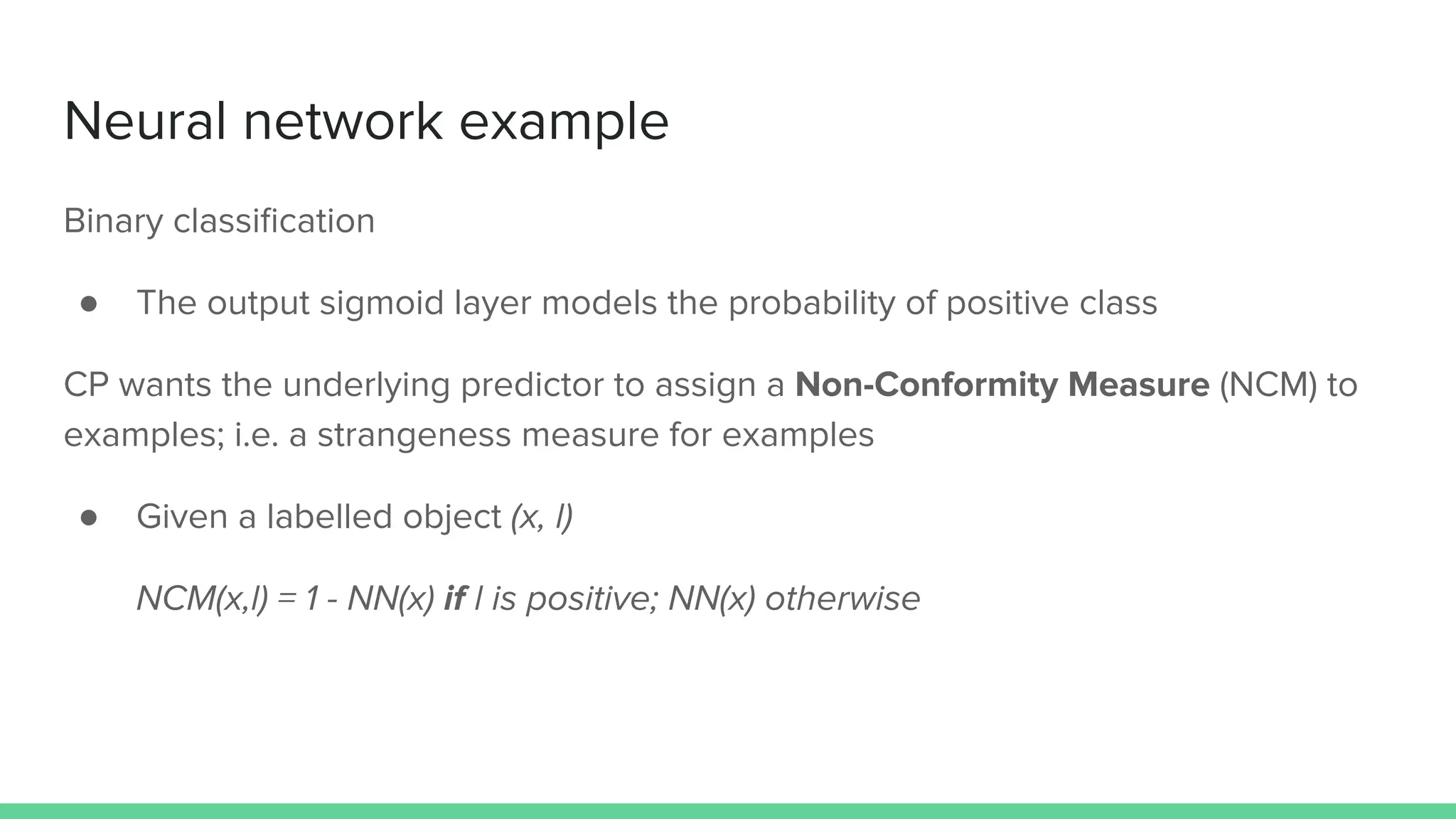
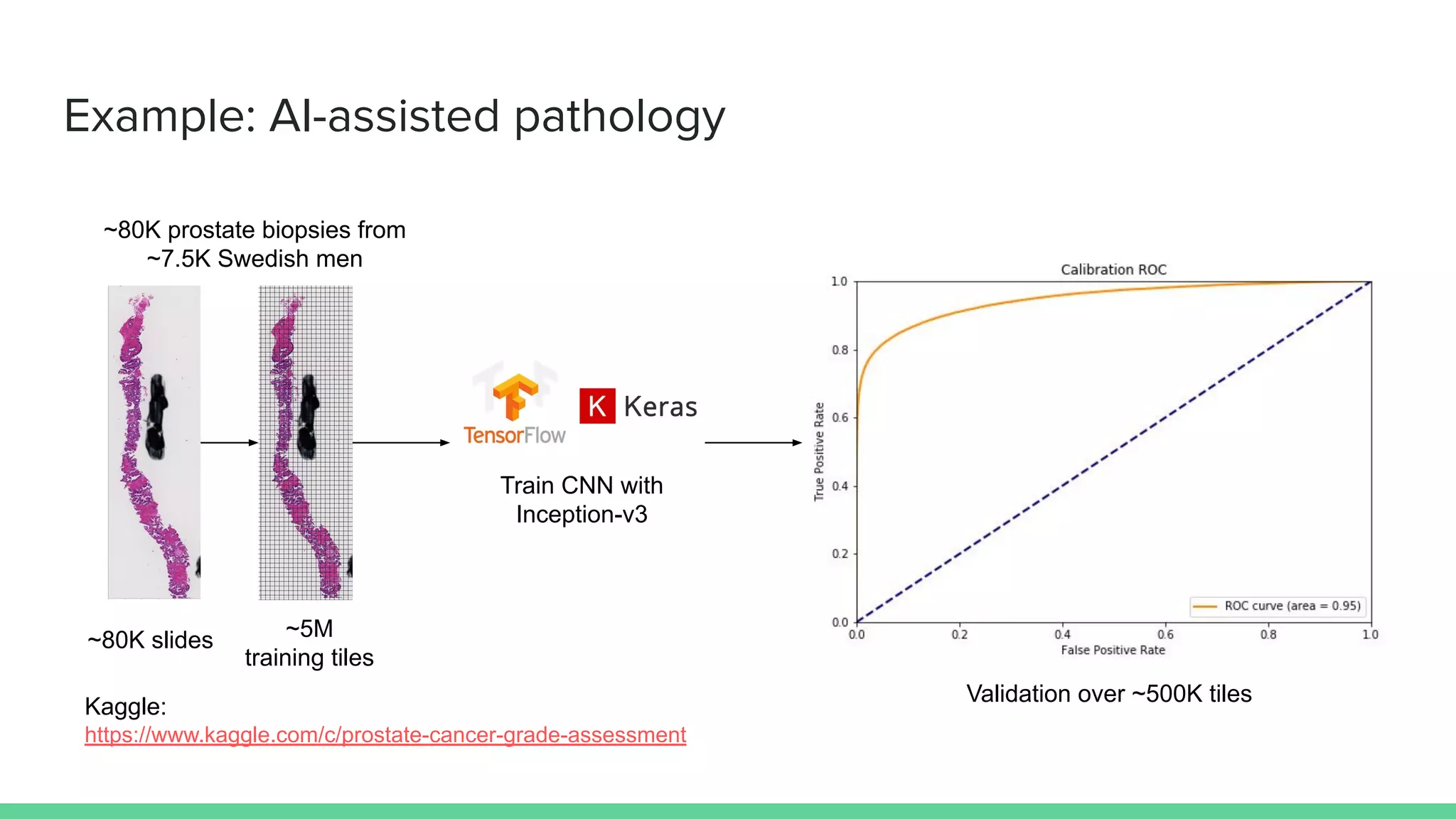
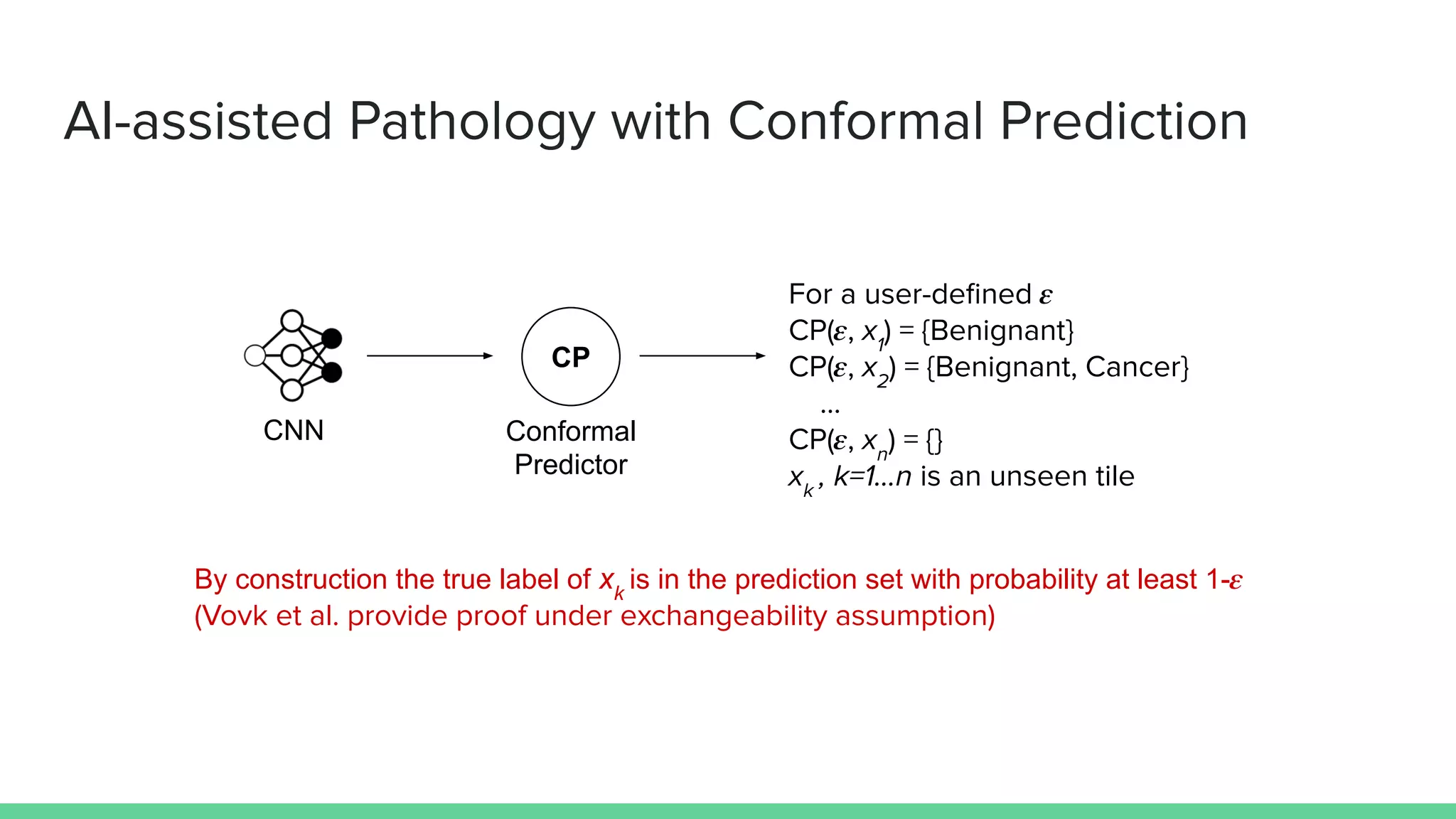
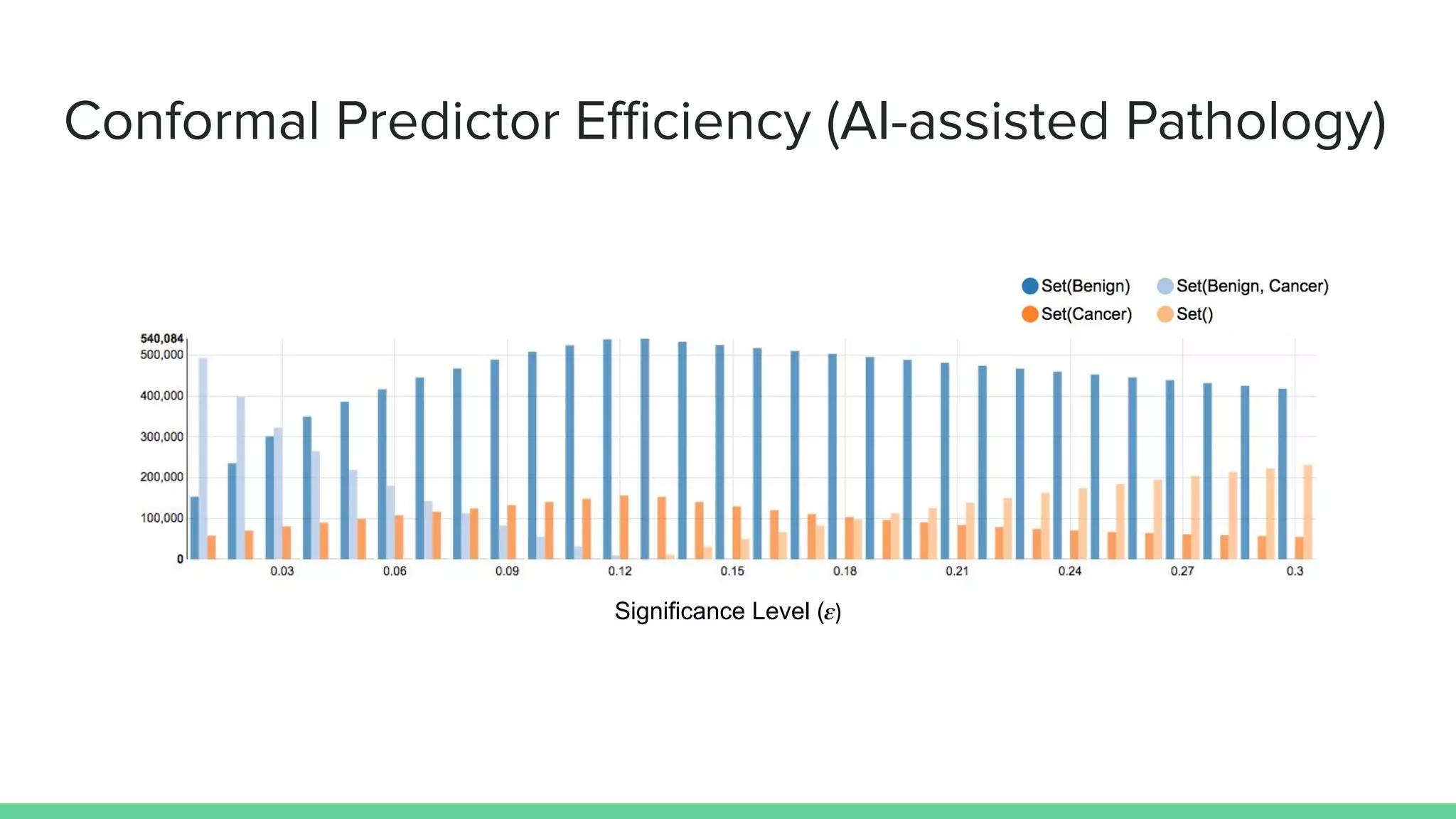
Marco Capuccini introduces conformal prediction, a framework for assigning confidence levels to predictions from machine learning models. Conformal prediction produces a prediction set for new data instances rather than a single prediction. It guarantees the true label will be in the prediction set at least 1 - ε percent of the time, where ε is a user-specified significance level. The approach works by calibrating a model's "non-conformity measures" on labeled data, and using these to determine prediction set membership. Capuccini provides examples of applying conformal prediction to neural networks and other models. He describes using it in an application of AI-assisted pathology to generate prediction sets for histology slides with calibrated confidence.