The document focuses on the essential skills and techniques for managers to effectively interview and select the best candidates for job positions, emphasizing the importance of structured interviews and unbiased evaluation of both internal and external candidates. It highlights the impact of a manager's interviewing skills on employee retention and company perception, urging adherence to legal guidelines and the creation of an equitable interview process. Additionally, it stresses the need for preparation, awareness of potential biases, and the significance of establishing a positive interview atmosphere.








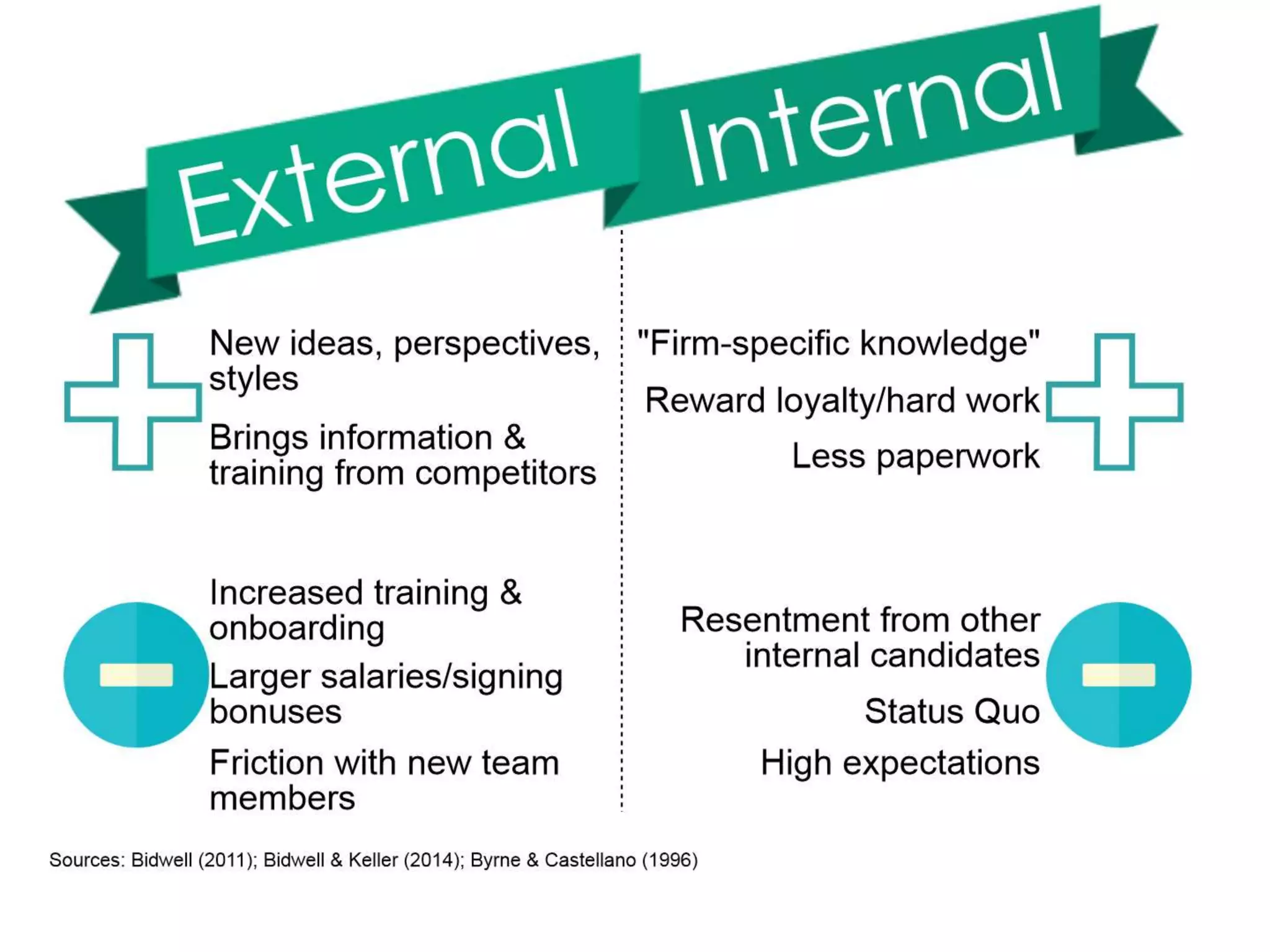
























![Bidwell, M. (2011). Paying more to get less: The effects of external hiring versus internal mobility. Administrative Science Quarterly 56(3), 369+.
doi: 10.1177/0001839211433562. Retrieved from Business Source Premier.
