This document provides information about conducting a literature search, including defining what literature is, the various sources and types of literature, and how to search for literature both online and offline. It discusses the purpose of literature reviews, primary and secondary sources, and techniques for effective searching including using Boolean operators, truncation, and limiting searches. It also outlines the steps for searching literature databases like PubMed and accessing full texts through resources like HINARI.





























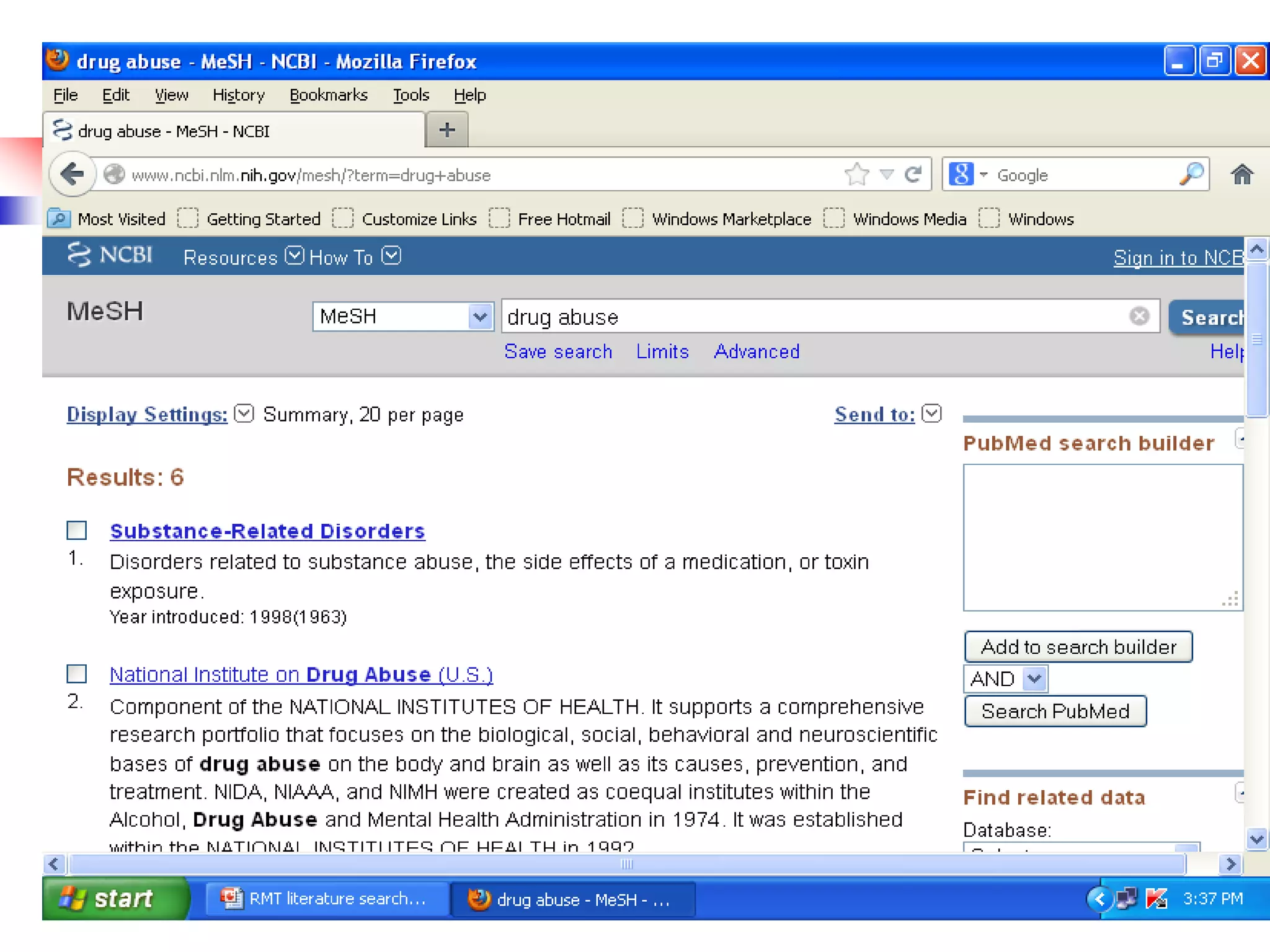
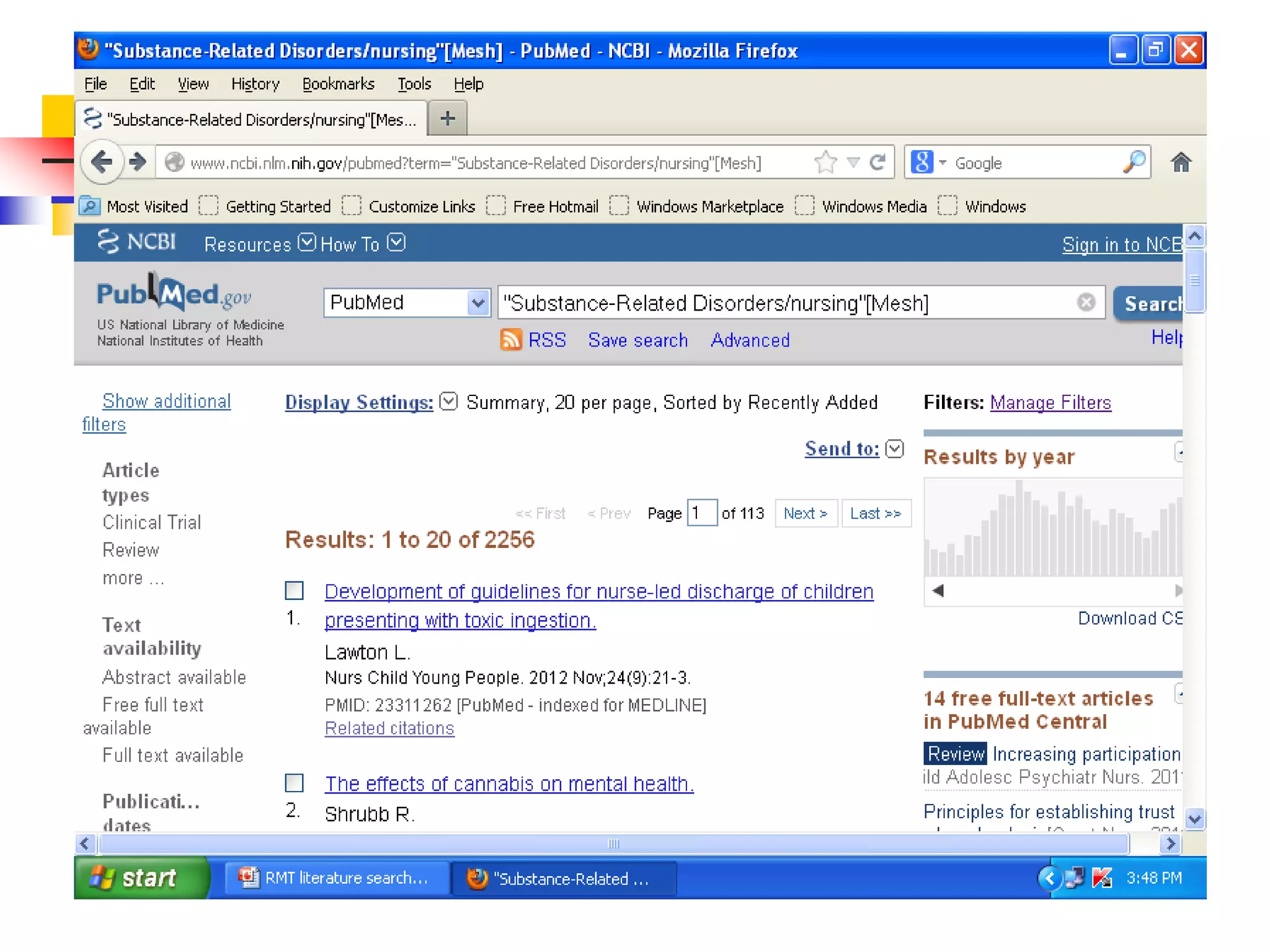



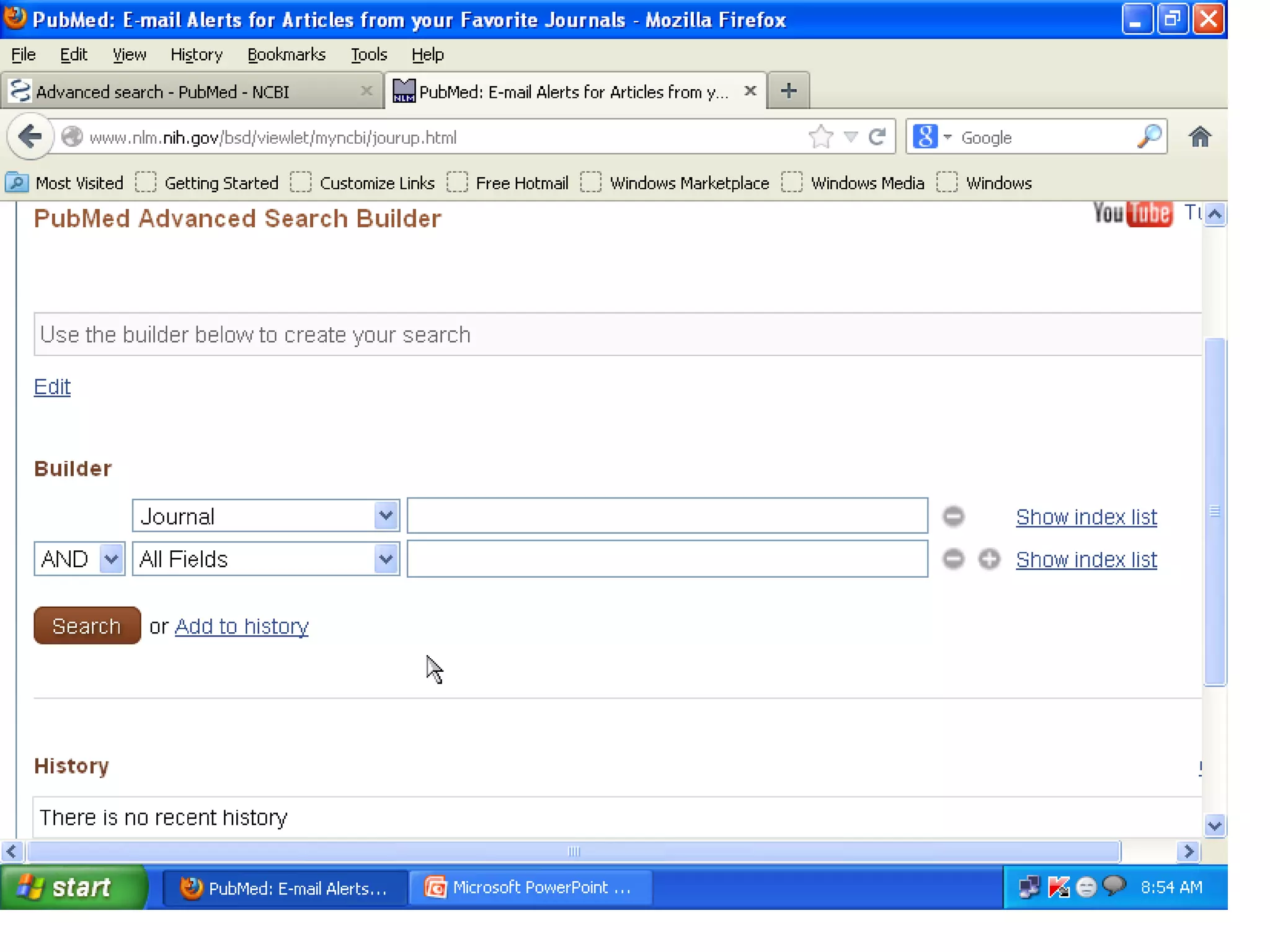
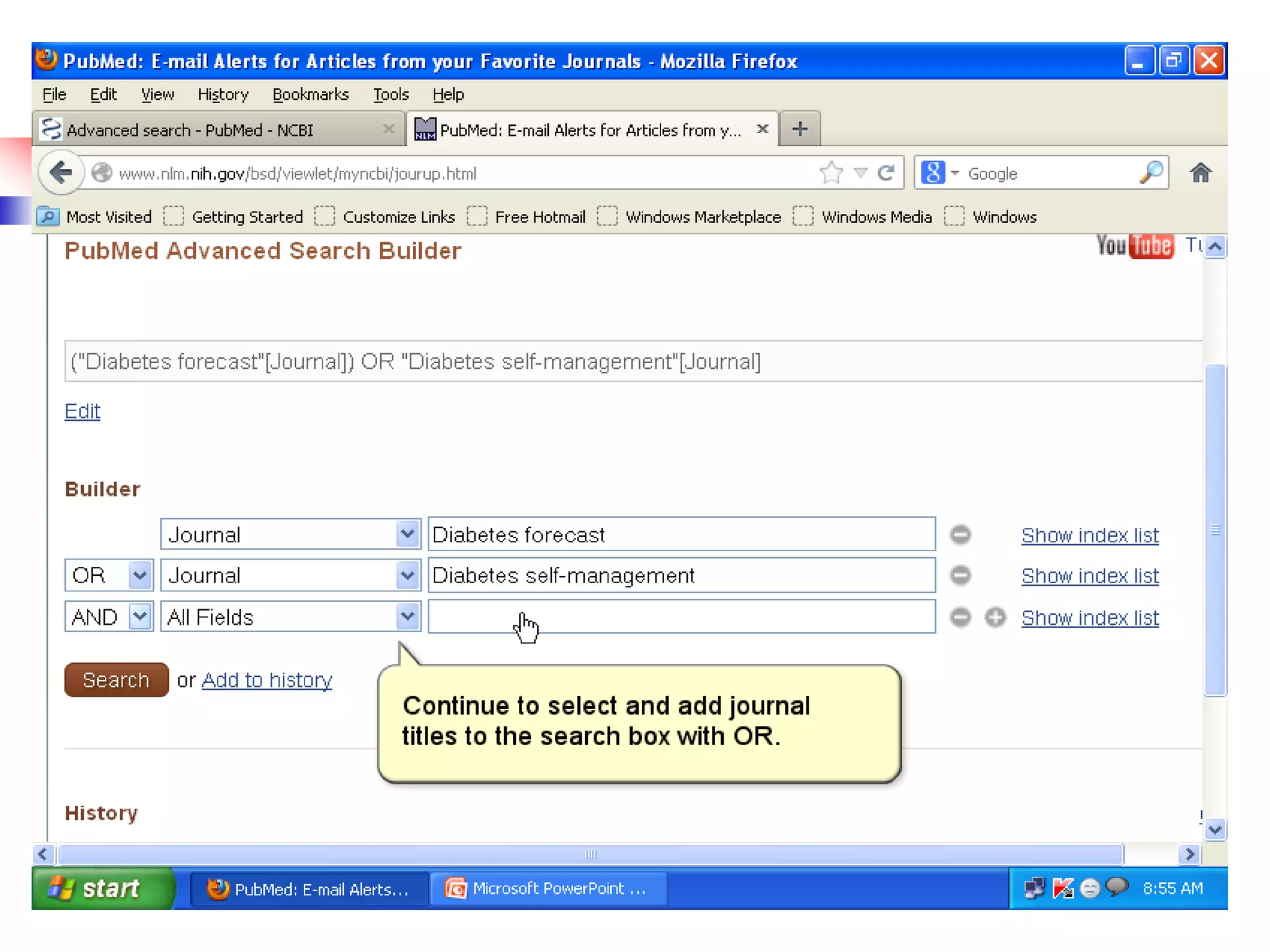
