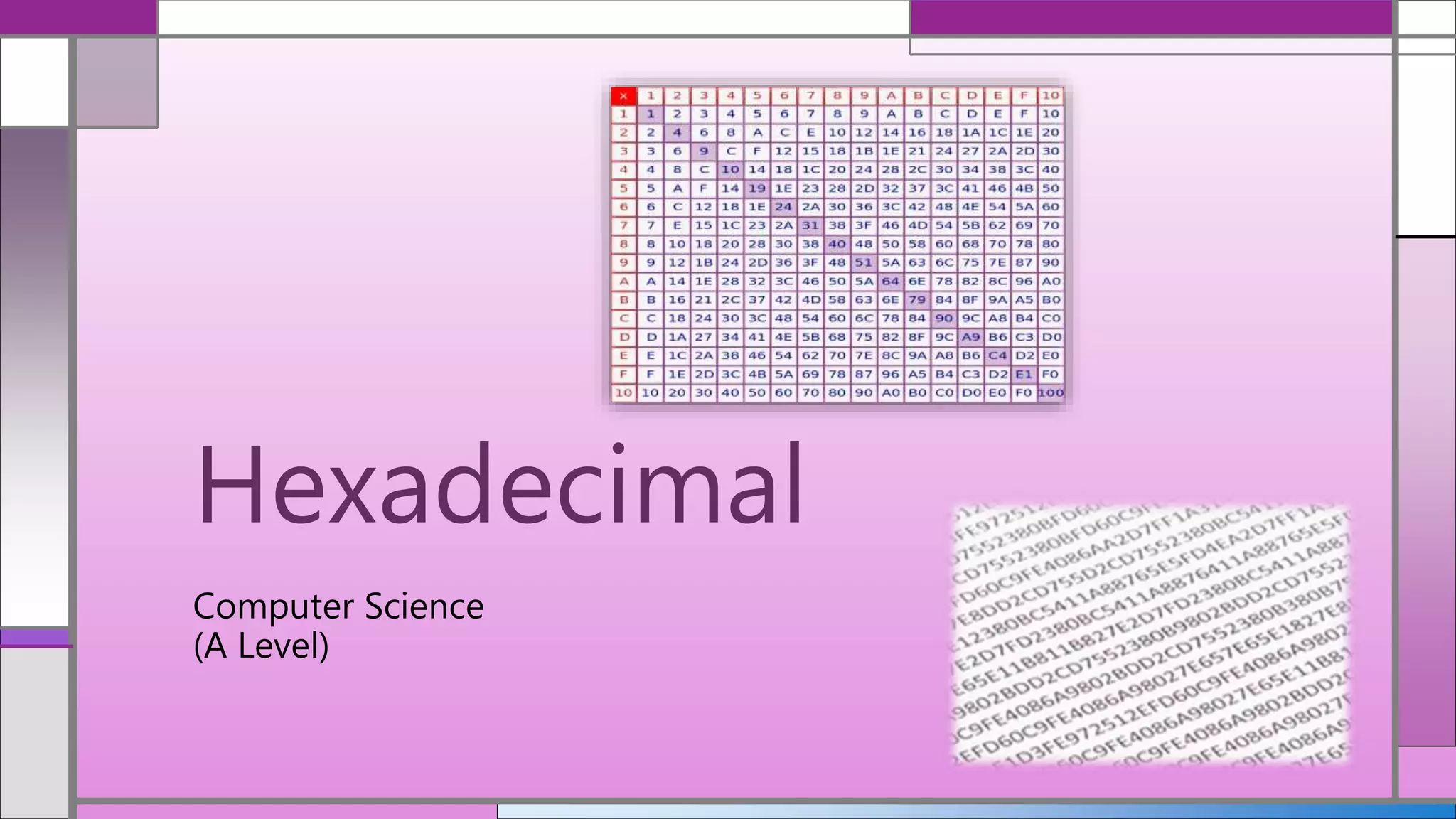
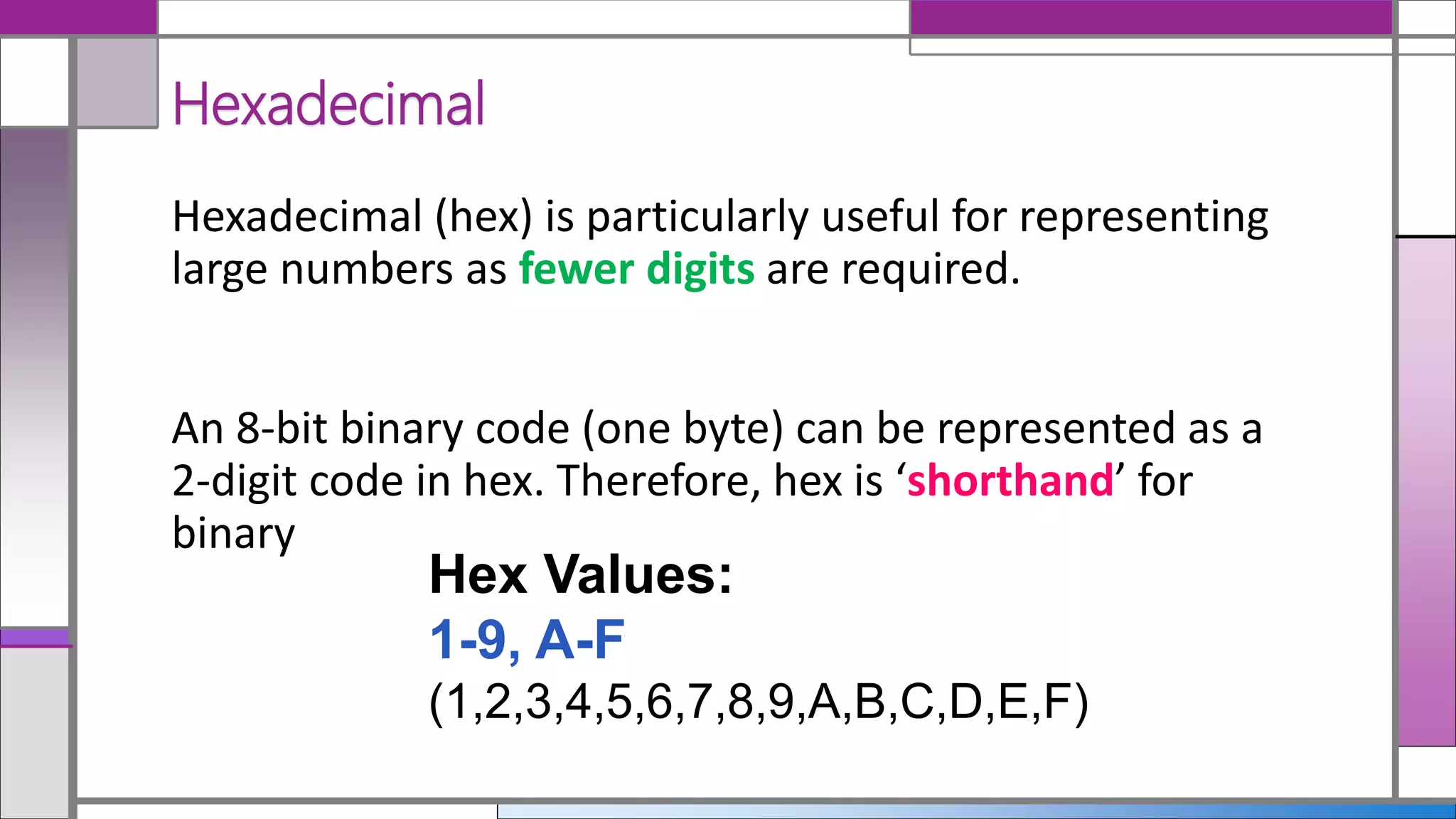
