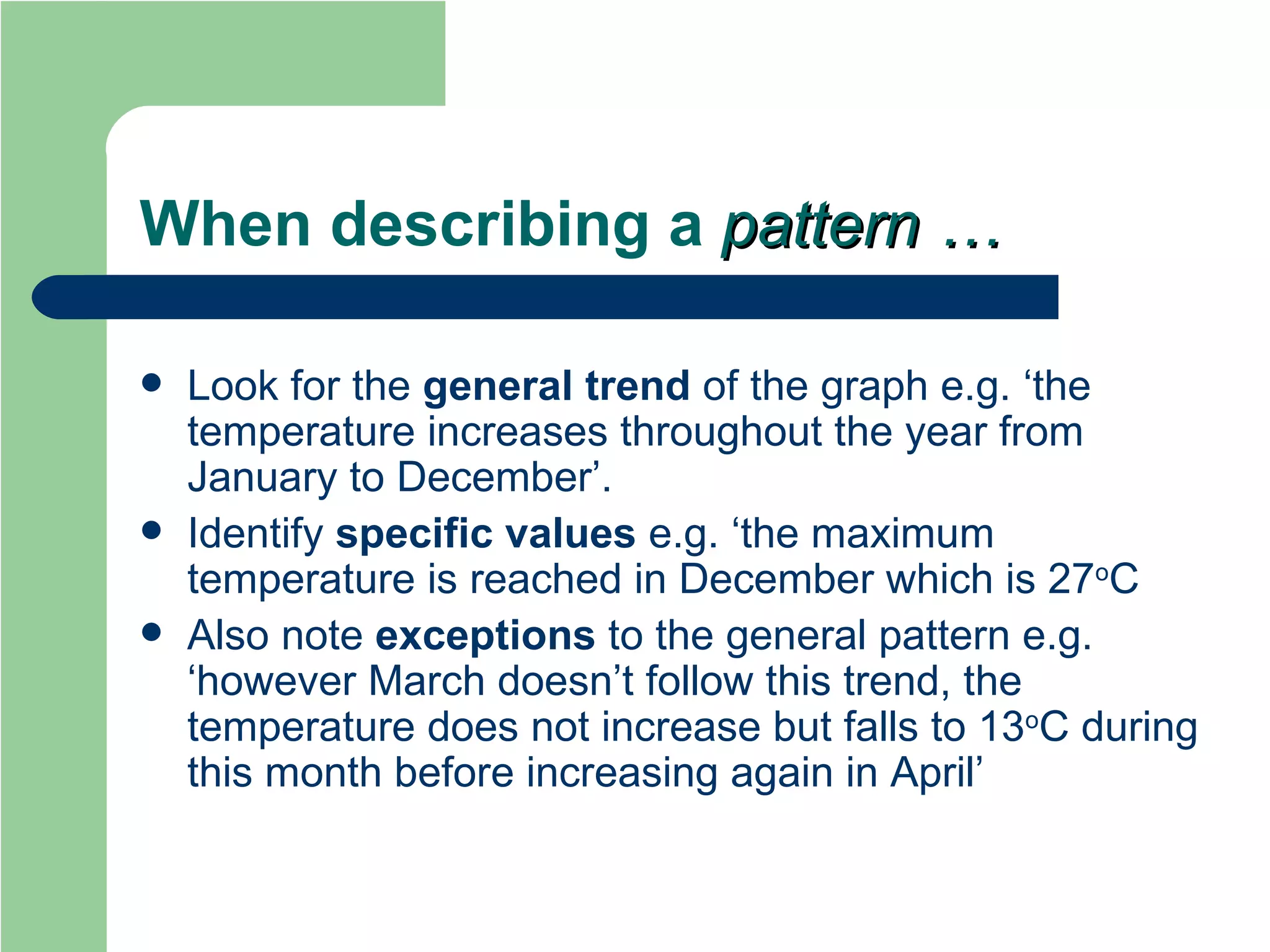
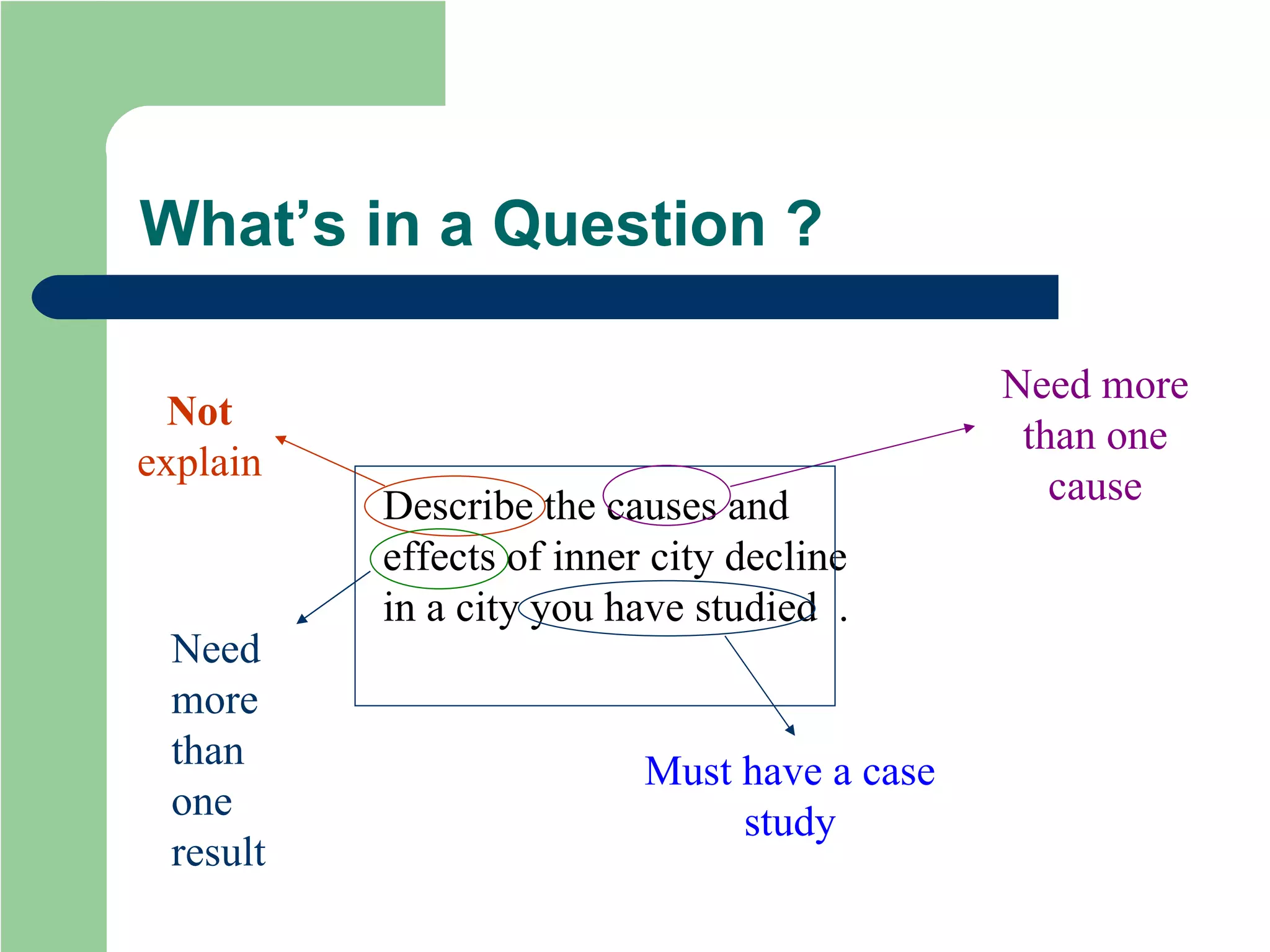
The document provides revision tips for GCSE Geography exams, including how to approach exam questions, what examiners look for in high-scoring answers, and common mistakes to avoid. It emphasizes reading questions carefully, using case study examples and evidence to support points, and achieving deeper levels of analysis and evaluation. Key advice includes highlighting command words, writing something for every question, and applying knowledge from case studies and coursework investigations to answers.