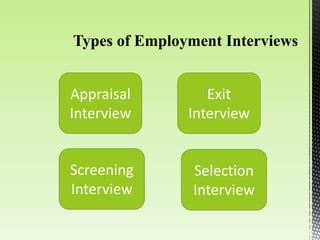
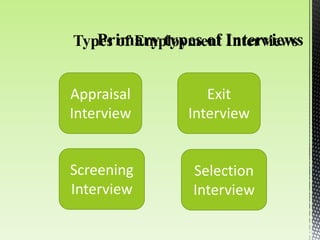
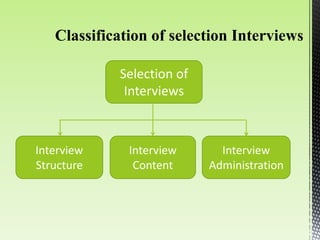
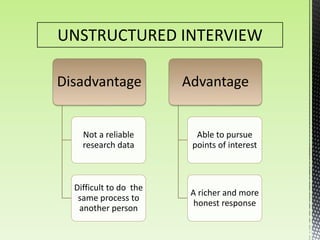
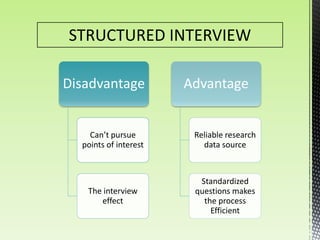
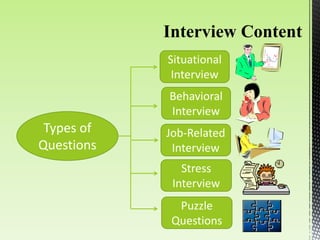
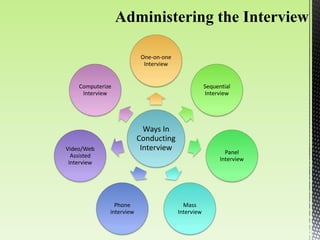
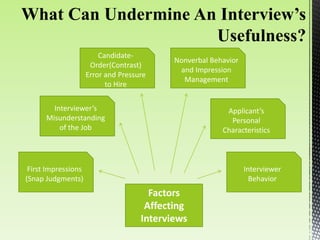
The document discusses best practices for conducting effective interviews, including structuring interviews with job-relevant questions, using the same questions for all candidates, and focusing interview questions on assessing a candidate's knowledge, experience, intellectual capacity, and personality fit for the job. It also outlines factors that can influence interviews such as first impressions, misunderstanding the job requirements, and personal characteristics of the candidate. Effective interviews should be prepared for, structured, and evaluate candidates based on their responses to job-relevant situational and behavioral questions.