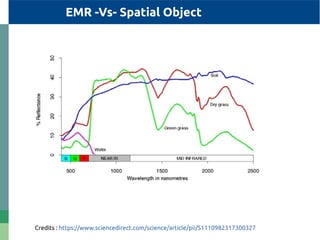
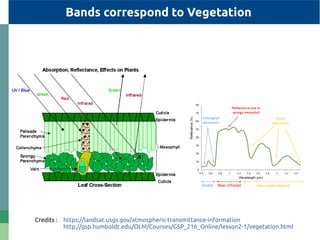
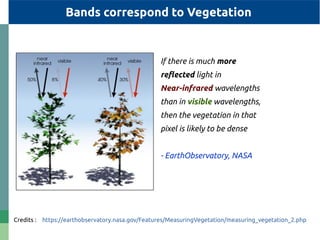
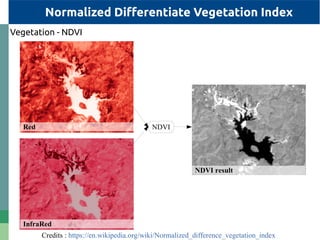
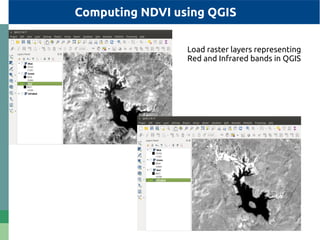
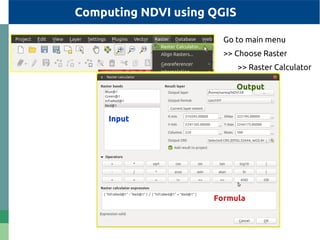
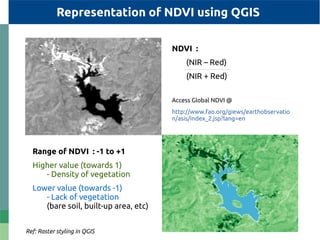
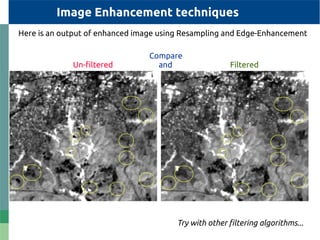
The document provides detailed specifications on the Landsat 8 bands, including their wavelengths and resolutions, focusing on the importance of using the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) to assess vegetation density. It outlines the process of calculating NDVI using QGIS and discusses resampling and filtering techniques for image enhancement. Additionally, it includes references for further reading and accessing global NDVI data.