This document provides an introduction to computer programming concepts including:
- A programming language is a set of rules that allows communication between humans and computers to perform operations. Different languages have evolved for different types of programs and problem domains.
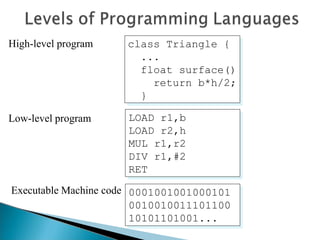
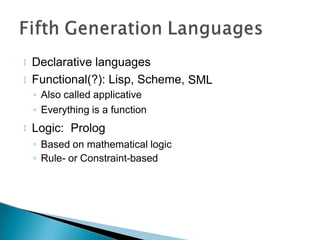
- Programs are written in high-level languages then compiled or interpreted into machine-readable code. Common language types include procedural, object-oriented, functional, and declarative languages.
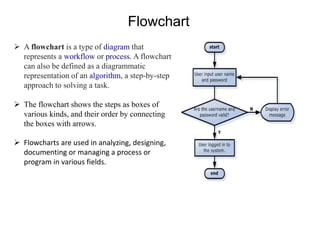
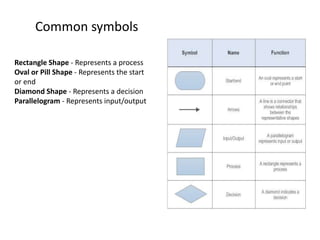
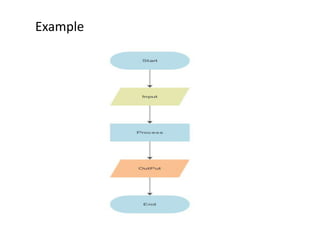
- The programming process involves understanding the problem, designing an algorithm, writing source code, compiling for errors, debugging, and executing the program. Flowcharts can help design the program logic.