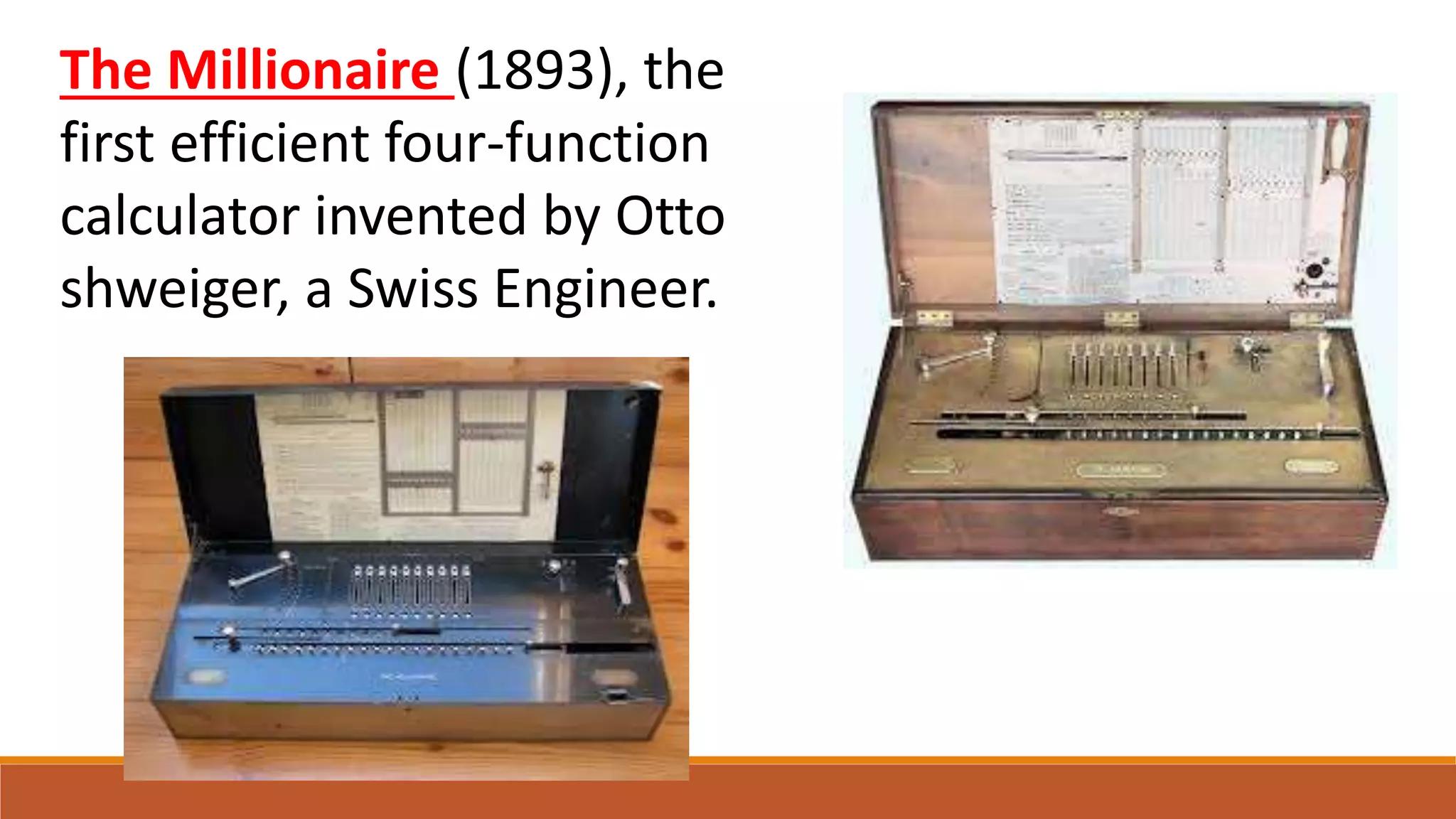
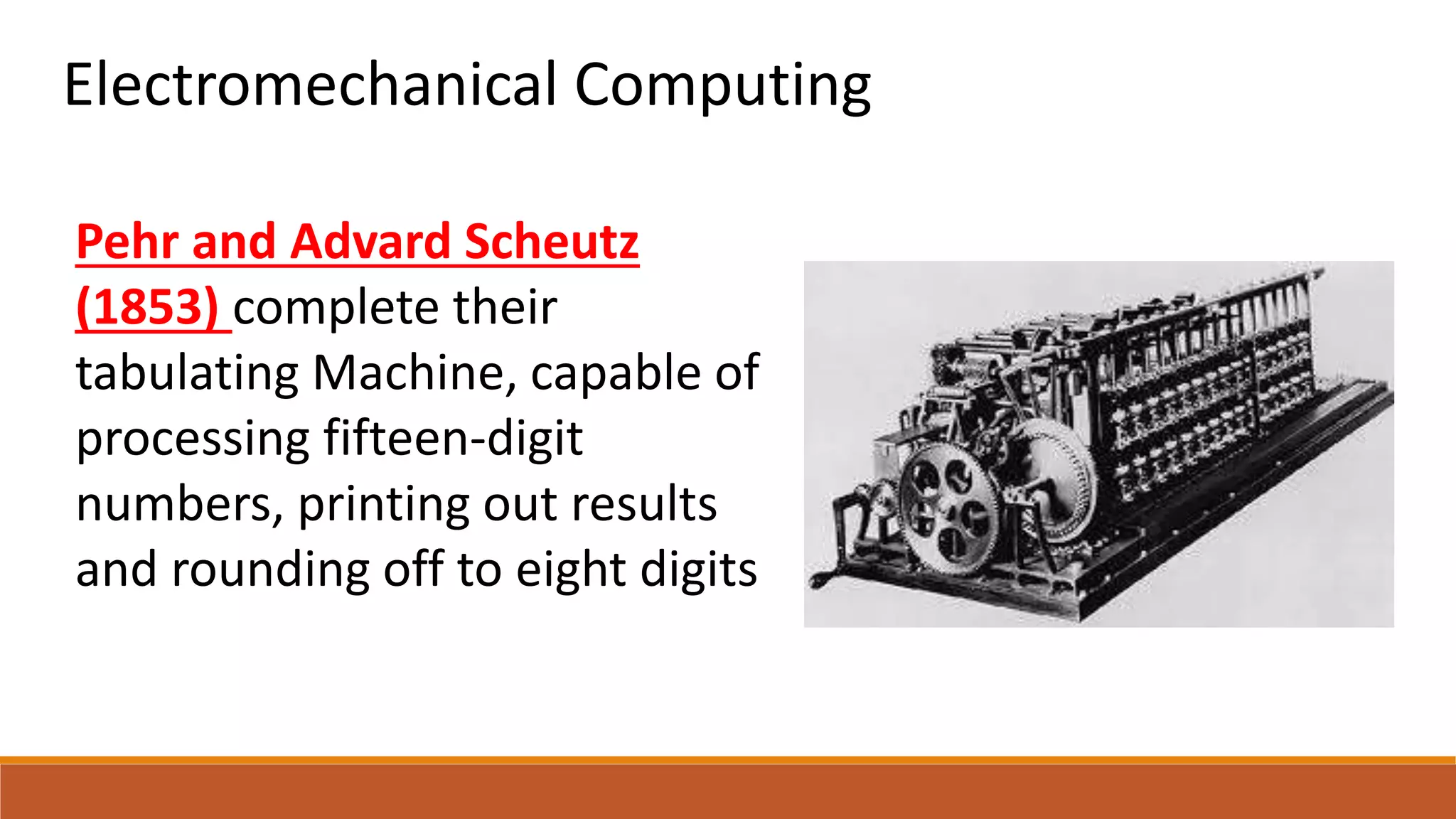
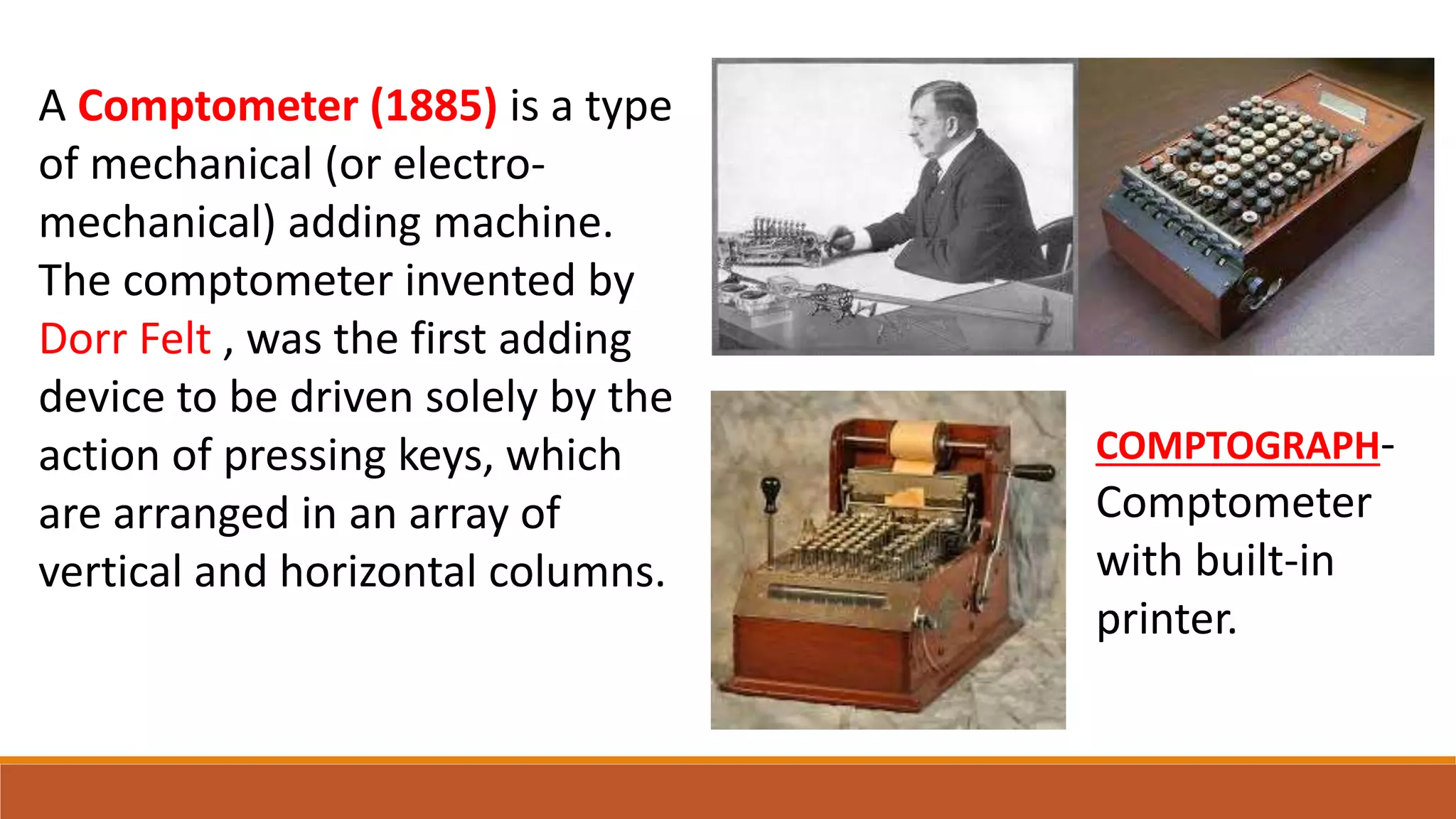
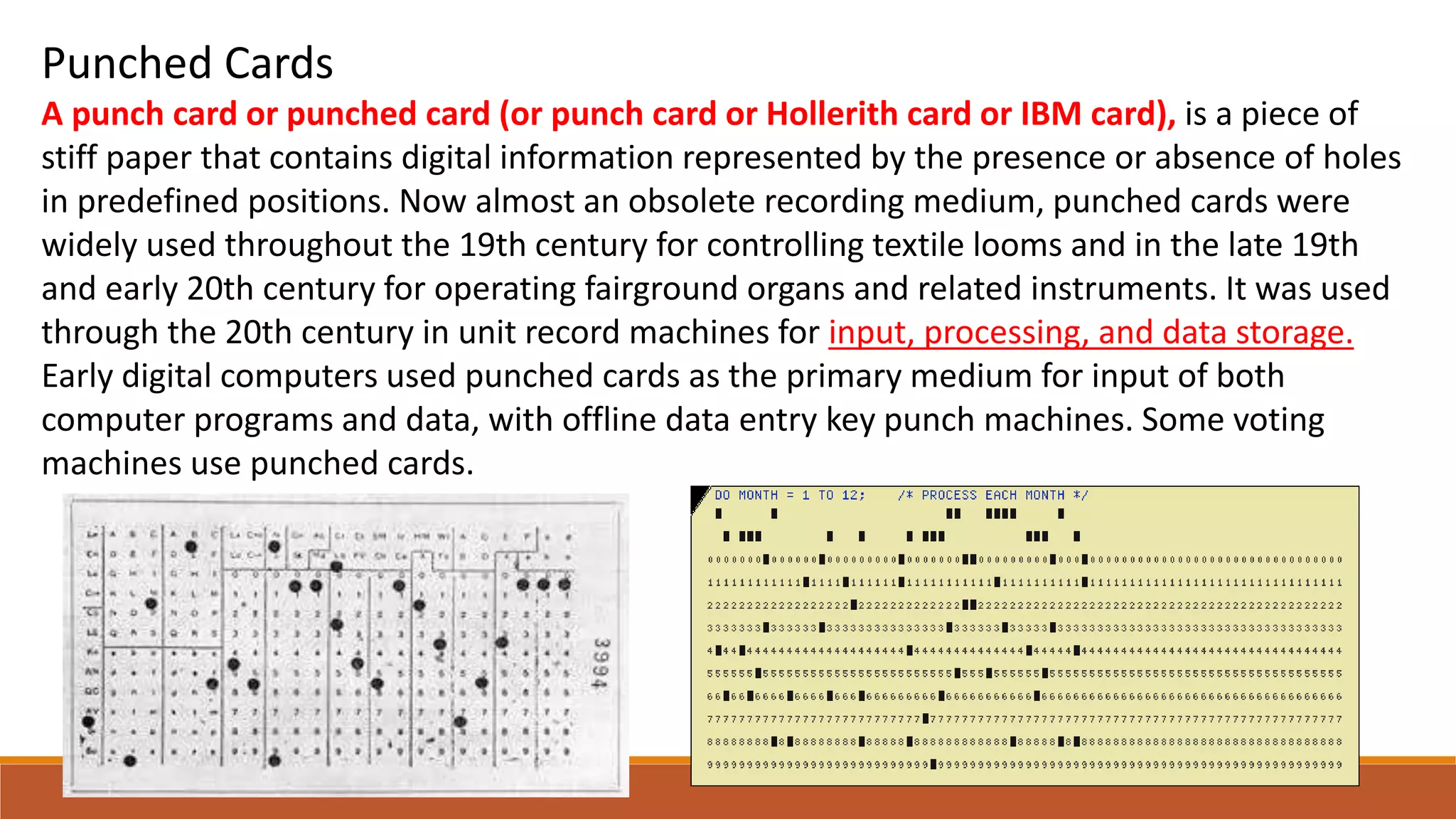
The electromechanical age from 1840-1940 saw important advances that enabled the development of early computers. Key inventions included Alessandro Volta's battery in 1800, which provided a reliable source of electricity and allowed information to be encoded as electrical signals. Samuel Morse invented the telegraph in 1832 for electrical communication of text messages. Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1876 for bidirectional voice communication. These inventions established telecommunication networks powered by electricity. Early electromechanical computing devices were also developed, such as tabulating machines in the 1850s, the Comptometer mechanical adding machine in 1885, and Herman Hollerith's punched card tabulating system used for the 1890 US Census. These early electromechanical devices demonstrated that




![Telephone
The first successful bi-directional
transmission of clear speech by Bell and
Watson was made on 10 March 1876
when Bell spoke into his device, “Mr.
Watson, come here, I want to see you.”
and Watson answered. Bell used Gray's
liquid transmitter design[9] in his
famous 10 March 1876 experiment, but
avoided describing the liquid transmitter
in his public demonstrations. The liquid
transmitter had the problem that waves
formed on the surface of the liquid,
resulting in interference.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/historyofcomputerelectromechanicalage-140616032523-phpapp01/75/History-of-computer-electromechanical-age-5-2048.jpg)

![The company which became IBM was
founded in 1896 as the Tabulating
Machine Company[6] by Herman
Hollerith, in Broome County, New York
(Endicott, New York, Where it still
maintains very limited operations). It
was incorporated as Computing
Tabulating Recording Corporation (CTR)
on June 16, 1911, and was listed on the
New York Stock Exchange in 1916. IBM
adopted its current name in 1924, when
it became a Fortune 500 company.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/historyofcomputerelectromechanicalage-140616032523-phpapp01/75/History-of-computer-electromechanical-age-10-2048.jpg)