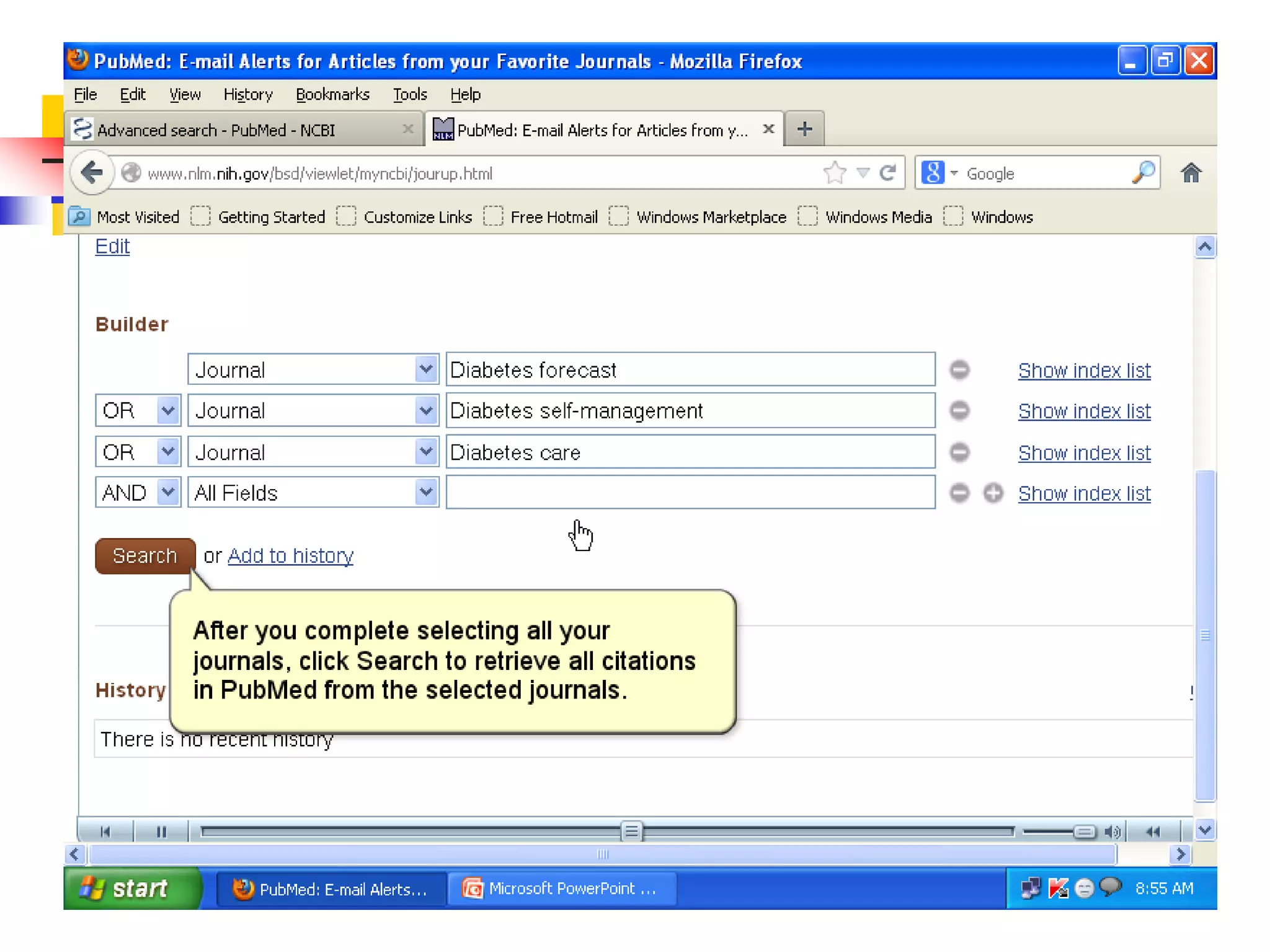
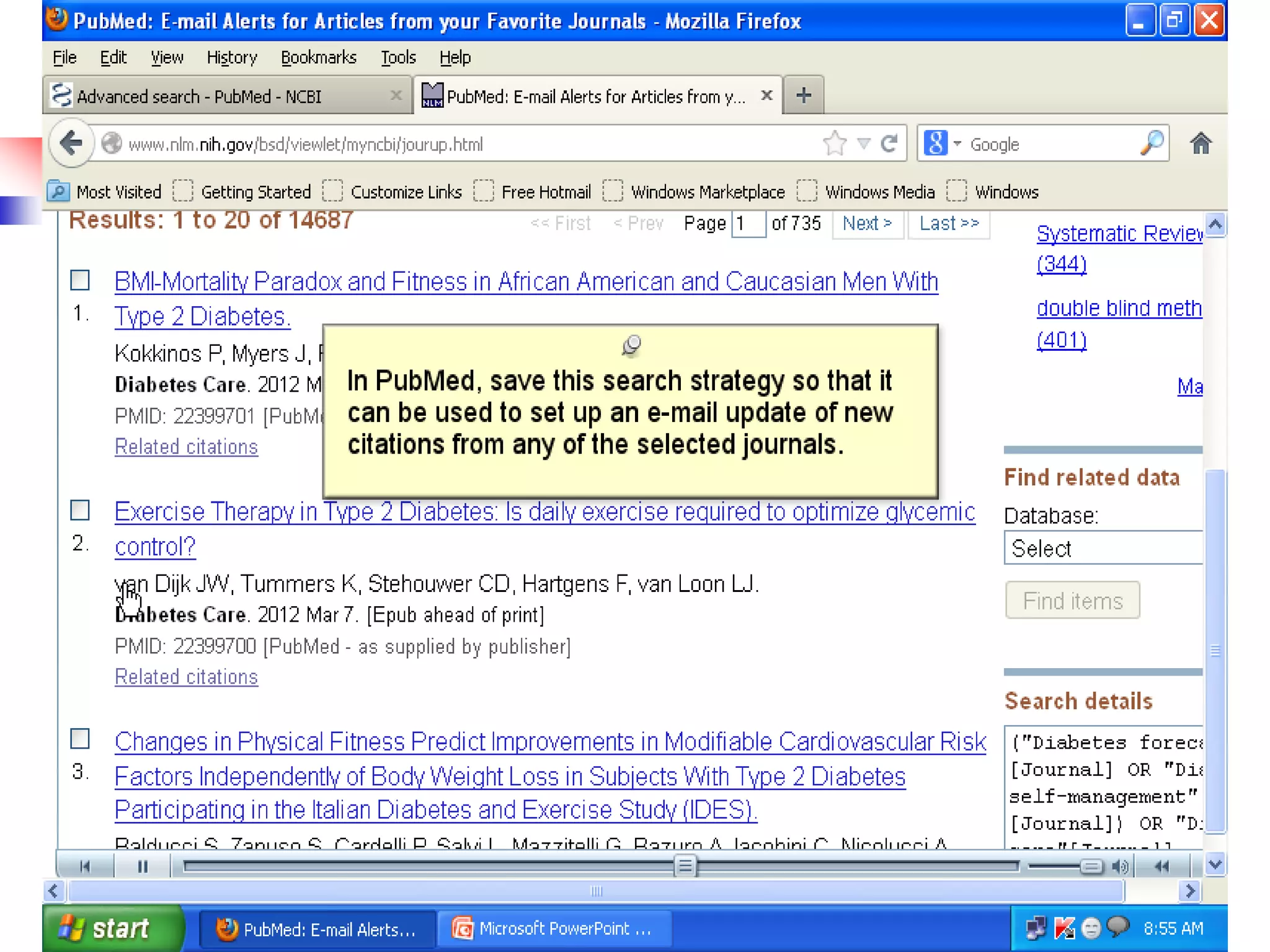
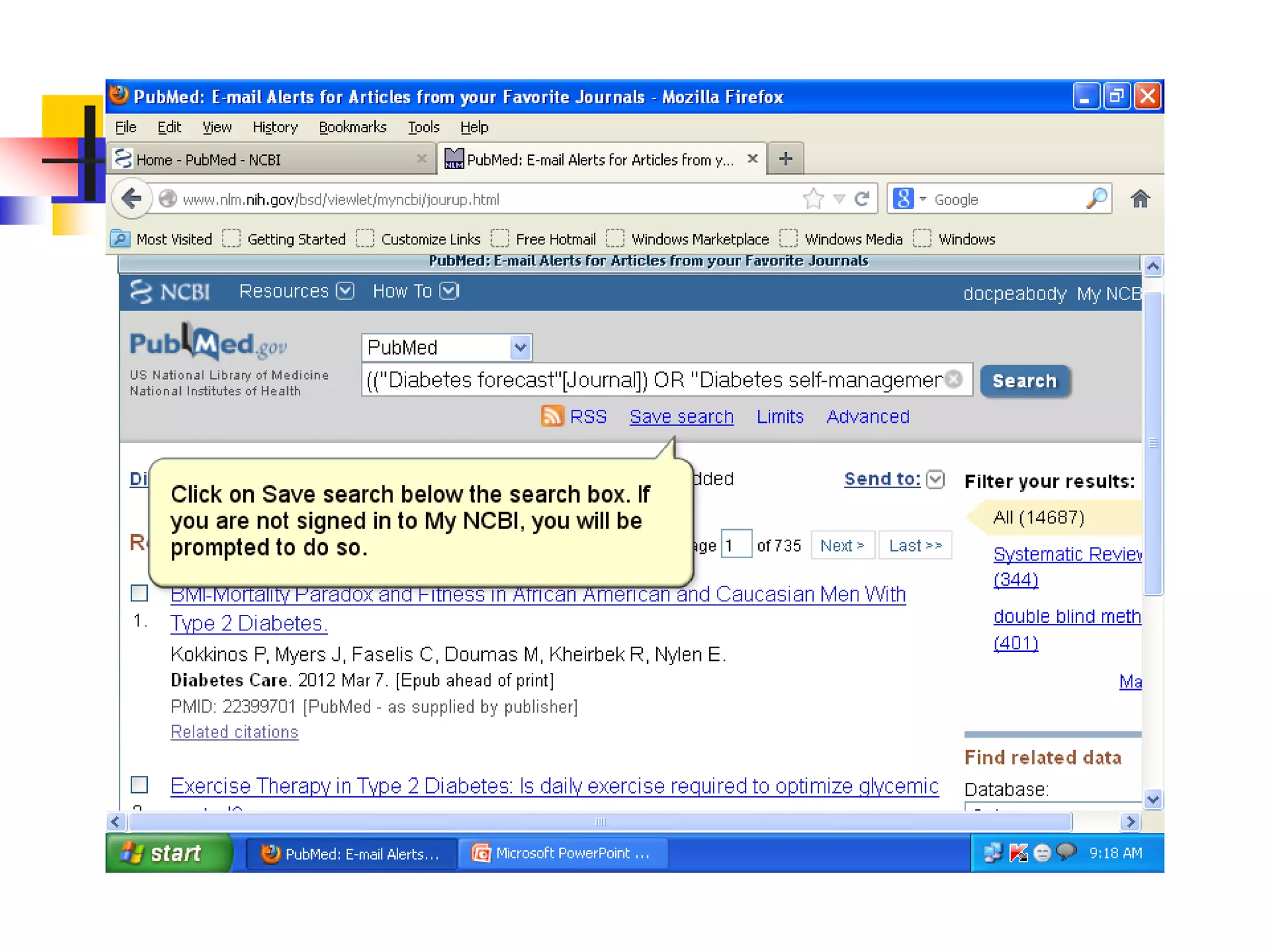
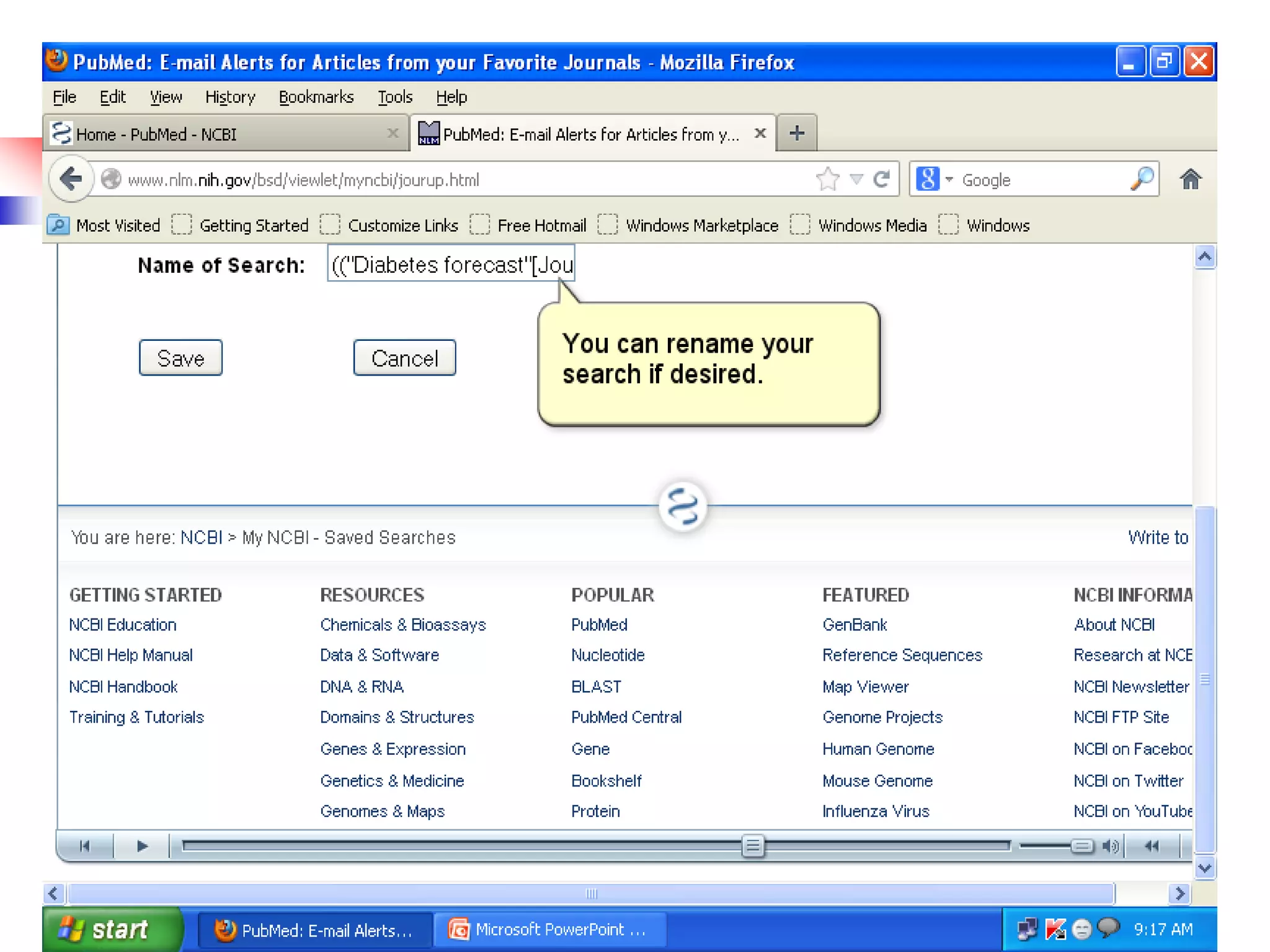
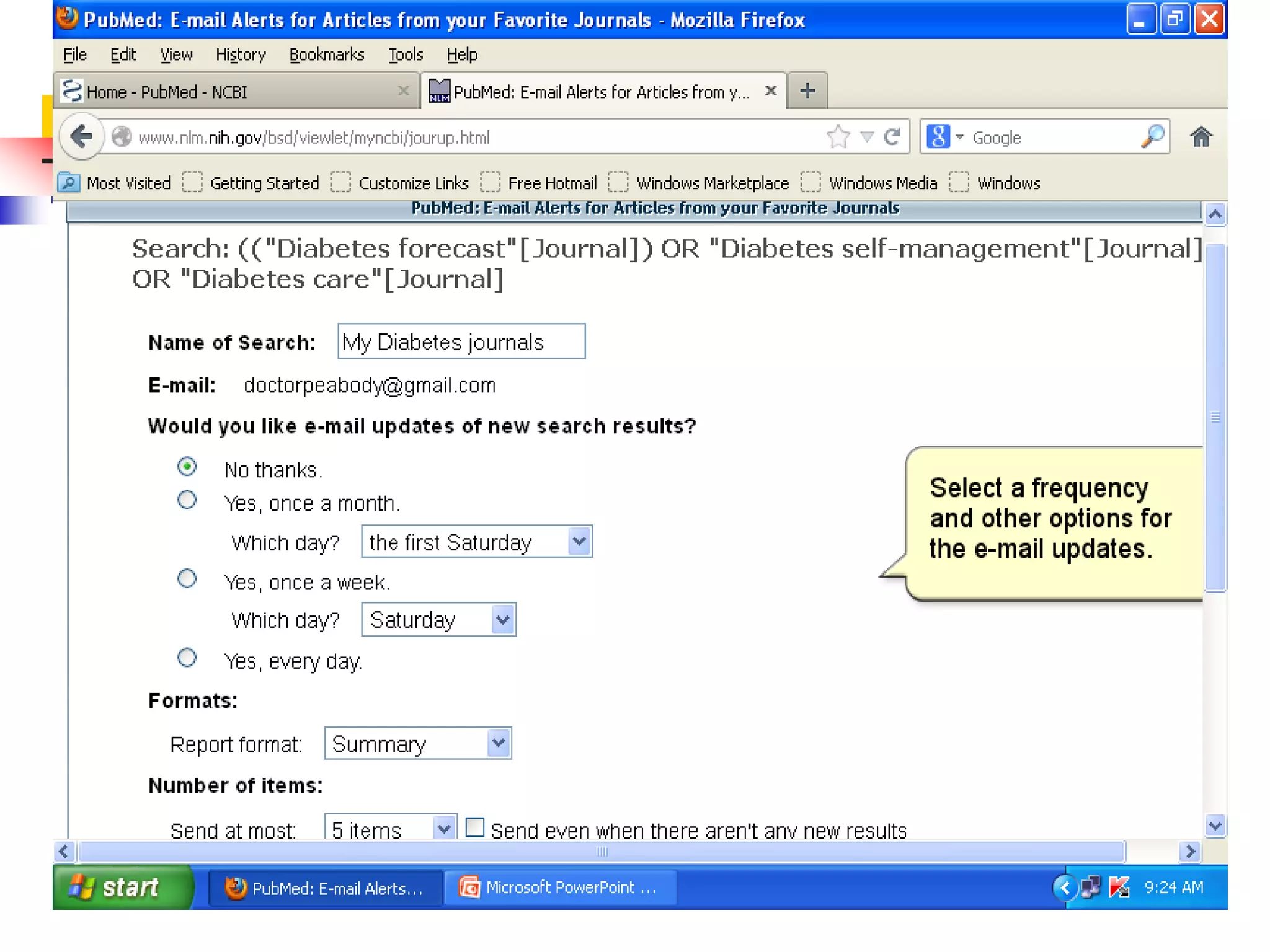
