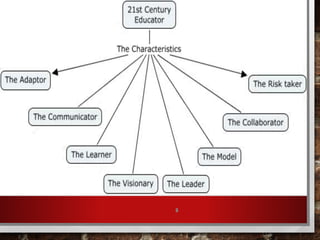
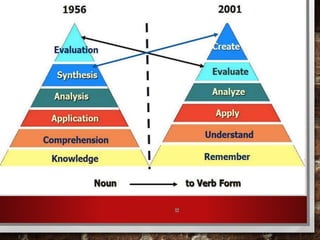
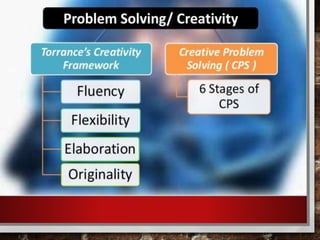
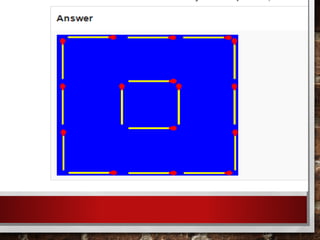
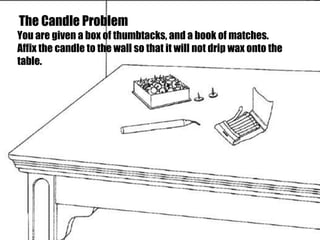
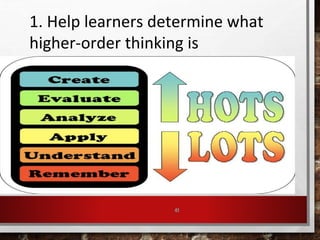
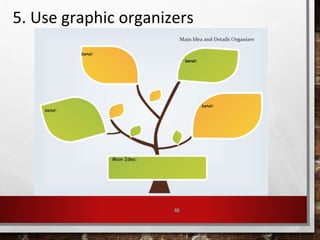
The document outlines strategies for educators to foster higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) among 21st-century learners through metacognition, creativity, and problem-solving techniques. It emphasizes the importance of a learner-centered approach, encouraging students to engage in complex thinking processes, personalized instruction, and collaborative projects. Key concepts include using Bloom's revised taxonomy, analyzing thought processes, and employing creative thinking activities to enhance learning outcomes.