Bidwell, M. & Keller, JR. (2014) Within or without? How firms combine internal and external labor markets to fill jobs. Academy of Management
Journal 57(4), 1035+. doi 10.5465/amj.2012.0119. Retrieved from Business Source Premier.
Blackman, M.C. (2002, Sep). Personality judgment and the utility of the unstructured employment interview. Basic & Applied Social Psychology
24(3), 241+. Retrieved from: http://eds.a.ebscohost.com.libproxy.chapman.edu/eds/detail/detail?sid=38ae7fc7-5056-433d-b108-
9dee7b836e2c%40sessionmgr4003&vid=0&hid=4202&bdata=JkF1dGhUeXBlPWlwLHVpZCZzaXRlPWVkcy1saXZl#db=aph&AN=7105670
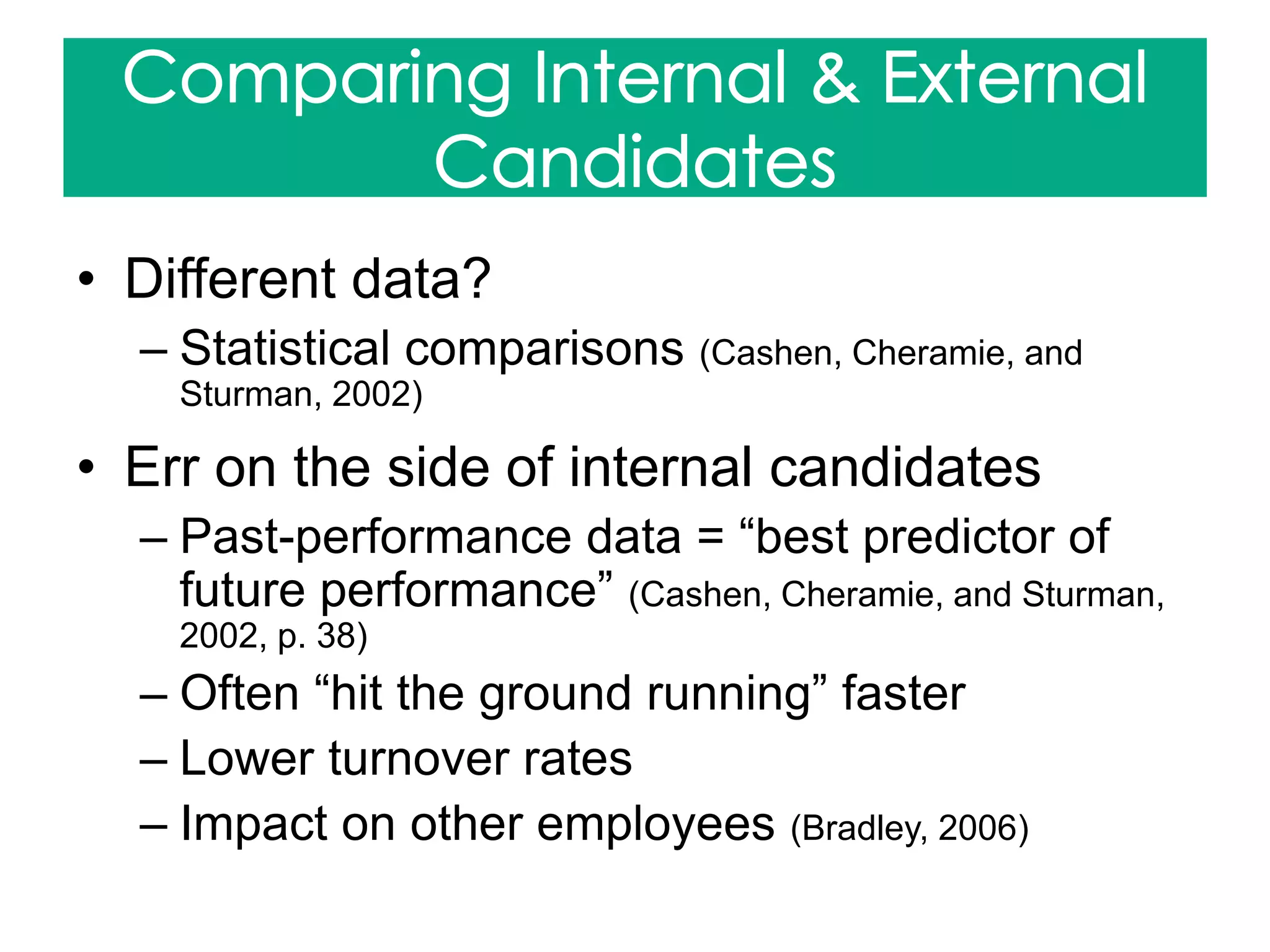
Bradley, L.M. (2006). Perceptions of justice when selecting internal and external job candidates. Personnel Review 35(1), 66+. doi:
10.1108/00483480610636795. Retrieved from ProQuest Psychology Journals.
Byrne, A., & Castellano, B. (1996). Hiring managers: promote or scout? Computer Reseller News (697), 201+. Retrieved from