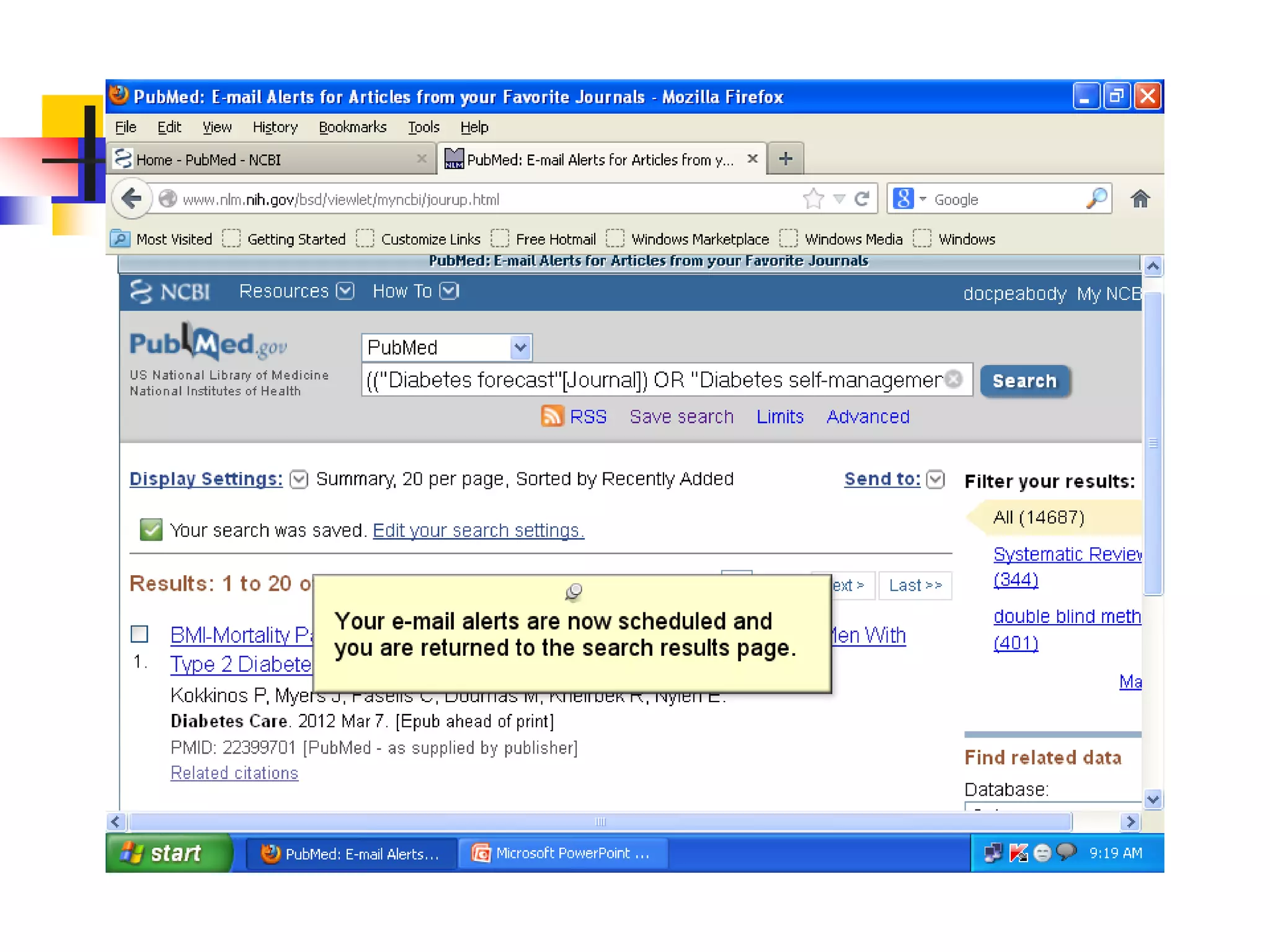
![Searching Pubmed
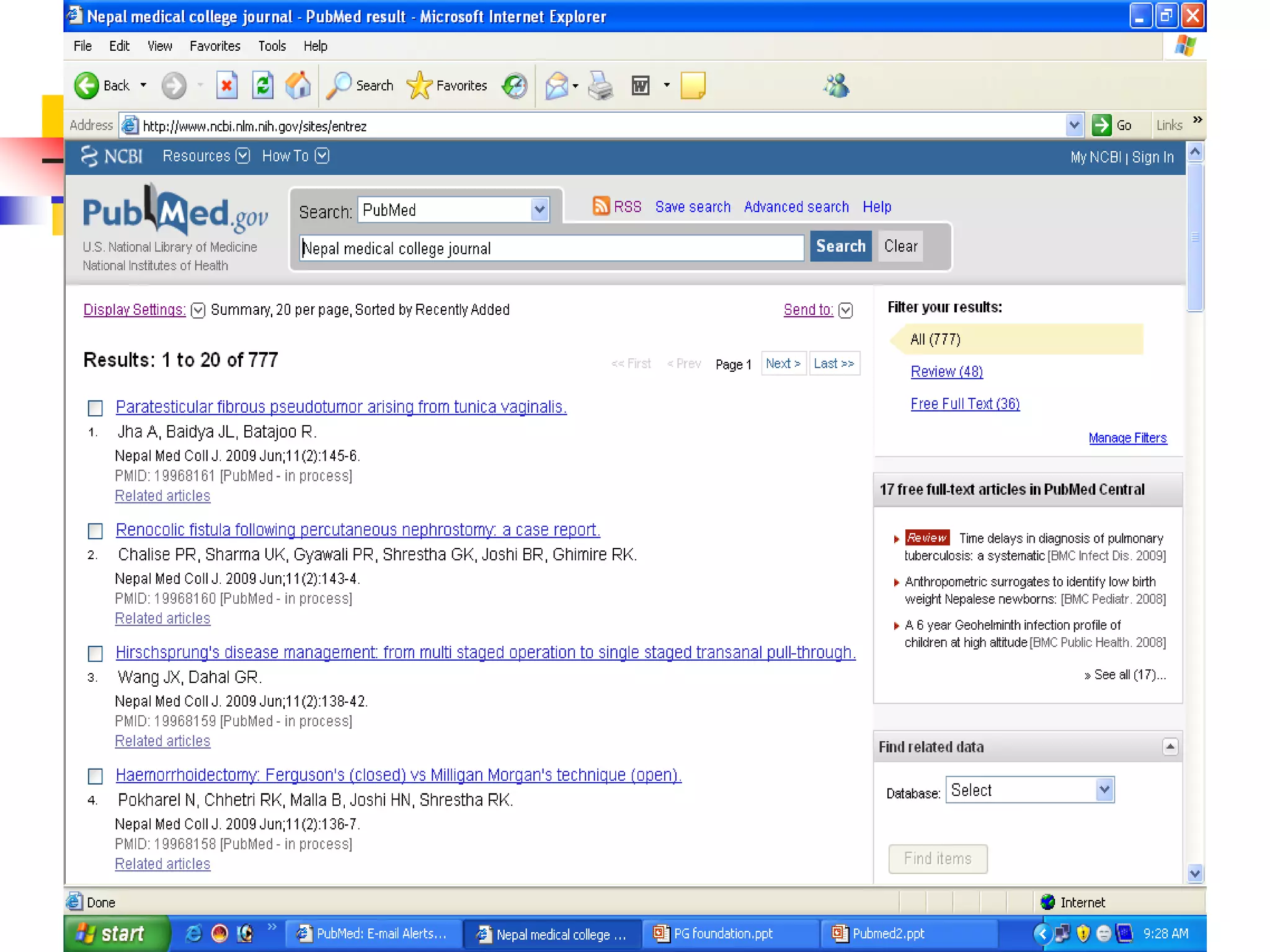
Search for a journal
Several ways to search PubMed from Specific journal.
