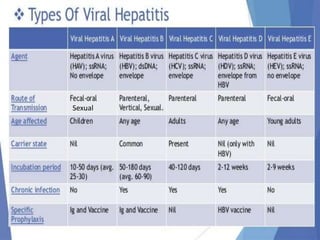
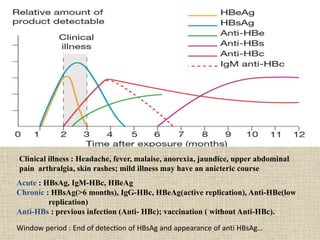
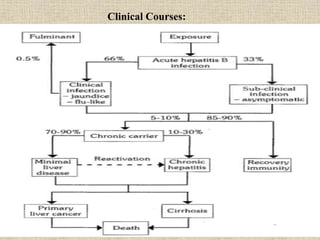
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver that can be caused by infectious agents like viruses or bacteria, as well as non-infectious causes such as alcohol, drugs, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic disorders. Hepatitis B is a major global health problem, with the highest prevalence in the Western Pacific and African regions. In Nepal, the prevalence of Hepatitis B is estimated to be 0.9% on average. It is transmitted parenterally or sexually and can be acute or develop into chronic infection. Diagnosis involves liver function tests and detecting serum markers. Treatment depends on the stage of infection, while prevention involves immunization, safe injection practices, and health education.