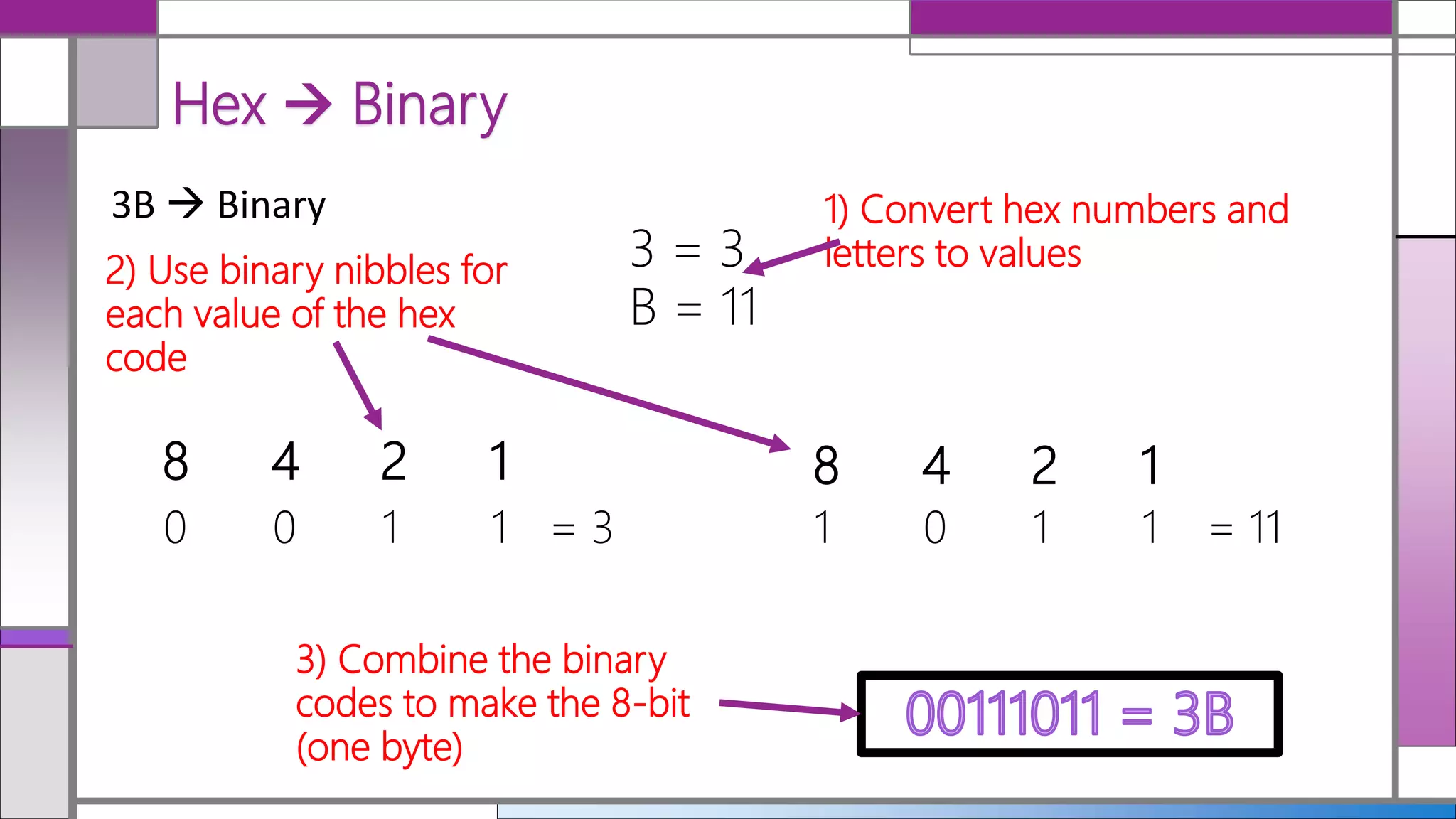
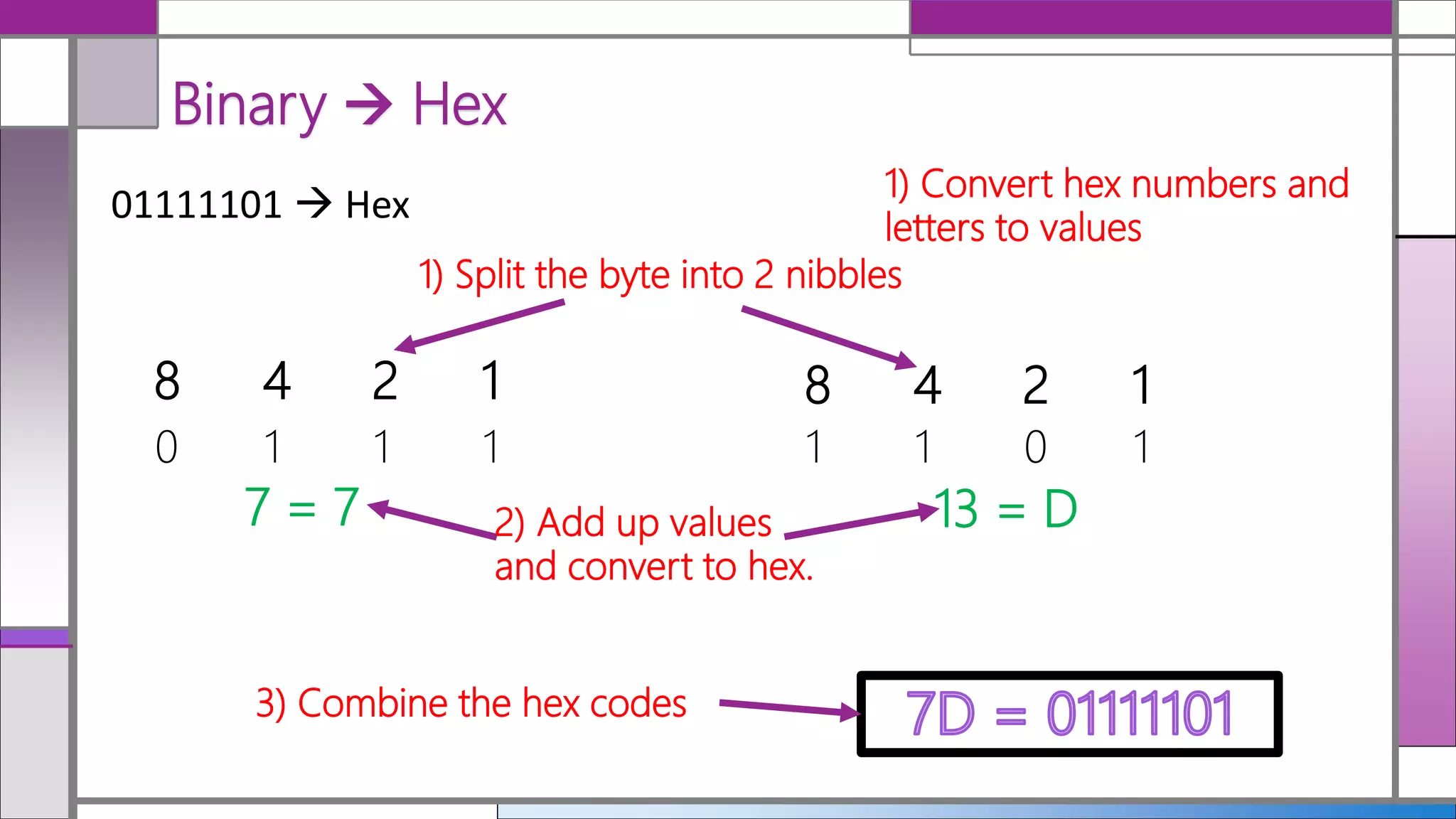
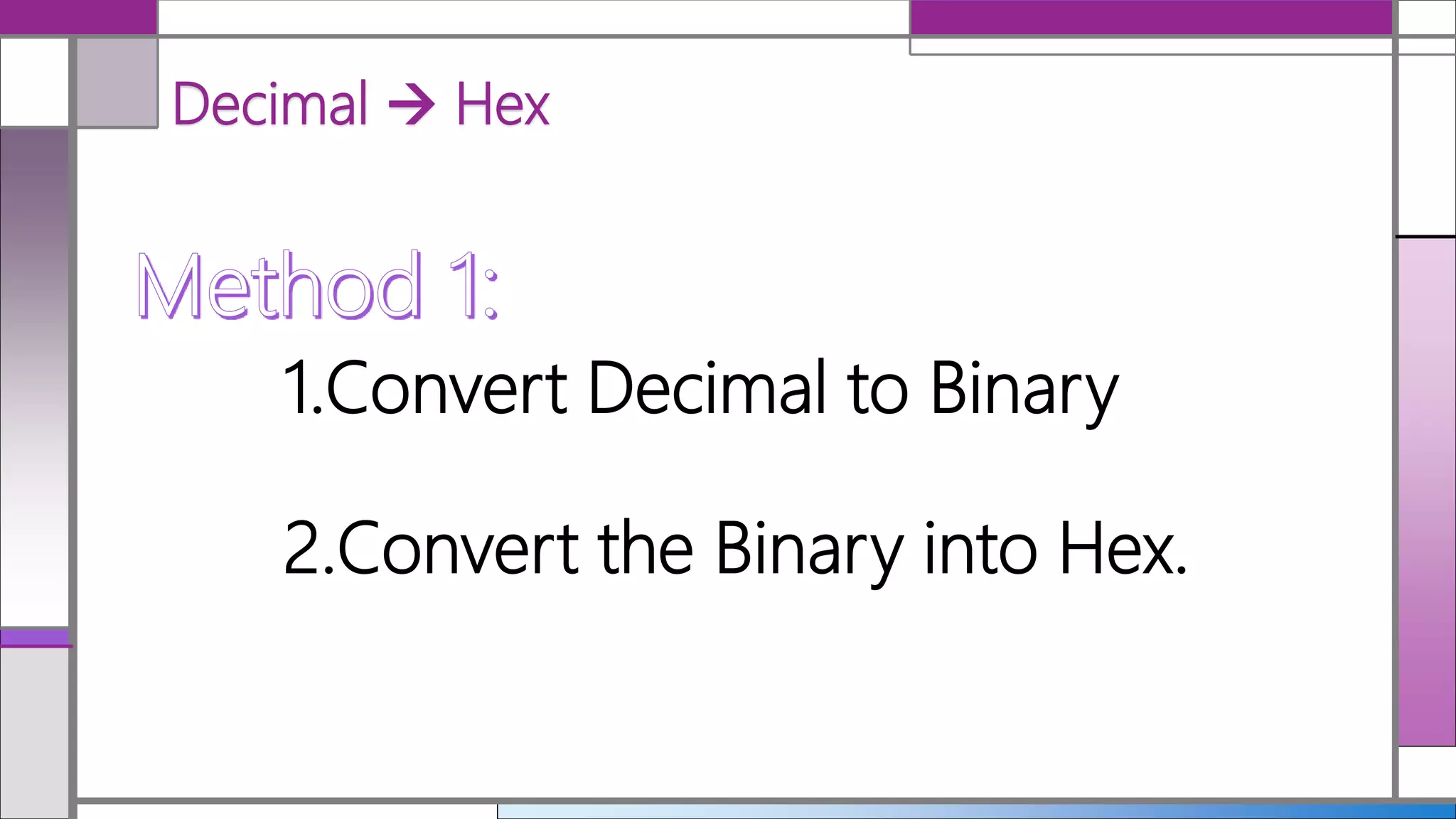
