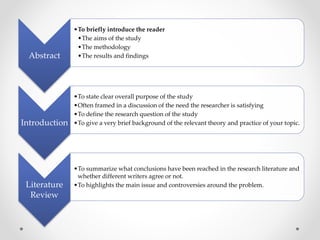
The document provides a comprehensive guide on how to write a research paper, outlining the importance of research and the systematic process involved in academic writing. It describes the essential sections of a research paper including the abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices, along with detailed explanations of each. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of avoiding plagiarism, adhering to formatting standards such as MLA and APA, and proofreading to ensure the quality of the final paper.






![Title
The title
summarizes the
main idea or ideas
of the study.
A good title
contains the fewest
possible words that
adequately describe
the contents and/or
purpose of the
research paper.
If the title is too long it usually
contains too many unnecessary
words,
e.g., "A Study to Investigate the...." On
the other hand, a title which is too short
often uses words which are too general.
For example, “Indian Politics" could be
the title of a book, but it does not provide
any information on the focus of a
research paper.
The following parameters can be used
to help to formulate a suitable
research paper title:
• The purpose of the research
• The narrative tone of the paper [typically
defined by the type of the research]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtowriteresearchpaper-220719032713-ace57941/85/How-to-write-research-paper-9-320.jpg)














