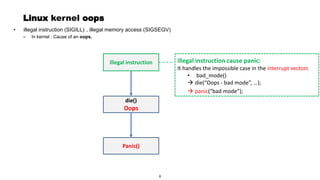
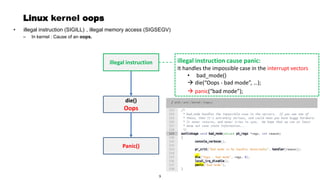
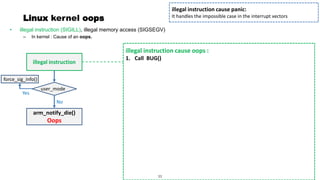
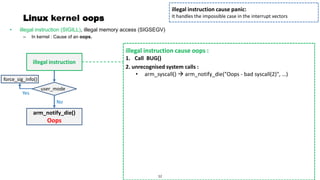
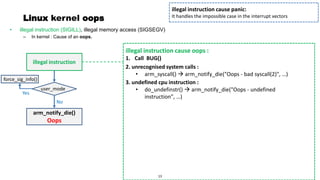
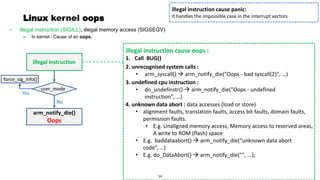
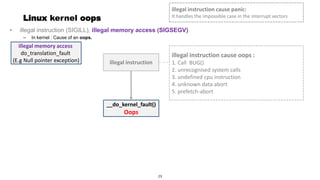
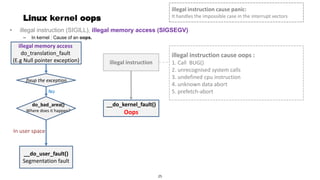
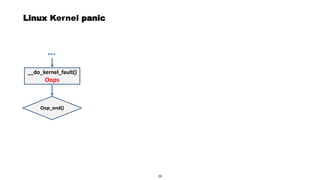
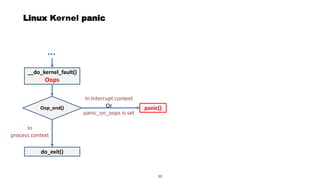
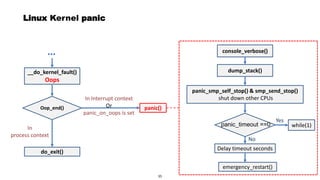
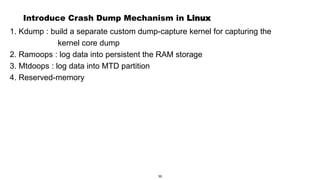
This document discusses Linux kernel oops and kernel panics. It explains that a kernel oops occurs when there is an illegal instruction or illegal memory access in kernel space, and will kill the offending process to keep the system running. A kernel panic means the system must stop immediately. Kernel oops can be caused by illegal instructions, unrecognized system calls, undefined CPU instructions, unknown data aborts, or prefetch aborts. These result in a call to the arm_notify_die() function and generate an oops. Illegal instructions that handle interrupt vectors can cause a panic directly. A kernel panic performs further actions like console output and stopping other CPUs before restarting or halting the system. Methods to capture crash