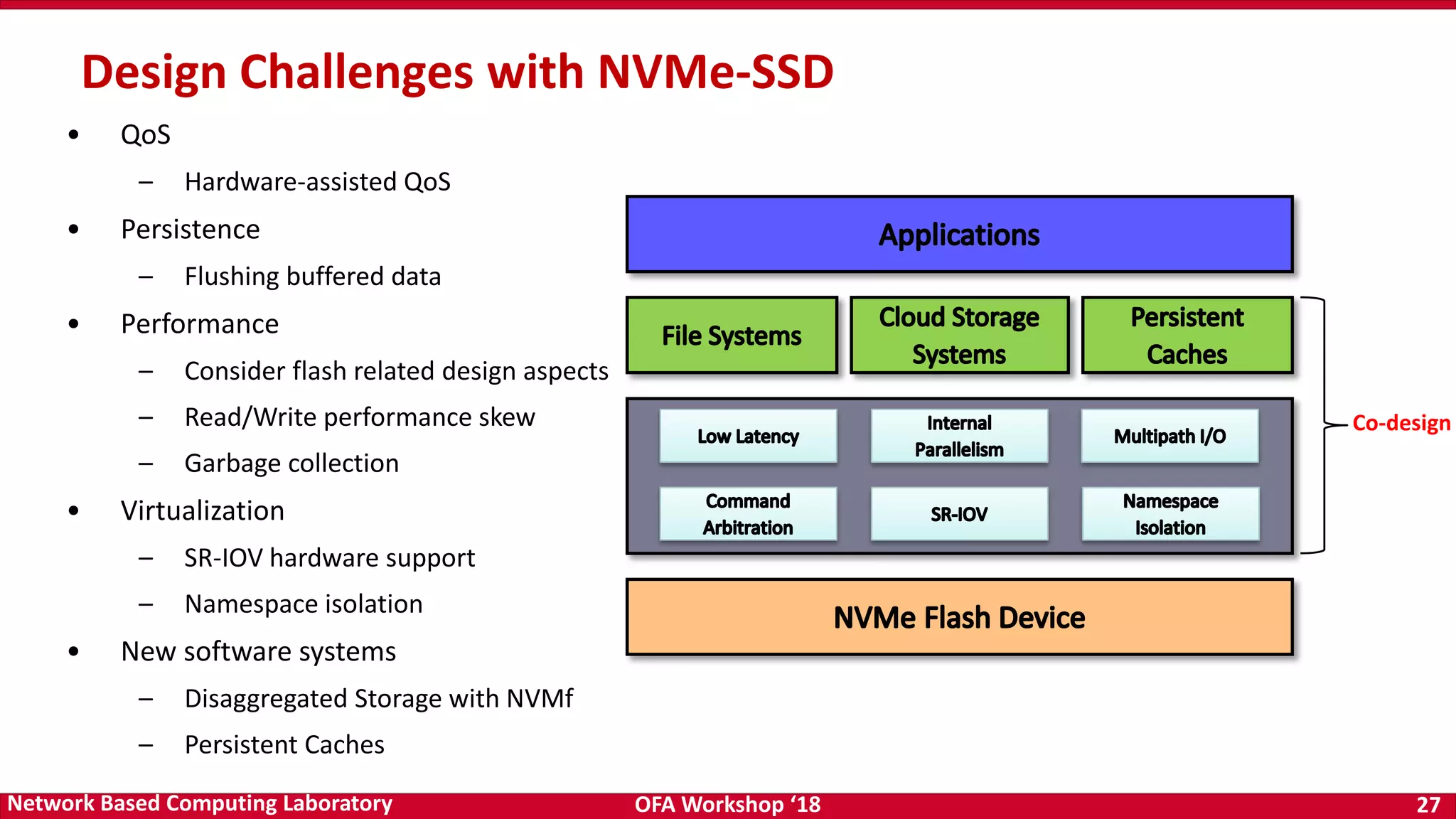
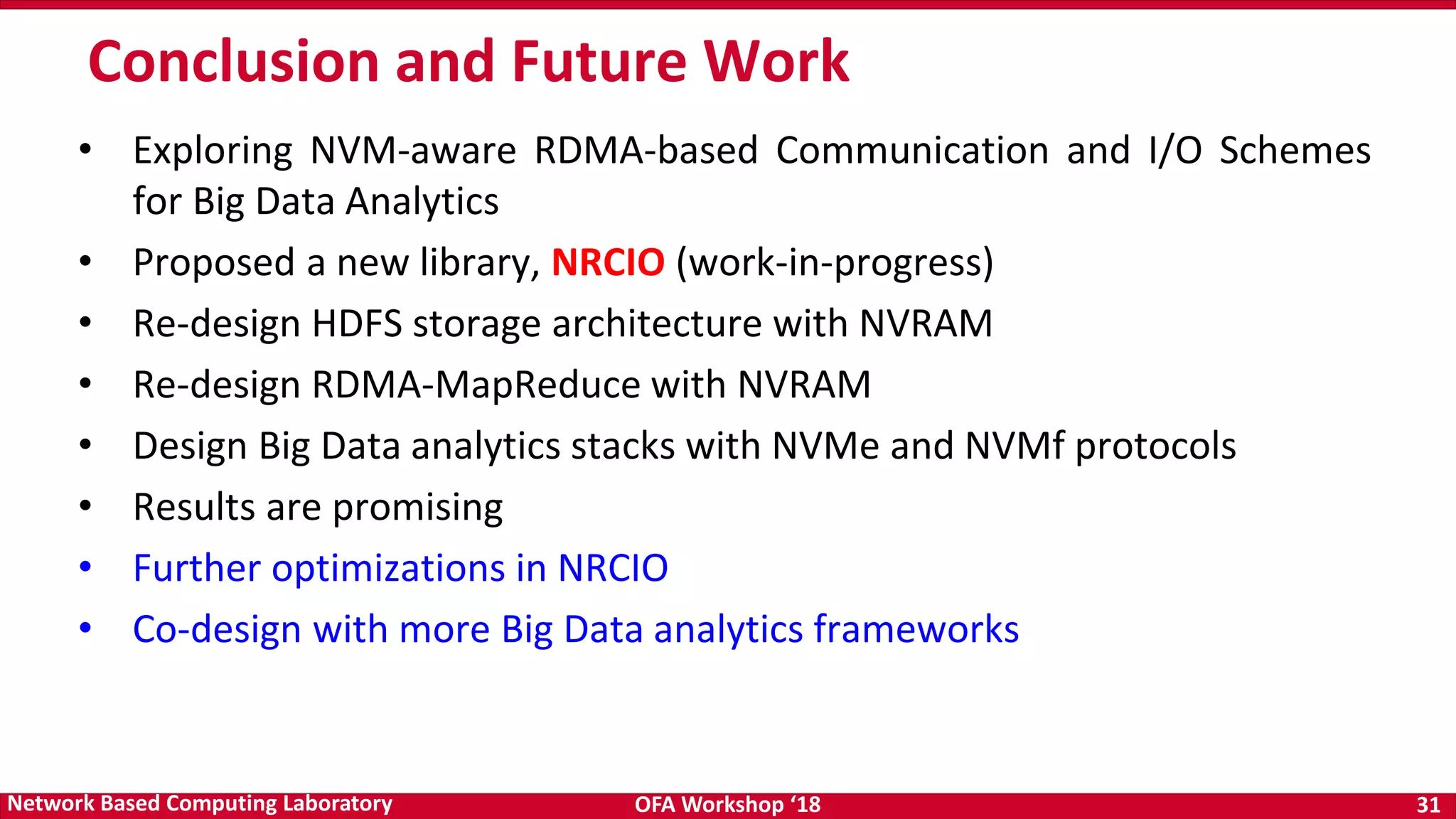
The document discusses high-performance big data analytics utilizing RDMA over NVM and NVMe-SSD technologies, highlighting their impact on data management systems. It details various processing frameworks like Apache Hadoop and Spark, explores the benefits of non-volatile memory in boosting throughput, and presents benchmarks demonstrating substantial performance improvements over traditional architectures. Additionally, it covers challenges and design considerations for integrating NVMe technologies with existing systems to optimize data processing operations.



