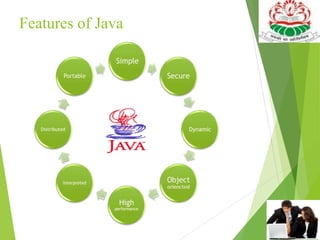
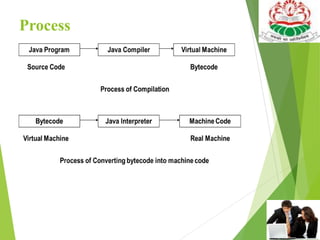
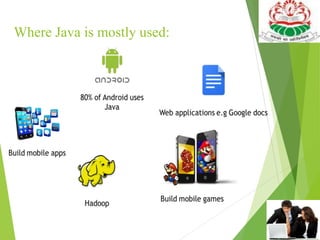
This document provides an introduction and overview of the Java programming language. It discusses that Java was developed by James Gosling in 1990 at Sun Microsystems to be a simple, secure, object-oriented language for developing applications on the internet. The document then covers Java's history, key features like platform independence and object orientation, and how Java programs are executed using the Java Virtual Machine. It also summarizes the different modules of Java - JSE, JEE, and JME - and provides a basic example Java program.









![An Example:
class First
{
int a=10;
Public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(“Welcome to JAVA”+a);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-150611100458-lva1-app6892/85/Core-Java-13-320.jpg)

