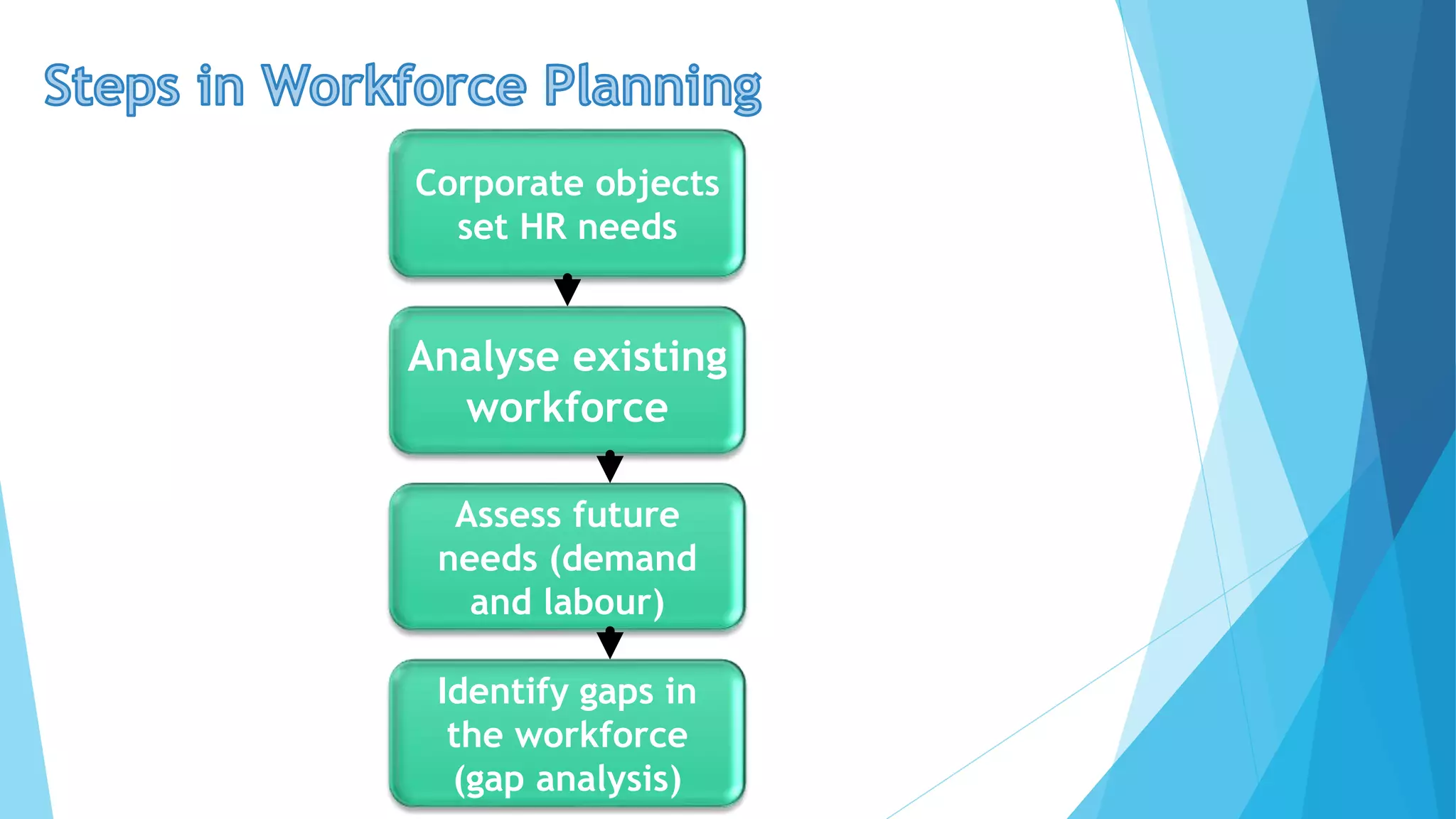
Workforce planning involves determining the quantity and types of workers needed by analyzing the existing workforce and assessing future demands to identify gaps. This process is shaped by corporate objectives and external factors such as market demand, economic conditions, and technology changes. Solutions such as recruitment, training, and flexible working options are essential for closing any identified workforce gaps.