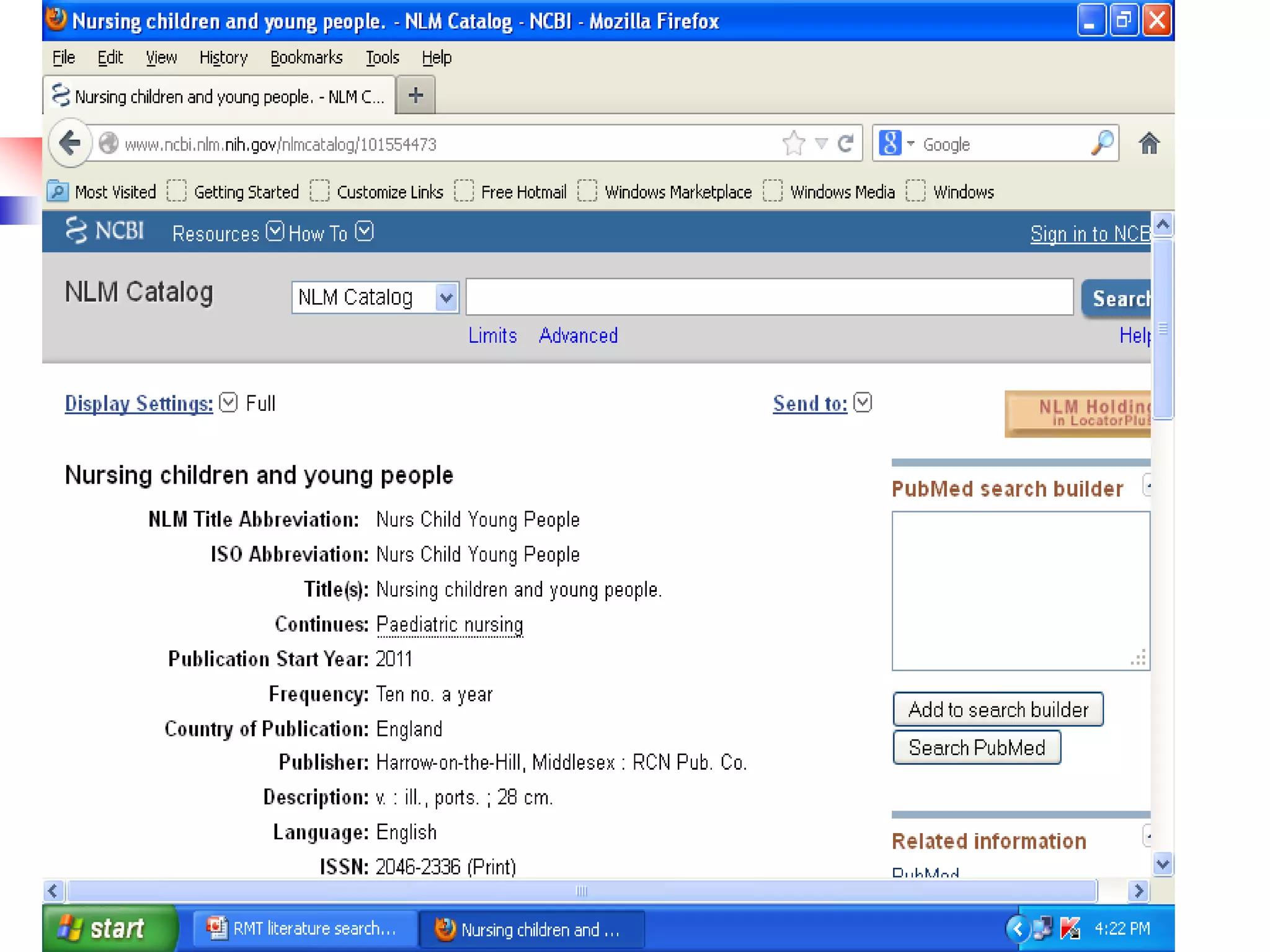
Enter title of the Journal, ISSN or or Journal
Abbreviation to get all the citation for that journal.
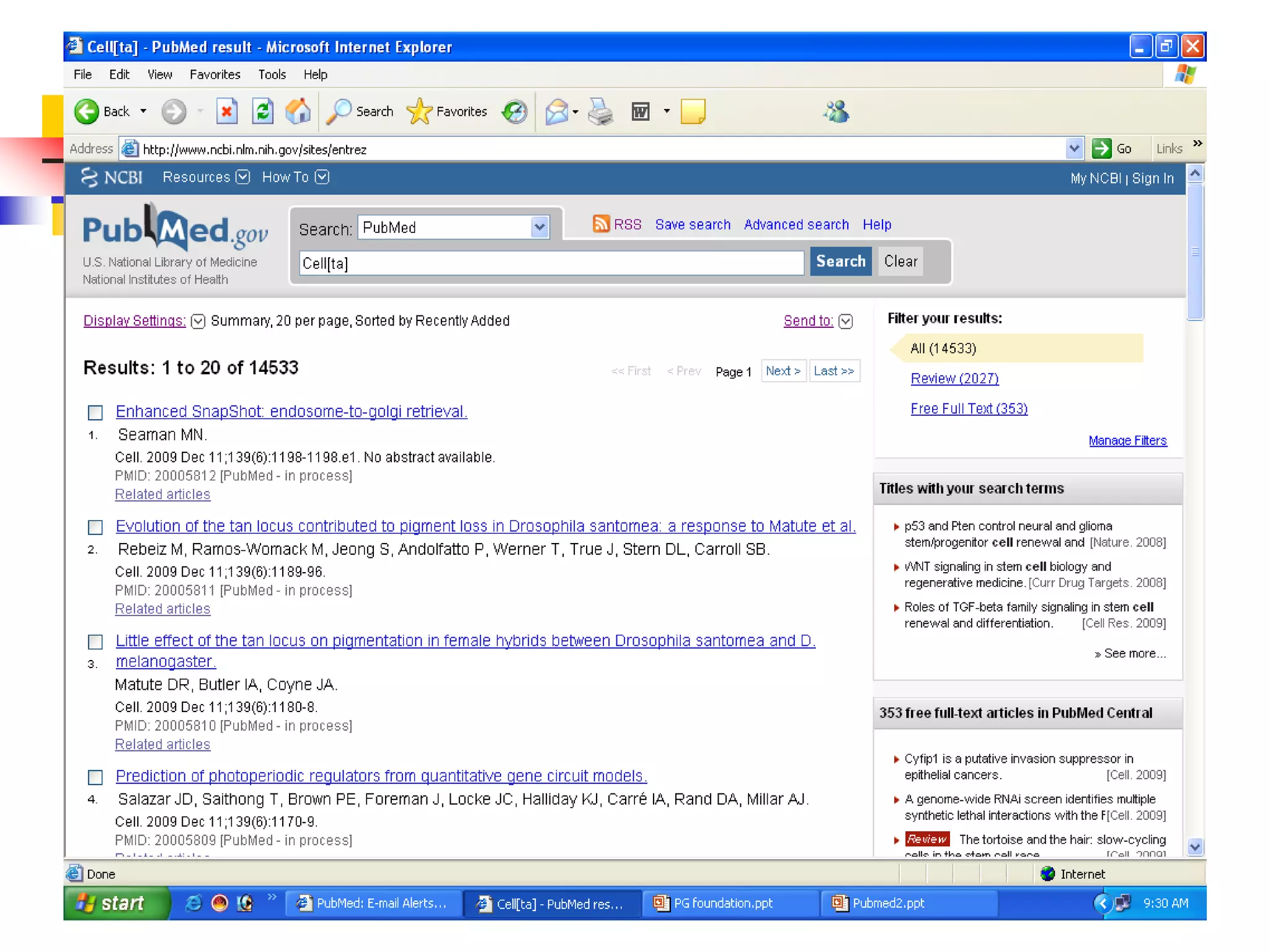
If the Journal title itself a subject term, then use the term
with [ta]
e.g. Cell [ta]
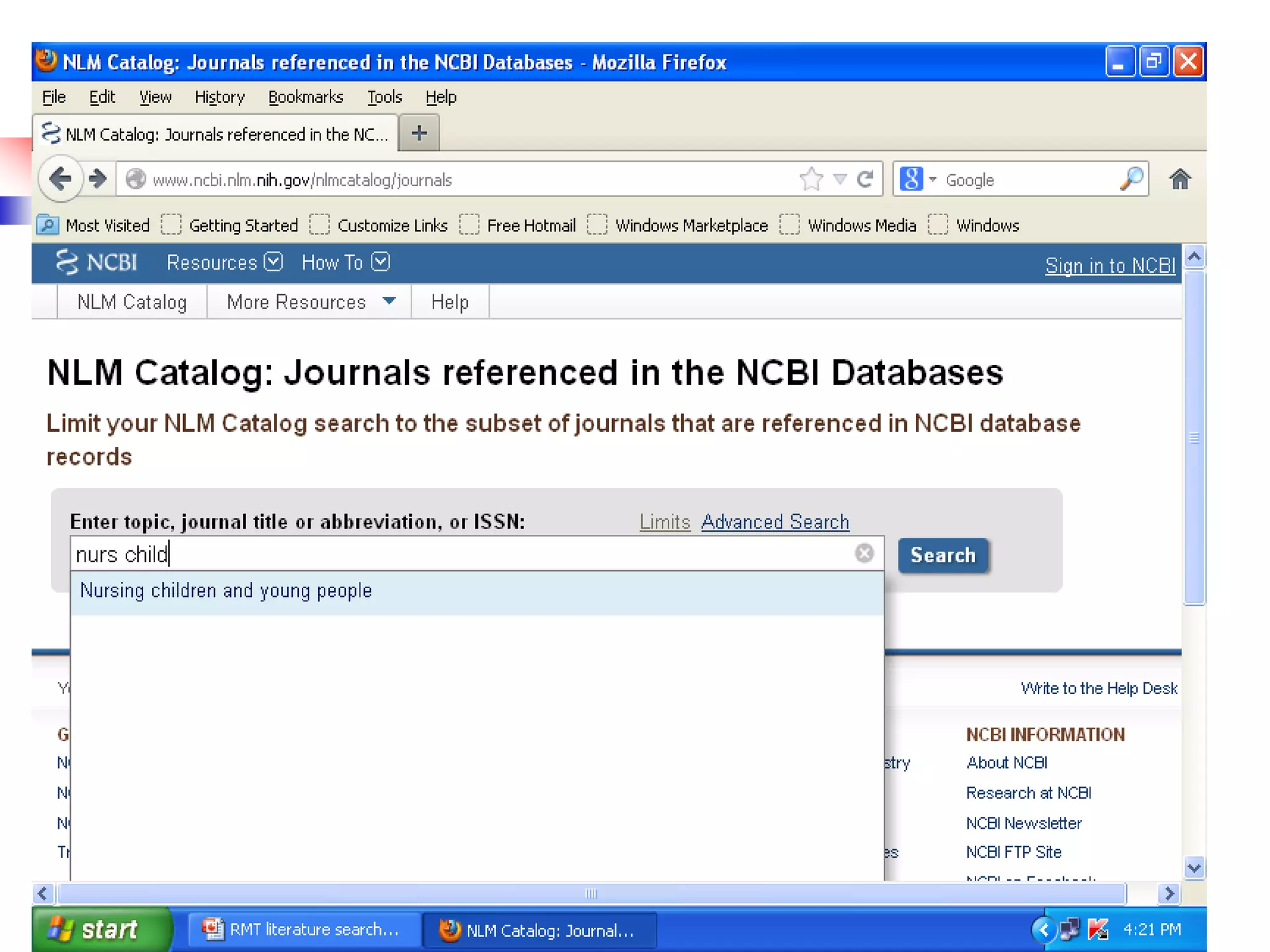
