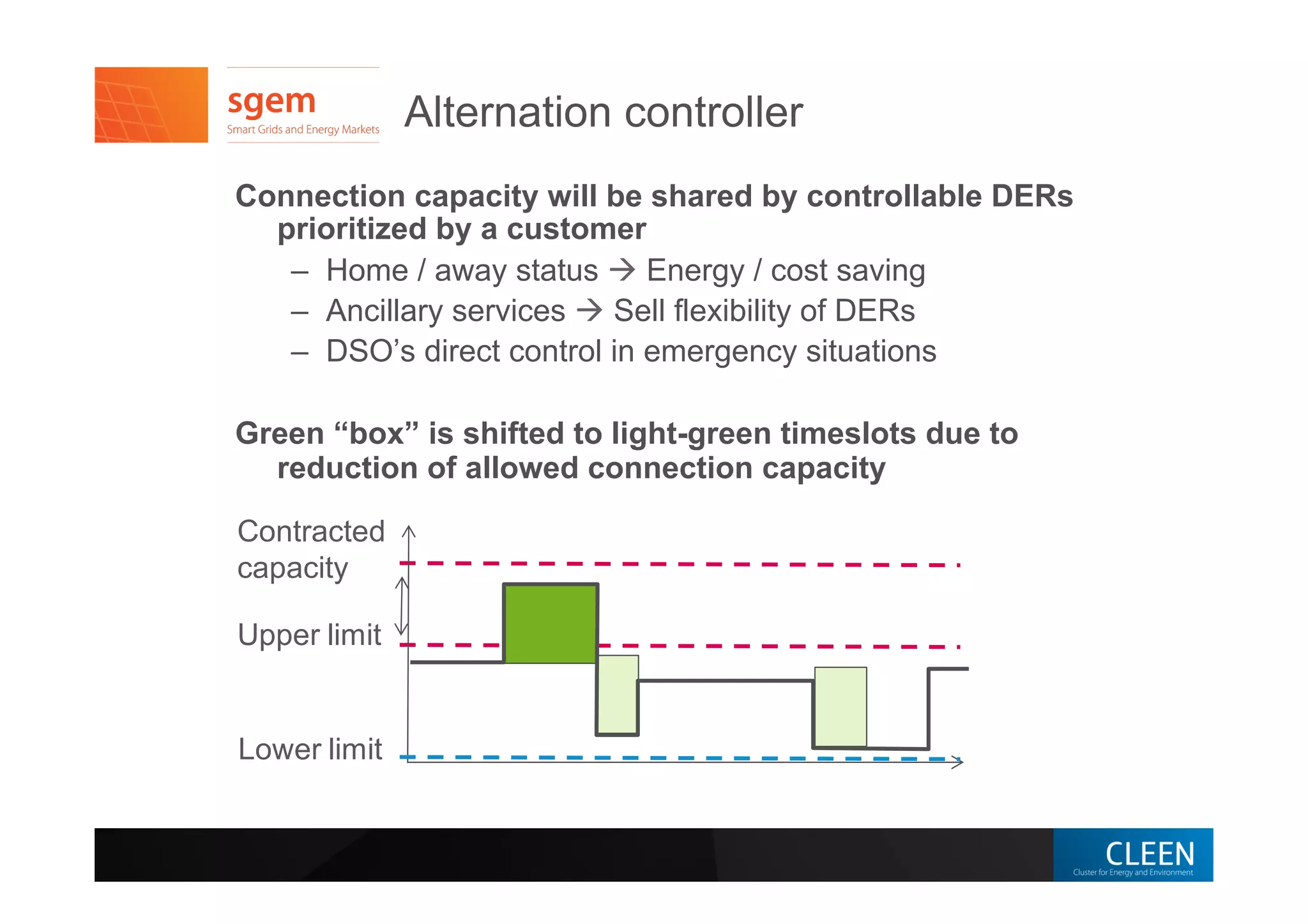
The document discusses the importance of Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) for Distribution System Operators (DSOs) in managing energy distribution networks. It highlights the benefits of real-time monitoring, integration of distributed energy resources, and the need for dynamic automation to enhance efficiency and responsiveness in electricity management. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of DSOs as neutral participants in the energy market while implementing HEMS to improve load balancing and support renewable energy sources.