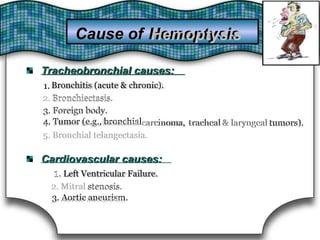
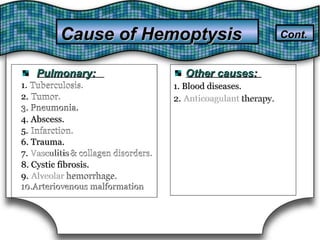
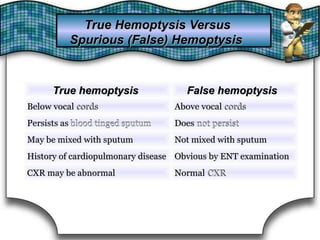
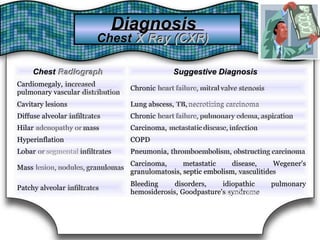
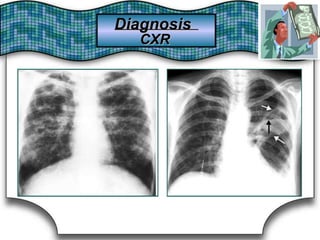
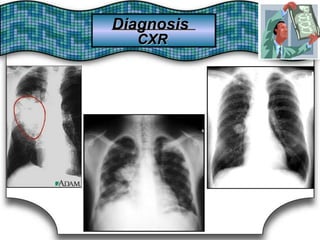
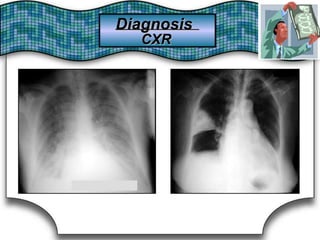
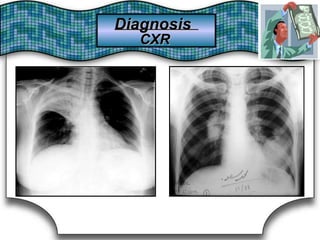
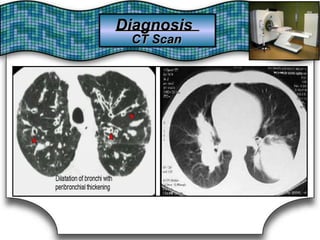
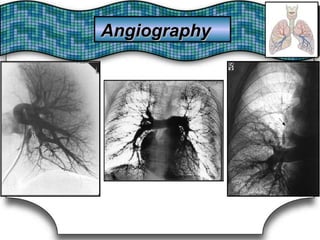
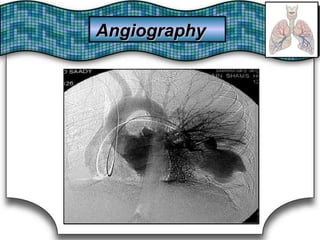
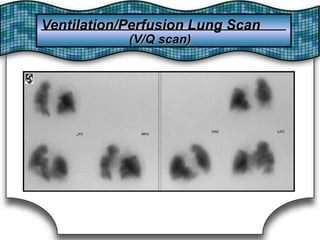
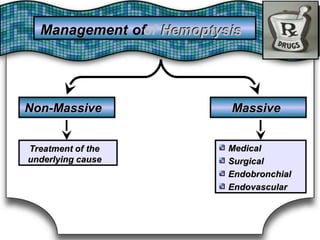
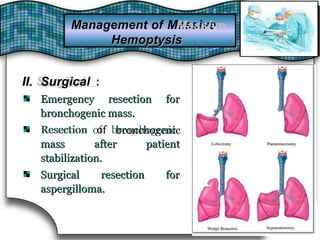
This document discusses pulmonary bleeding (hemoptysis). It defines hemoptysis as coughing up blood from the lungs or respiratory tract. The document outlines various causes of hemoptysis including infections like tuberculosis, lung cancers, vascular abnormalities and coagulation disorders. It also describes how to differentiate true hemoptysis from false, evaluates severity, provides clues from history and examination to suggest potential diagnoses, and lists relevant diagnostic tests and treatments.


![Pulmonary Bleeding
Pulmonary Bleeding (or pulmonary haemorrhage) is
an acute bleeding from the lung, from the upper respiratory tract and
the trachea, and the alveoli. When evident clinically, the condition is
usually massive.[1] The onset of pulmonary hemorrhage is characterized
by cough productive of blood (hemoptysis) and worsening of oxygenation
leading to cyanosis.[1] Treatment should be immediate and should include
tracheal suction, oxygen, positive pressure ventilation, and correction of
underlying abnormalities (e.g. disorders of coagulation). A blood
transfusion may be necessary.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zubairpulmoppt-190301145525/85/HEMOPTYSIS-3-320.jpg)