![OFA Workshop ‘18 6Network Based Computing Laboratory
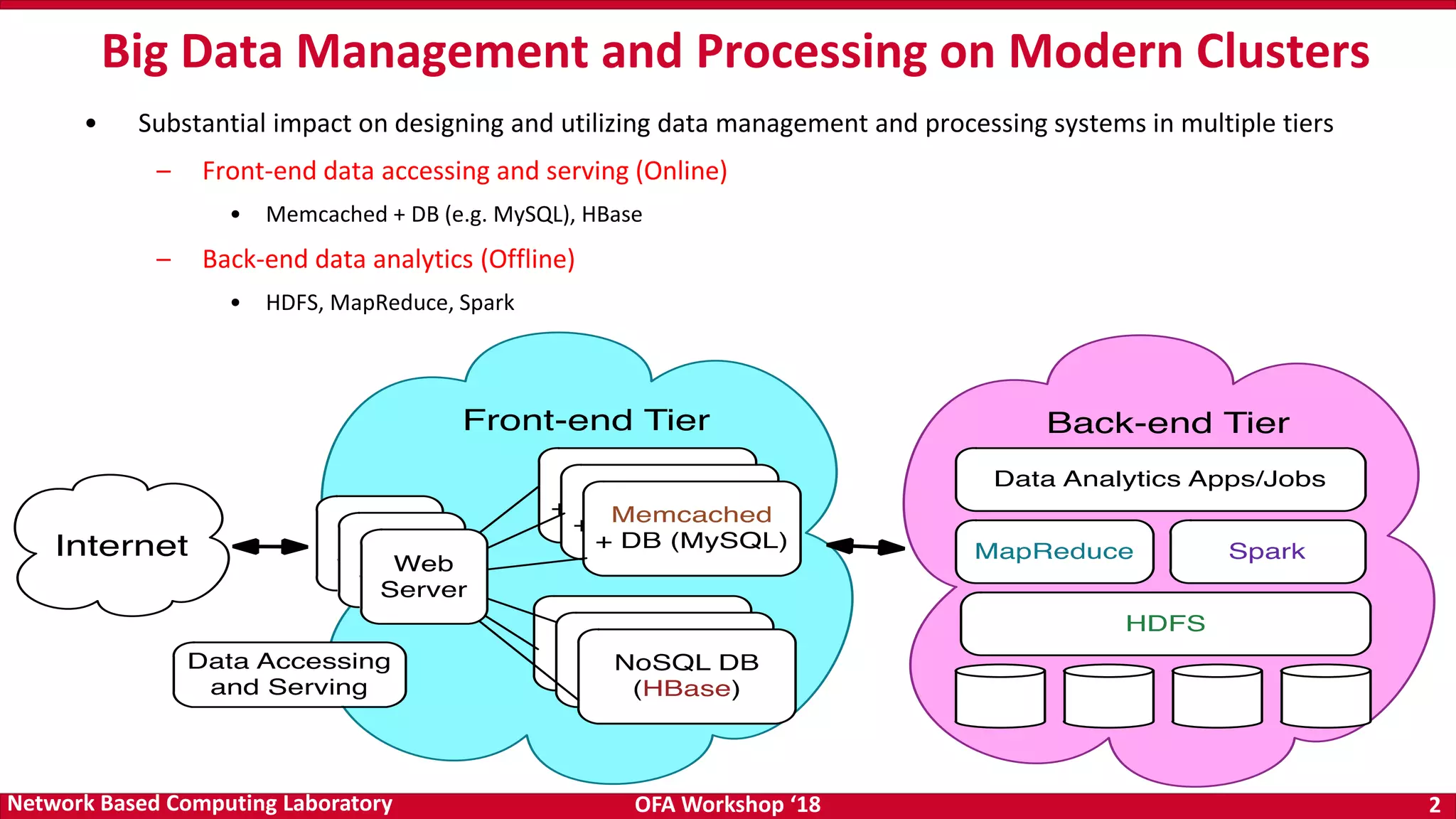
Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) and NVMe-SSD
3D XPoint from Intel & Micron Samsung NVMe SSD Performance of PMC Flashtec NVRAM [*]
• Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) provides byte-addressability with persistence
• The huge explosion of data in diverse fields require fast analysis and storage
• NVMs provide the opportunity to build high-throughput storage systems for data-intensive
applications
• Storage technology is moving rapidly towards NVM
[*] http://www.enterprisetech.com/2014/08/06/ flashtec-nvram-15-million-iops-sub-microsecond- latency/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/luxi-180528151337/75/High-Performance-Big-Data-Analytics-with-RDMA-over-NVM-and-NVMe-SSD-6-2048.jpg)