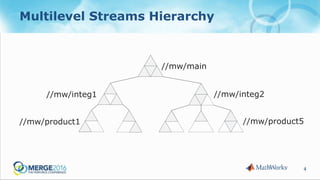
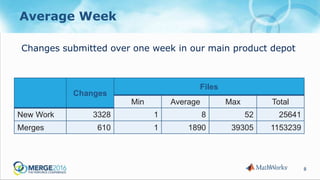
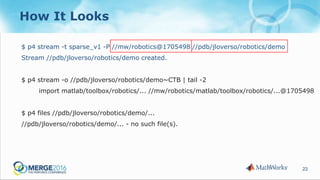
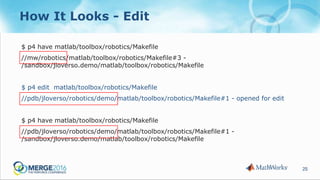
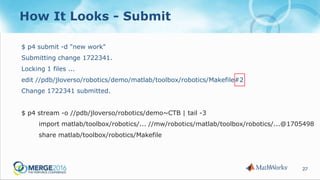
The document discusses strategies to reduce database load in software development through the implementation of sparse branching, which allows files to only branch when modified, minimizing database usage. It outlines technical challenges faced by a large company and introduces concepts such as winked-in files and the process of merging changes efficiently. The approach involves creating two branching techniques: branch on edit and branch on submit, where the latter provides better control over the changes and reduces unnecessary database usage.