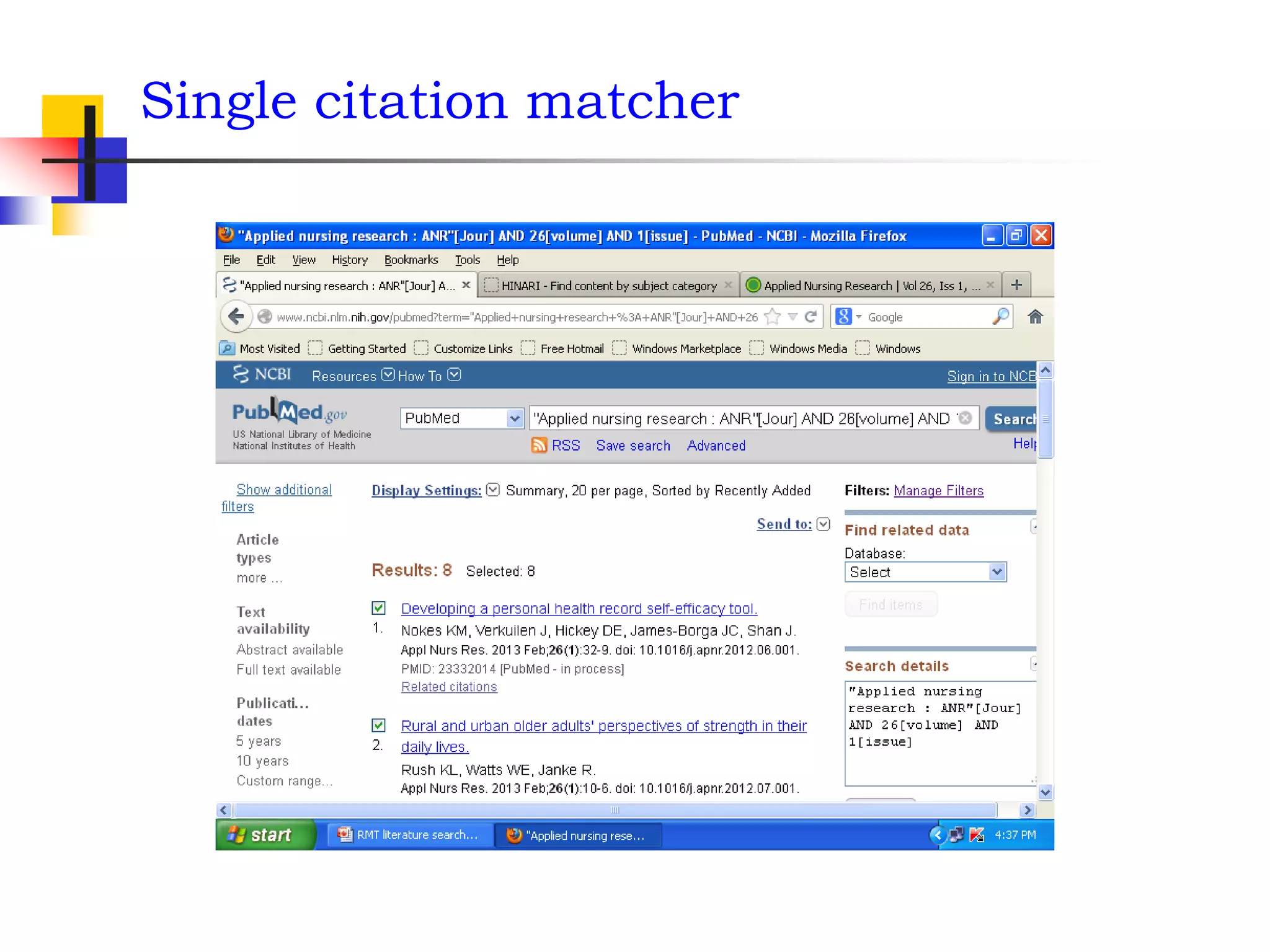
Easy way to search PubMed by Single Citation Matcher
from Homepage
enter full title or title abbreviation
(when you type the auto feature suggests)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-140508052006-phpapp01-220910172723-b9c0e61e/75/1-140508052006-phpapp01-pdf-37-2048.jpg)