http://go.galegroup.com.libproxy.chapman.edu/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA18622903&v=2.1&u=chap_main&it=r&p=AONE&sw=w&asid=3c046bb30
70b4700079ab308c4cf3407
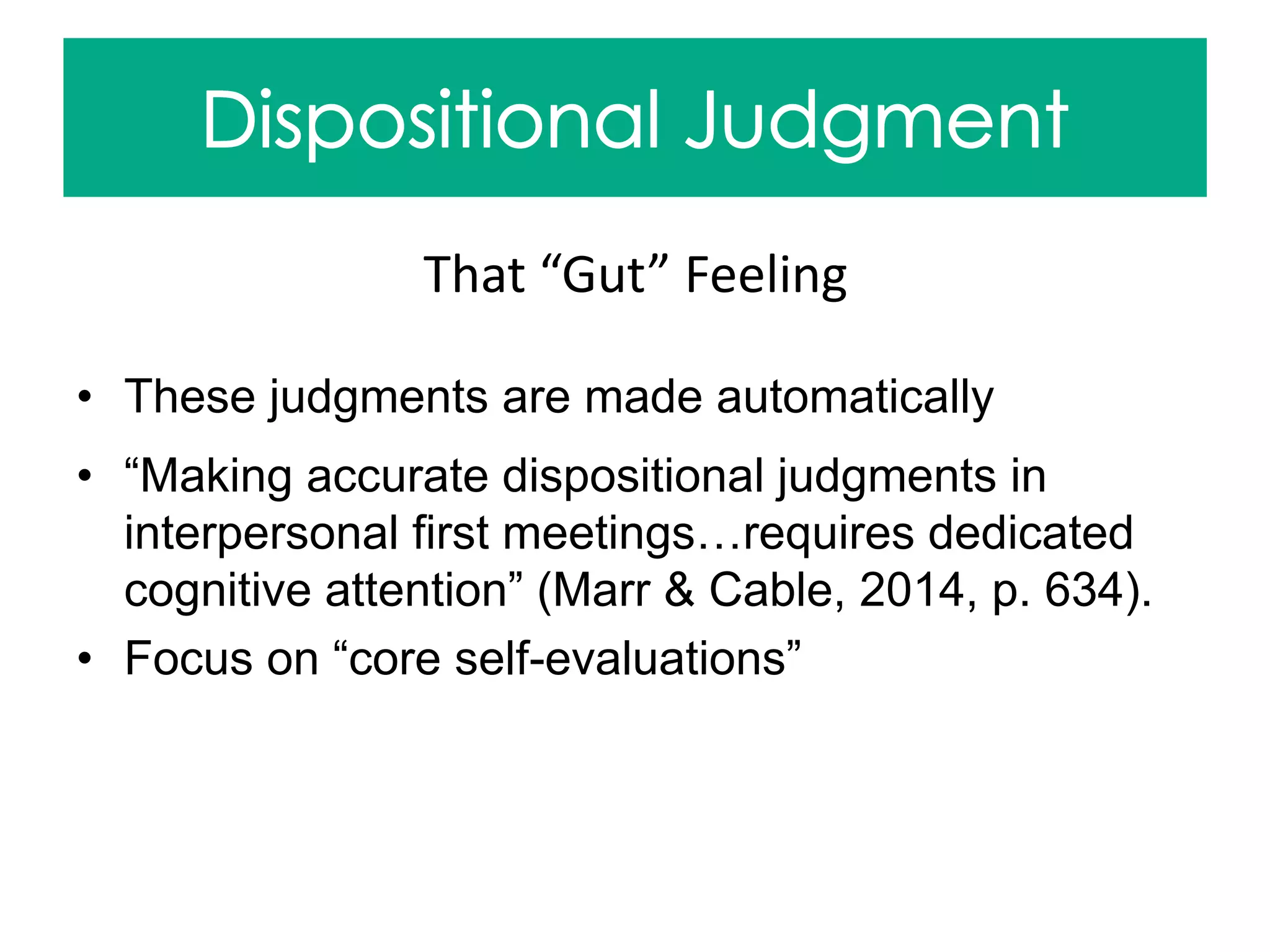
Cable, D.M., & Marr, J.C. (2014). Do interviewers sell themselves short? The effects of selling orientation on interviewers’ judgments [PDF
Document]. Academy of Management Journal 57(3), 624+. Retrieved from: https://eds-b-ebscohost-
com.libproxy.chapman.edu/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=10&sid=1a9375d1-0670-4bbd-aed7-ef185f3349ac%40sessionmgr115&hid=122
Cashen, L. H., Cheramie, R. A., & Sturman, M. C. (2002, August). How to compare apples to oranges: balancing internal candidates' job-
performance data with external candidates' selection-test results. (Human Resources). Cornell Hotel & Restaurant Administration Quarterly
43(4), 27+. Retrieved from
http://go.galegroup.com.libproxy.chapman.edu/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA92285349&v=2.1&u=chap_main&it=r&p=AONE&sw=w&asid=311f572c2
858c640b61058e77db27751
Clement, M. C. (2013). Hiring good colleagues: What you need to know about interviewing new teachers. Clearing House 86(3), 99+.
doi:10.1080/00098655.2013.769930
Cottrell, T. (2012). Interviewing efficiencies or interviewing efficiently?. Bottom Line: Managing Library Finances 25(3), 102+.
doi:10.1108/08880451211276548](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-visuals-hiringthebestcandidate-150501102524-conversion-gate01/75/Hiring-the-Best-Candidate-46-2048.jpg)
![DeSimone, R. L., & Werner, J. M. (2012). Human resource development (6th ed). Mason, OH: South-Western.
Engel, D., & Robbins, S. (2009). Telephone Interviewing Practices within Academic Libraries. Journal Of Academic Librarianship, 35(2), 143-
151.
