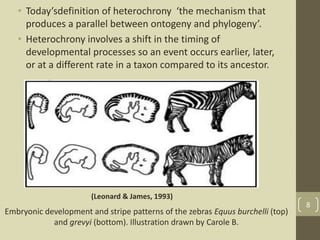
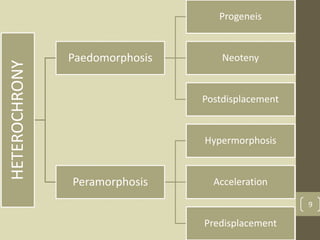
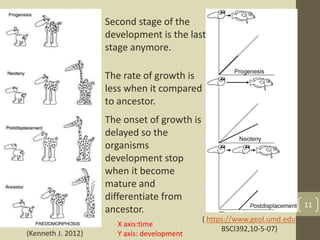
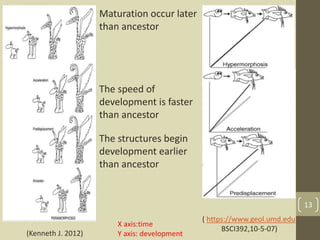
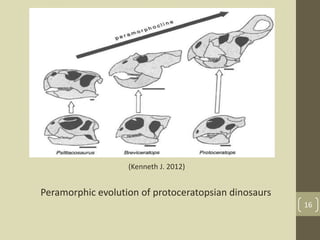
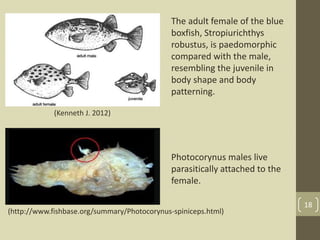
The document discusses heterochrony, the evolutionary process affecting developmental timing and morphological traits across species. It outlines various types of heterochrony, including paedomorphosis and peramorphosis, which describe how growth rates and timings of development differ between ancestors and descendants. The conclusion highlights the significance of heterochronic genes in the evolution of organisms, underscoring the interaction between development and evolution.