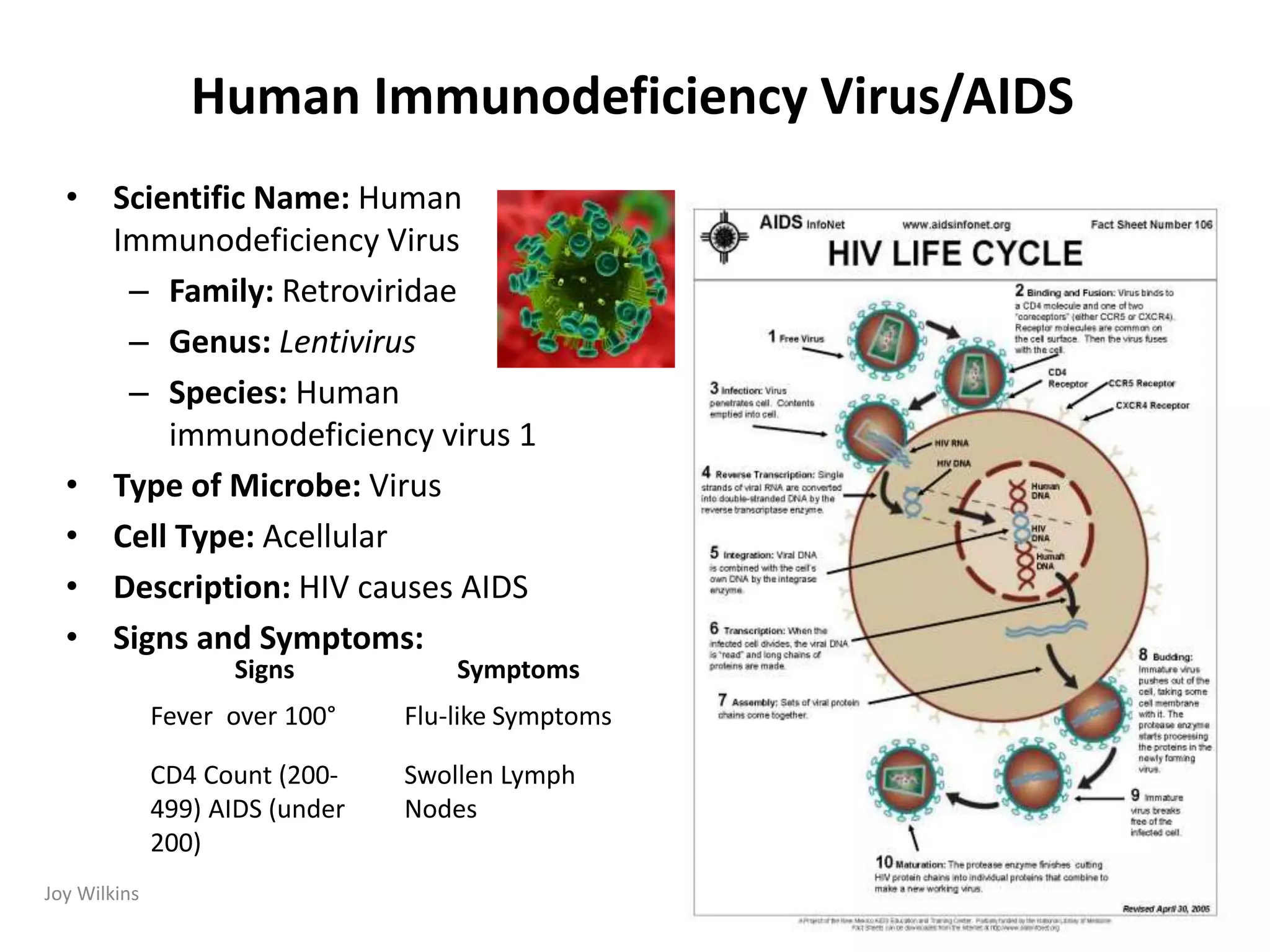
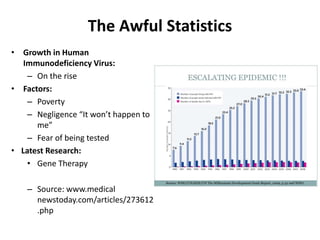
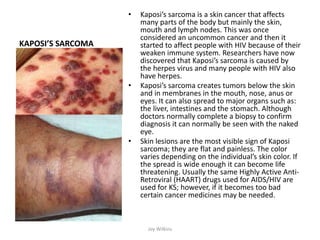
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that causes AIDS by infecting and destroying CD4+ T cells in the immune system. HIV belongs to the genus Lentivirus and species HIV-1. It is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus that inserts its genetic material into the DNA of host cells. While antiretroviral medications can control HIV, there is no vaccine. HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids and progresses from initial infection to AIDS as the CD4 count declines below 200. Groups most at risk include African Americans, homosexual and bisexual men, substance abusers, and inmates. Common co-infections are hepatitis B and C viruses.