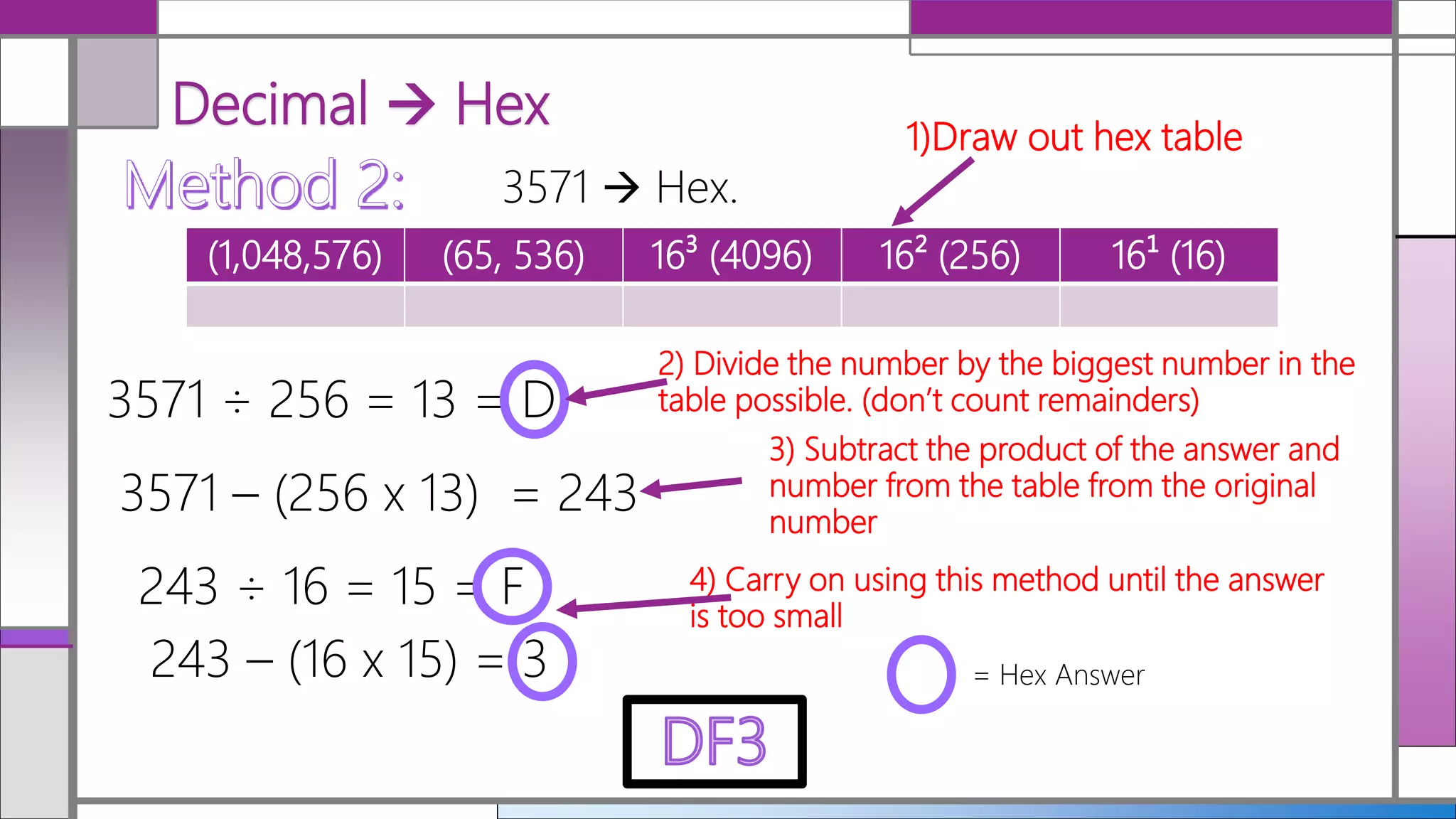
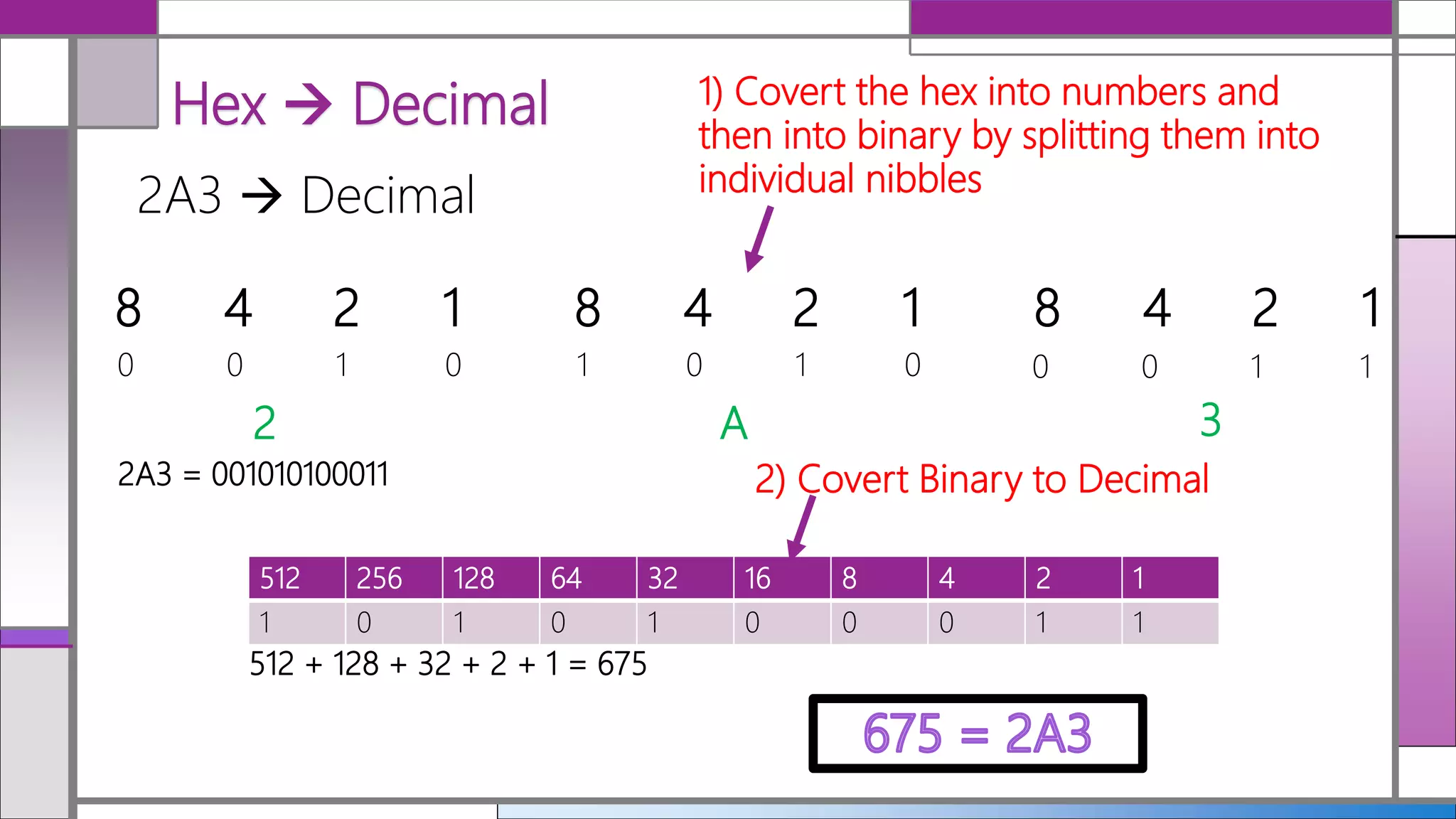