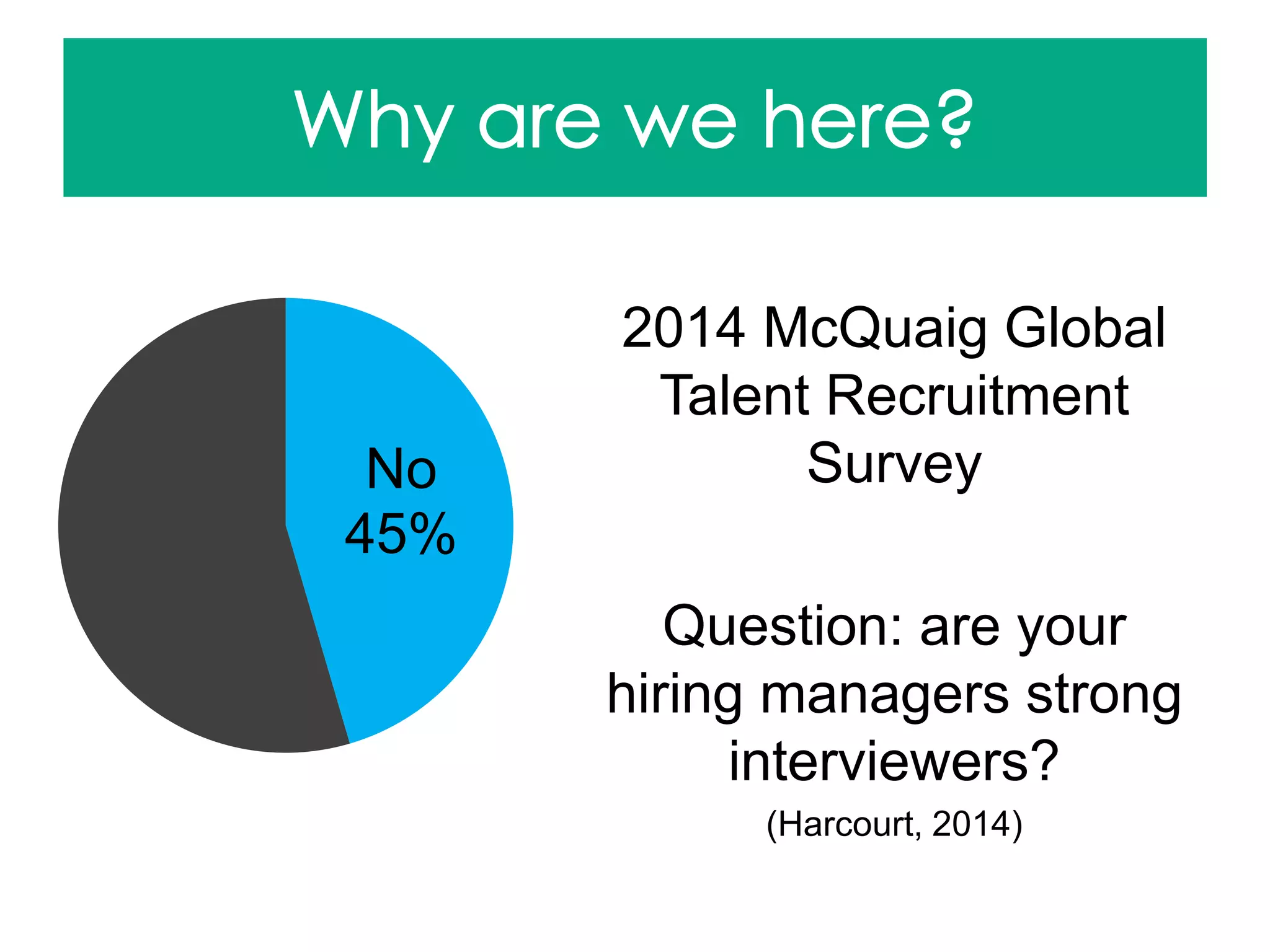
Harcourt, K. (2014, July 31). 4 tips to help hiring managers develop interview skills. Talent Talk. Retrieved from http://blog.mcquaig.com/blog/4-
tips-to-help-hiring-managers-develop-interview-skills.
Keenan, A., & Wedderburn, A. (1975). Effects of the non-verbal behaviour of interviewers on candidates' impressions. Journal Of Occupational
Psychology, 48(2), 129+.
