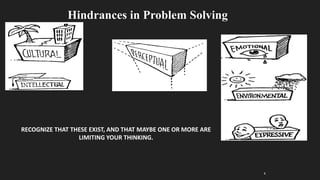
This document discusses common hindrances to problem solving. It identifies 5 main categories of hindrances: perception, work environment, expression, emotion, and intellectual.
Under perception, it explains how perspectives can influence how problems are seen. Factors like attitudes, motives, and experiences of the perceiver as well as characteristics of the target and situation can impact perception.
The work environment can provide supportive or non-supportive atmospheres for problem solving. Distractions, unsupportive management, and lack of resources are discussed.
Poor expression of problems and solutions can lead to miscommunication hindering the process. Emotions like anxiety, impatience, and fear of failure or risk can also create blocks.