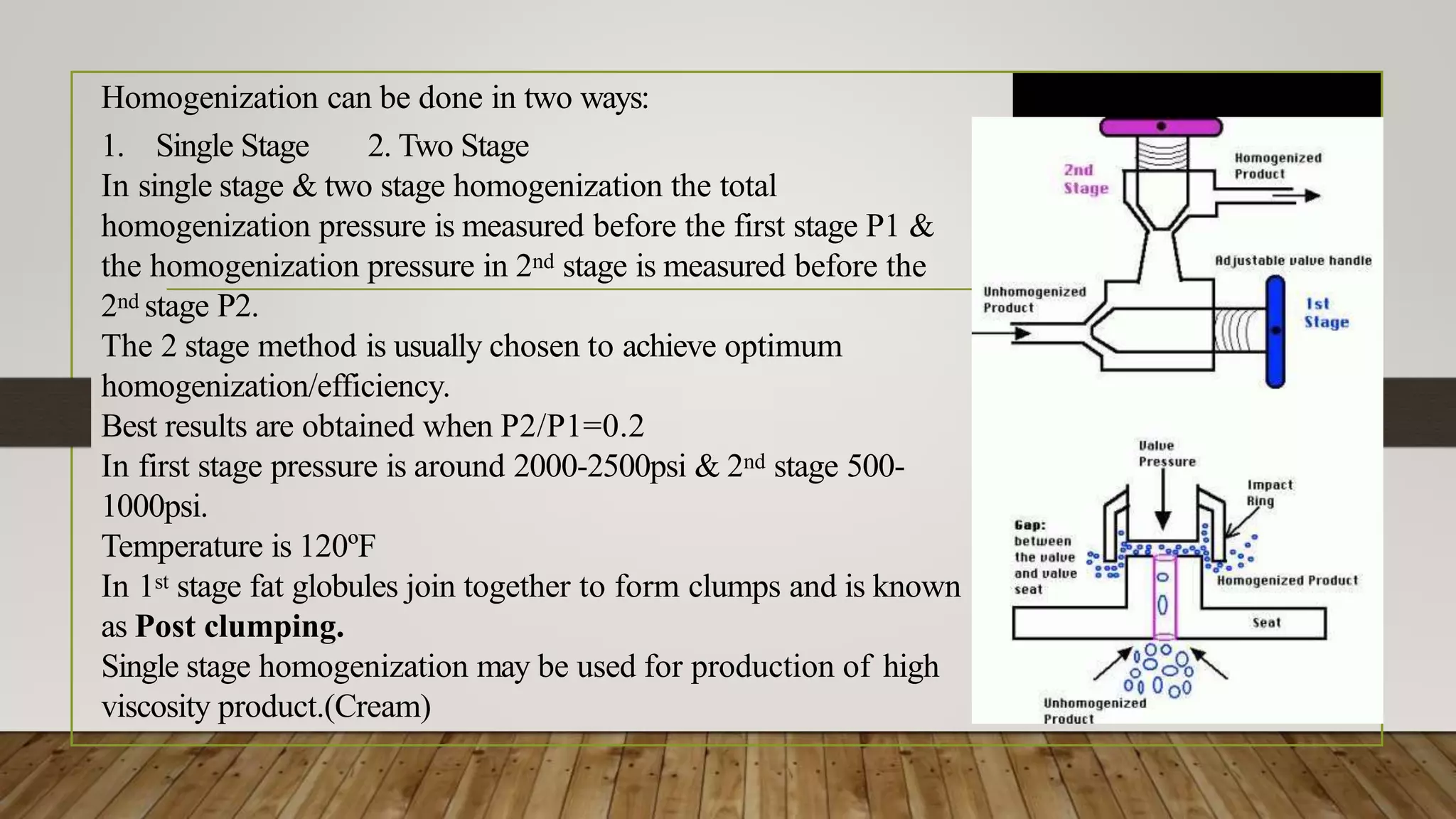
Homogenization is a process that breaks up fat globules in milk to a uniform small size so they remain suspended instead of separating. It involves pushing milk under high pressure through a narrow opening, breaking up fat globules into smaller sizes around 0.5-2 microns. This process improves the taste and appearance of milk by preventing cream separation and making the color whiter. Homogenization allows for easier production of other dairy products and makes the fat distribution more even. The main factors affecting homogenization are milk temperature, pressure levels, and fat content.