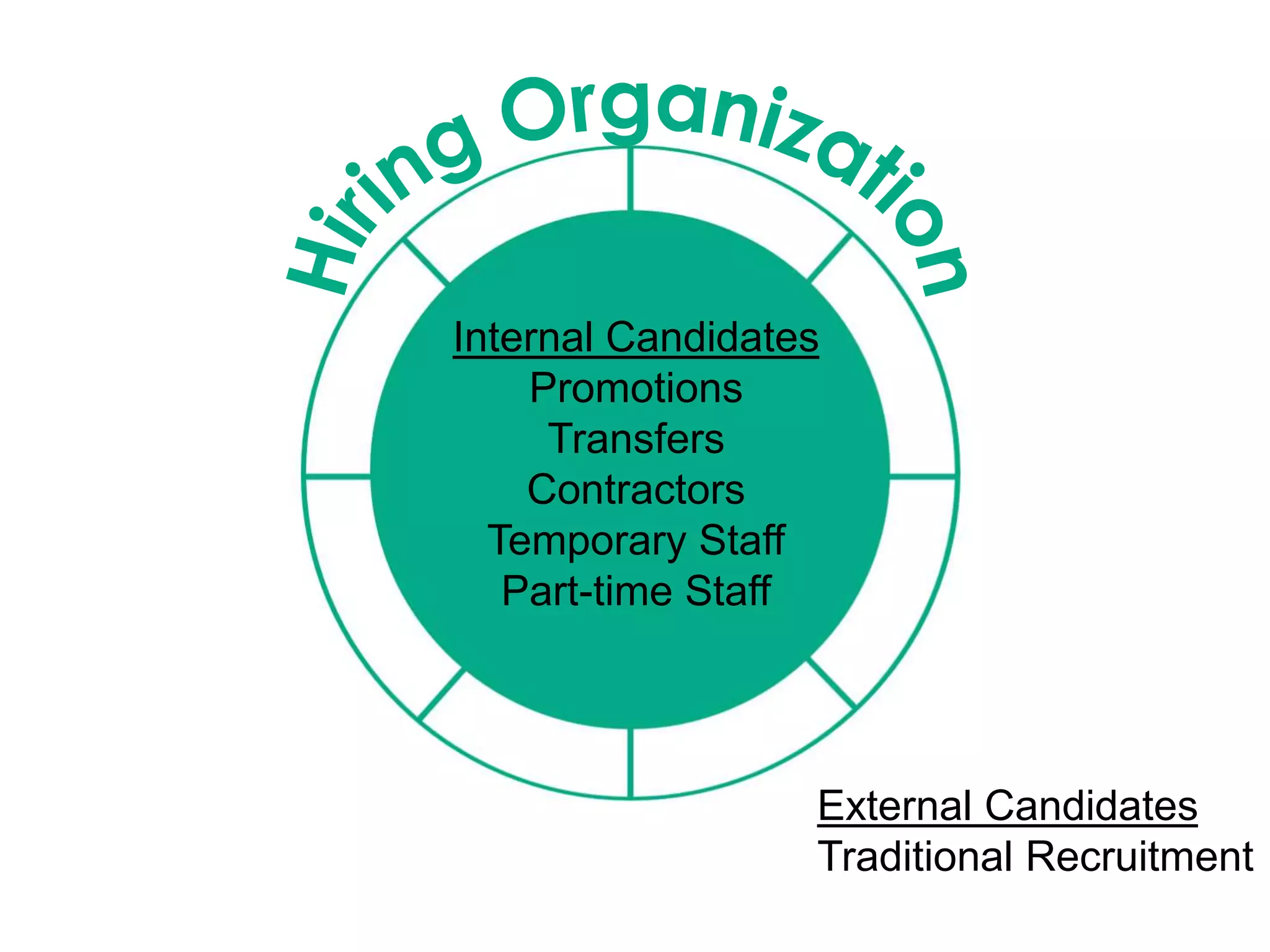
Kenyon College Office of the Provost. (n.d.) Protocol for Searches with Internal Candidates. Retrieved from
http://www.kenyon.edu/directories/offices-services/office-of-the-provost/faculty-resources-information/hiring/protocol-for-searches-with-internal-
candidates/
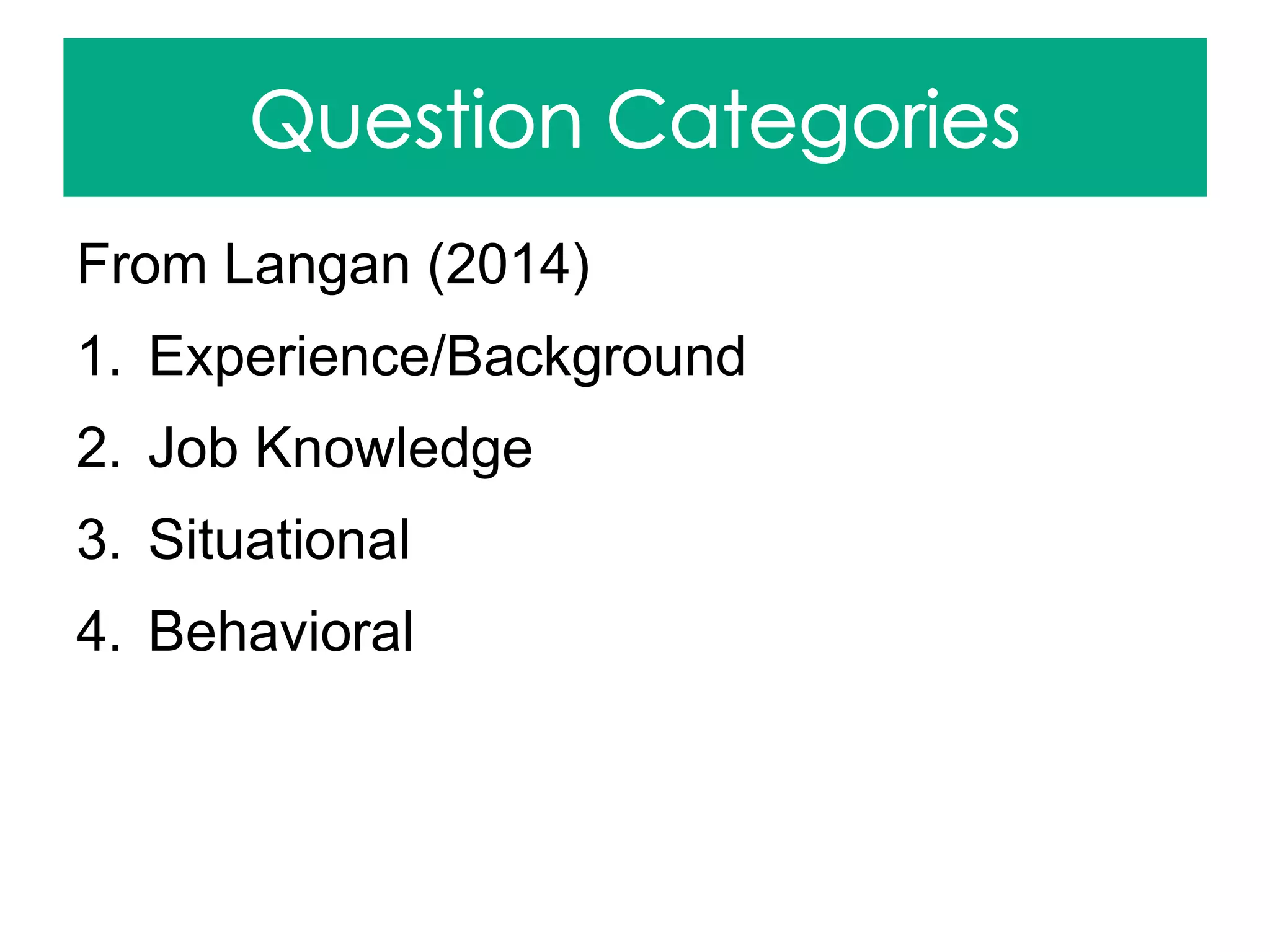
Langan, S. (2014, Feb 10). Selection planning: maximizing the testing process [PowerPoint]. IPMA Training Course.
Lee Flores, M. (2014). How to avoid the most common pitfalls when hiring employees: Nationally and in California. Employee Relations Law
Journal, 40(3), 34+.
Lewis, C. (1980). Investigating the employment interview: A consideration of counseling skills. Journal Of Occupational Psychology, 53(2),
111+.