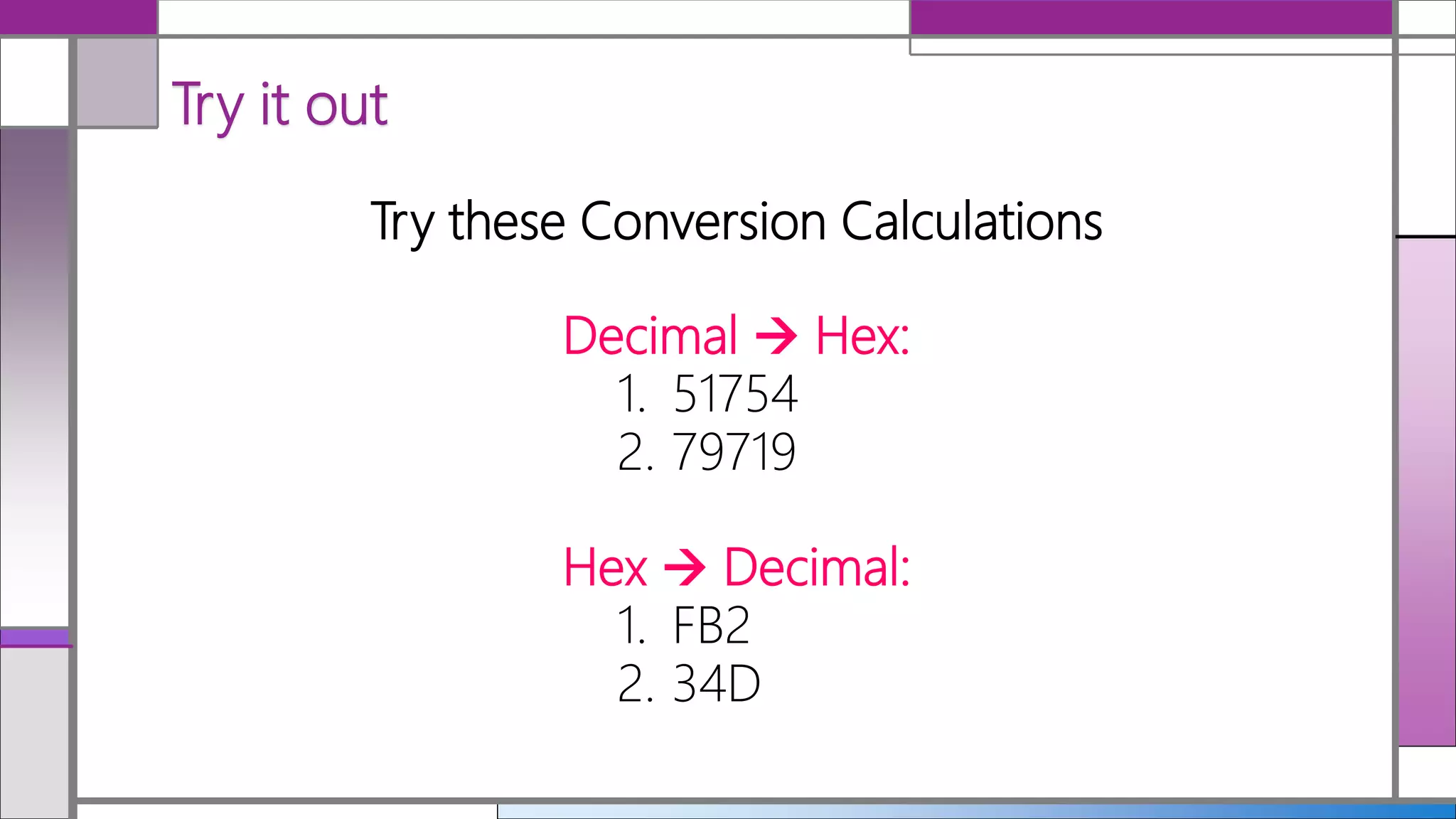
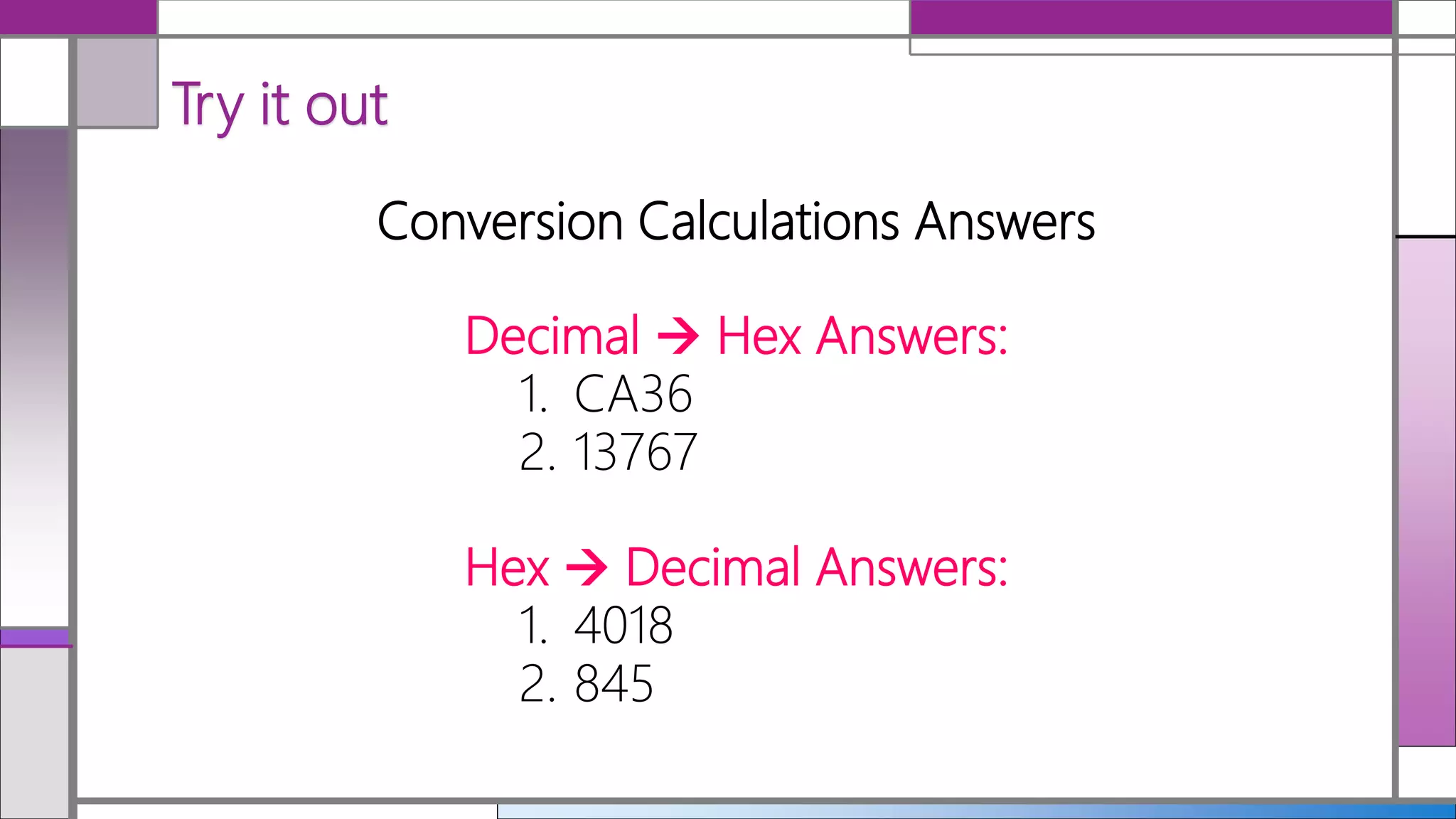
Hexadecimal (hex) is a base-16 numbering system that simplifies the representation of binary numbers, making them shorter and easier to read. Conversion between decimal, hex, and binary is detailed, with methods for translating hex to decimal and vice versa provided. The document includes examples and practice calculations to reinforce understanding of these conversions.