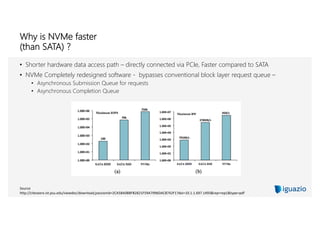
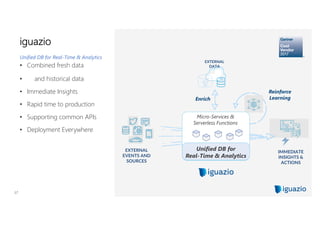
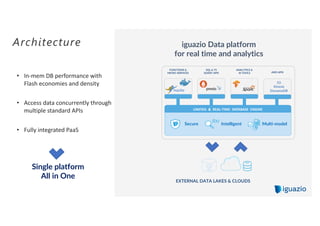
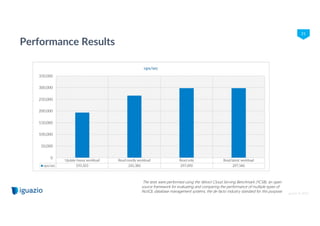
The document discusses using flash memory to build a high performance data platform. It notes that flash memory is faster than disk storage and cheaper than RAM. The platform utilizes NVMe flash drives connected via PCIe for high speed performance. This allows it to provide in-memory database speeds at the cost and density of solid state drives. It can scale independently by adding compute nodes or storage nodes. The platform offers a unified database for both real-time and analytical workloads through common APIs.