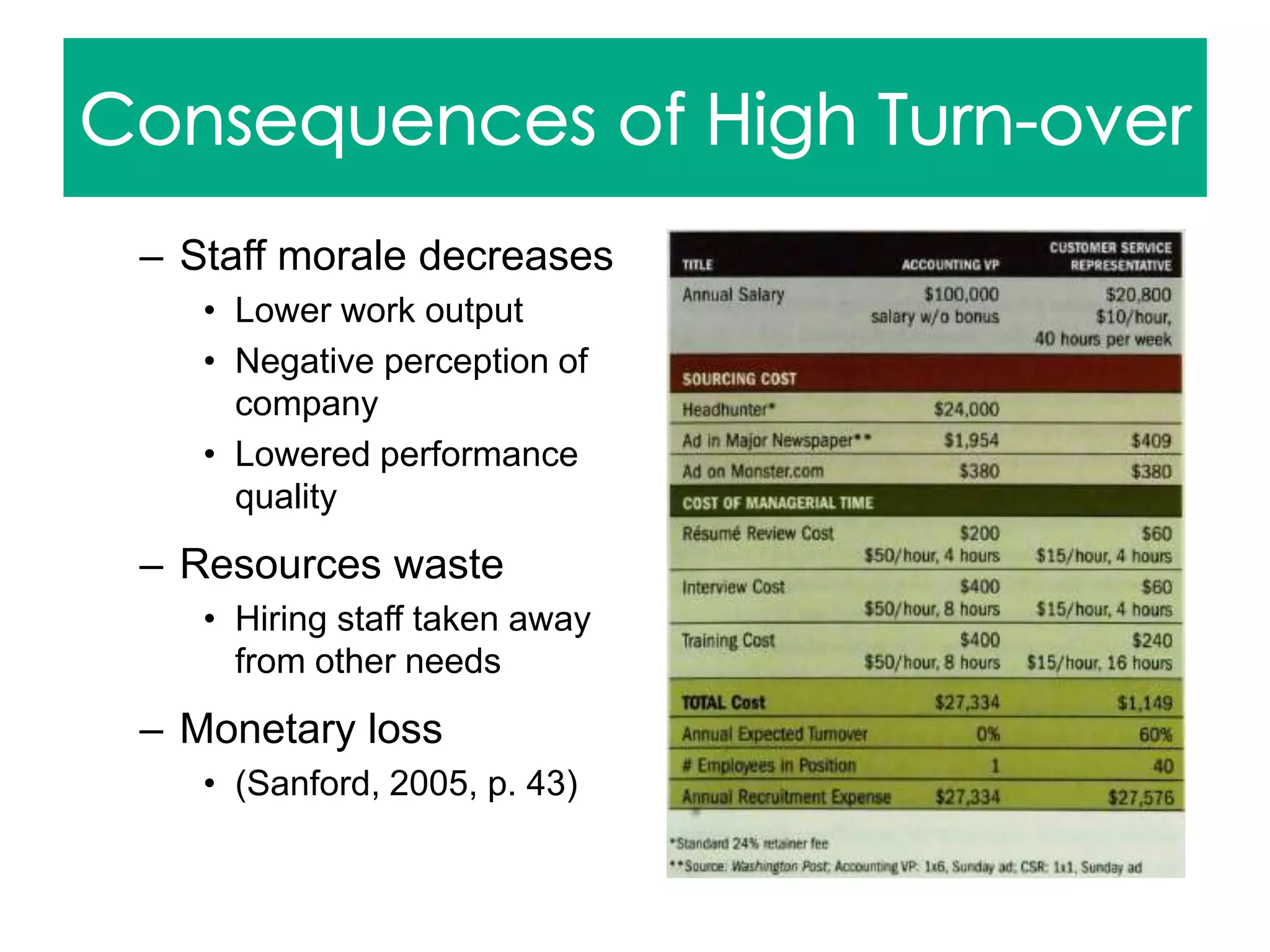
Sanford, J. (2005). Making Cents Out of the Hiring Process. Strategic Finance 87(6), 41+.
Schement, J. R. (2002). Encyclopedia of Communication and Information. New York: Macmillan Reference USA.
The Bridgespan Group. (2010). Considering and evaluating internal candidates for senior-level nonprofit positions. Retrieved from
http://www.bridgespan.org/getdoc/78804d86-00bc-4e75-9563-95b9d7f80aa6/Considering-Evaluating-Internal-Candidates.aspx#.VN0Oc_WtvMI
University of North Carolina (Dec 2014). Interviewer biases [PDF Document]. Retrieved from:
http://www.uncsa.edu/humanresources/forms/InterviewerBiases.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-visuals-hiringthebestcandidate-150501102524-conversion-gate01/75/Hiring-the-Best-Candidate-47-2048.jpg)
