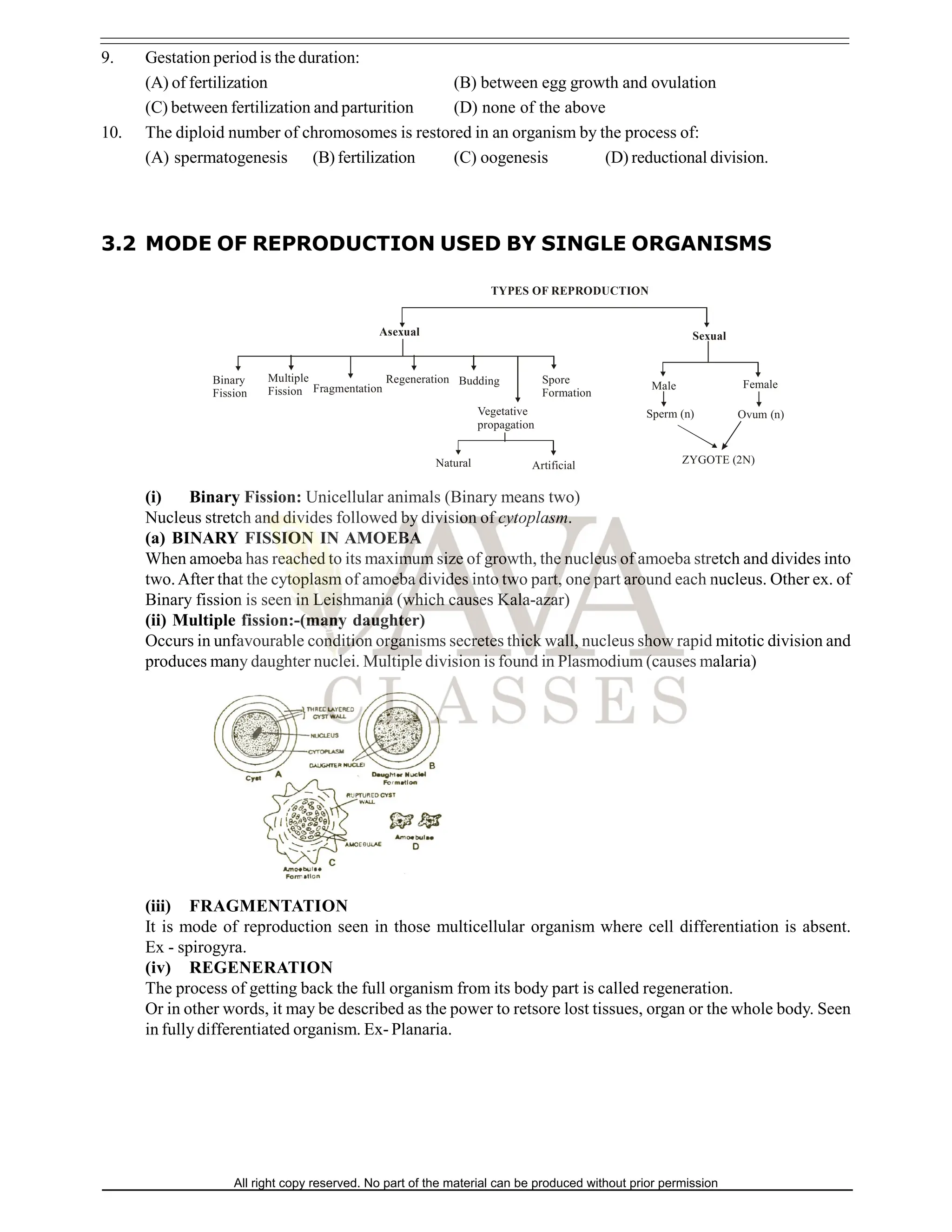
The document discusses reproduction in organisms, explaining both sexual and asexual methods. It includes detailed sections on various reproductive processes in plants and humans, such as pollination, fertilization, and the stages of human reproduction. Additionally, the document contains questions and exercises related to the concepts covered.






![This process is c/a Fertilization.
Zygote
fusion of both nuclei
Tail left out
.
.
(4) The Zygote then divides by Mitosis to form large no of cells. Ultimately zygote grows and develops to
become a new body.
(8) HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Male
Reproductive Organ
(MRS)
HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Female
Reproductive Organ
(FRS)
(9) MRS Testis {Seminiferous Tubules and Leydig cell}
Present in Scrotum (2 C Lower)
o
germinal
epithelium
sertoli
cells
Testosterone
Epididymis (coiled tube)
[Temprary storge and functional
maturation of spermatids to spermatozoa]
Vas deferens
Seminal Vesicle [storgae of sperm/ Fructose energy]
EJACULATORY DUCT (form by the union of duct from seminal
vesicle and vas deferens)
Urethra
Penis
Opens
Joins
Cowper's gland
Prostate
gland
(Male Sexual Organ)
(10)FRS
Ovaries [graffian follicle]
changes to ovum
Corpus Leuteum
Corpus albicans Progestrone
secretes
Oviduct/fallopian tube
[site of fertilization]
Uterus [Highly vascular and Muscular. Inner layer of uterus is
endometrium uterus is site of implantation]
Vagina
Labia Minora
[ Vulva]
Note: Vulva is external part of female genitalia. It comprise of labia minora, labia majora, pubis and glands
All right copy reserved. No part of the material can be produced without prior permission](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07howdoorganismsreproduce-240315095520-94f76084/75/how-do-organisms-reproduce-class-10-study-material-download-pdf-8-2048.jpg)

![(13)Fertilization (Internal)
2-3 ml semen 300 million of sperm is discharged into vagina by penis.
sperm fuse with ovum
Zygote
Mitotis Foetus (implants in Utreus)
(1) Stopage of Menstrual cycle after implantation
(2) formation of Placenta
(14)Gestation Period time period between the fertilization upto the birth of the body.
(Human 270 days)
(15)Parturition process of giving birth
Placenta Relaxin
hormone [Relax Pubic symphysis]
Pitutary Oxytocin (contraction and Relaxation in Uterus)
It occurs in 3 stages
(a) Dilation (b) Expulsion (c) Final contraction
(16)Population control
Population Control Methods
Mechanical Surgical Chemical
Vasectomy Tubectomy Abortion
Spermicide birth control
pills
(17)PARTHENOGENESIS
The process of Reproduction in which a new animal is produced from an unfertilized egg of the female is
c/a Parthenogenesis. e.g. Lizard – Sexicola
Try yourself
11. Female gonad and gamete are respectively
(A) DNA (B) Ova and Sperm (C) Ovary and Ova (D) Ova & Ovary
12. The major source of variations in populations of organism is due to
(A) Regeneration (B) Fragmentation
(C) Inaccuracy in DNA copying mechanism (D) All of these
13. The male reproductive part of angiosperm.
(A) Pistil (B) Carpel (C) Stamen (D) Sepal
14. Part of plant forming fruit
(A) Anther (B) Ovule (C) Ovary (D) Style
15. During puberty
(A) Sexual maturation take place.
(B) the rate of general body growth begins to slow down
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
*****
All right copy reserved. No part of the material can be produced without prior permission](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07howdoorganismsreproduce-240315095520-94f76084/75/how-do-organisms-reproduce-class-10-study-material-download-pdf-10-2048.jpg)




