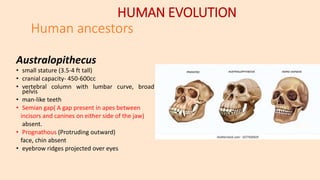
Human evolution progressed from early hominins like Australopithecus that walked upright and had small brains, to later species like Homo habilis with larger brains who used tools, to Homo erectus who hunted and controlled fire. Neanderthals had even larger brains and were fully bipedal, while Cro-Magnon created fine tools and cave paintings. Modern Homo sapiens emerged around 11,000 years ago with features adapted for upright walking and tool use. Theories of evolution include Lamarck's inheritance of acquired traits and Darwin's natural selection, where favorable variations are selected over generations of reproduction.